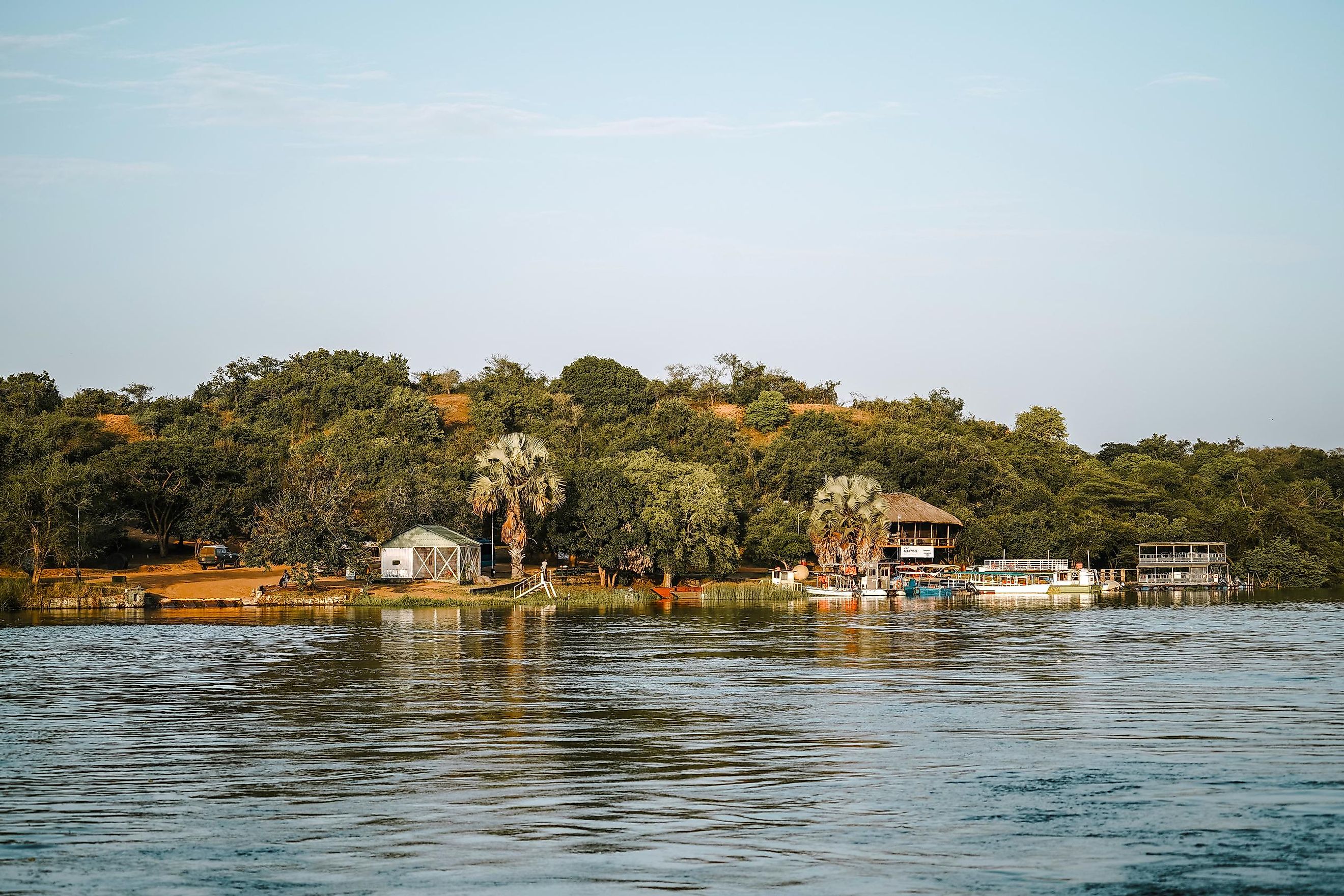
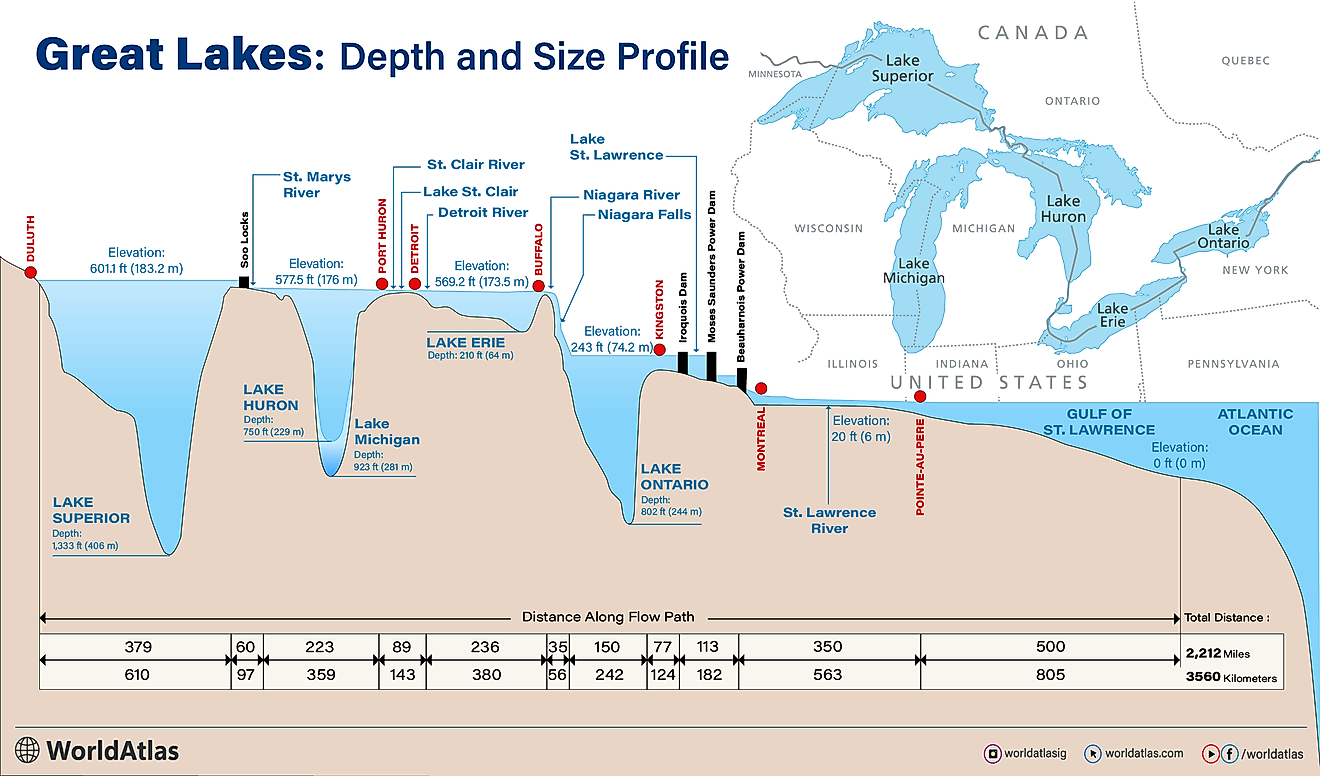
Lake Kyoga
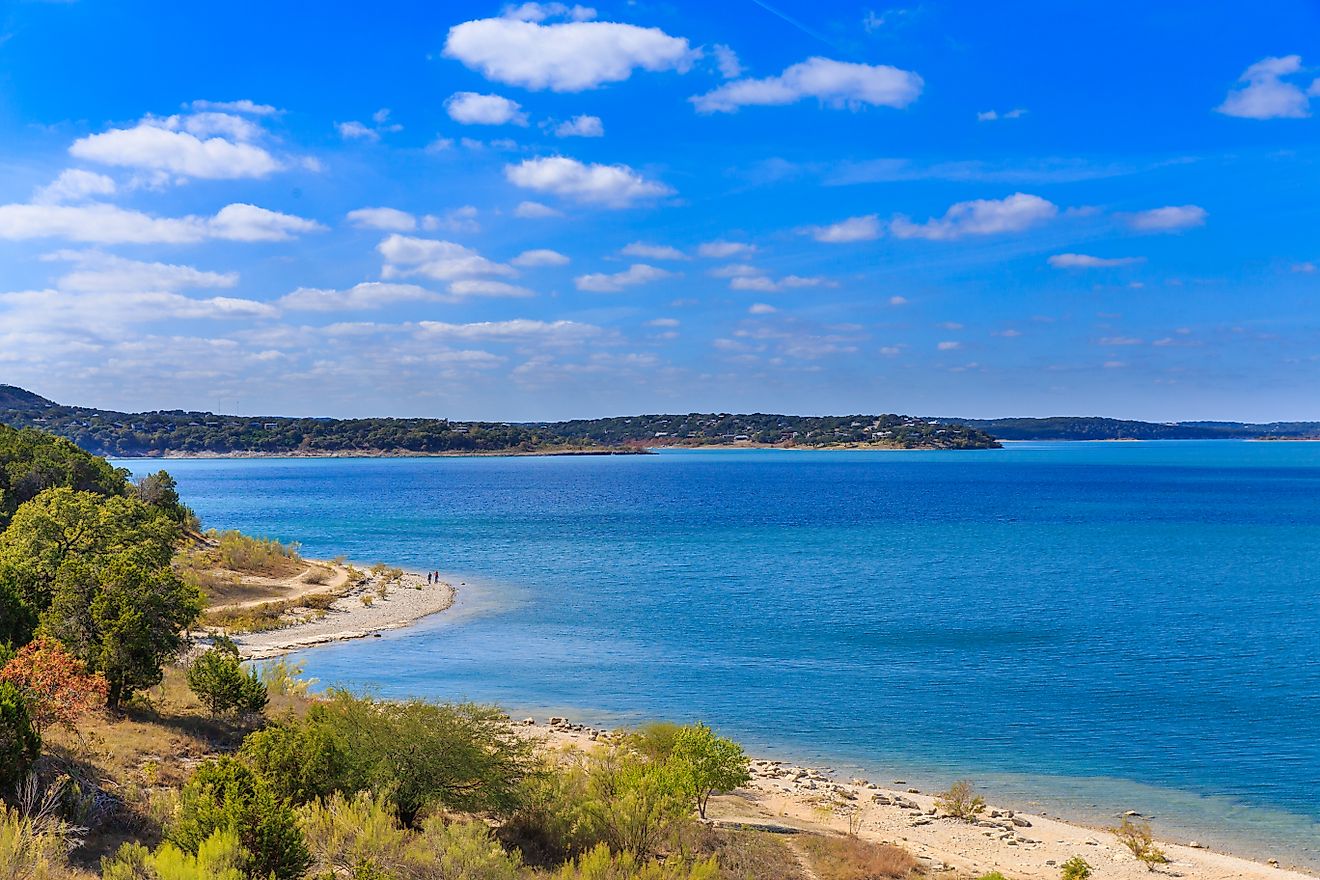
Found in Central Uganda, Lake Kyoga stands as a captivating natural marvel celebrated for its ecological diversity, distinctive features, and vital role in the region's water supply. Serving as a conduit for the Nile River as it traverses neighboring lakes, Lake Kyoga spans an impressive area of about 660 mi2 (1,720 km2) and rests at an elevation of 3,389 ft (1,033 meters). The expansive, glistening waters, rich biodiversity, and intriguing historical narrative have propelled Lake Kyoga to international recognition. From its formation and geological significance to its varied ecosystem and cultural relevance, Lake Kyoga emerges as a remarkable natural wonder deserving of global attention. Let's embark on a journey to explore this stunning body of water nestled in the heart of the African continent.
Geography Of Lake Kyoga
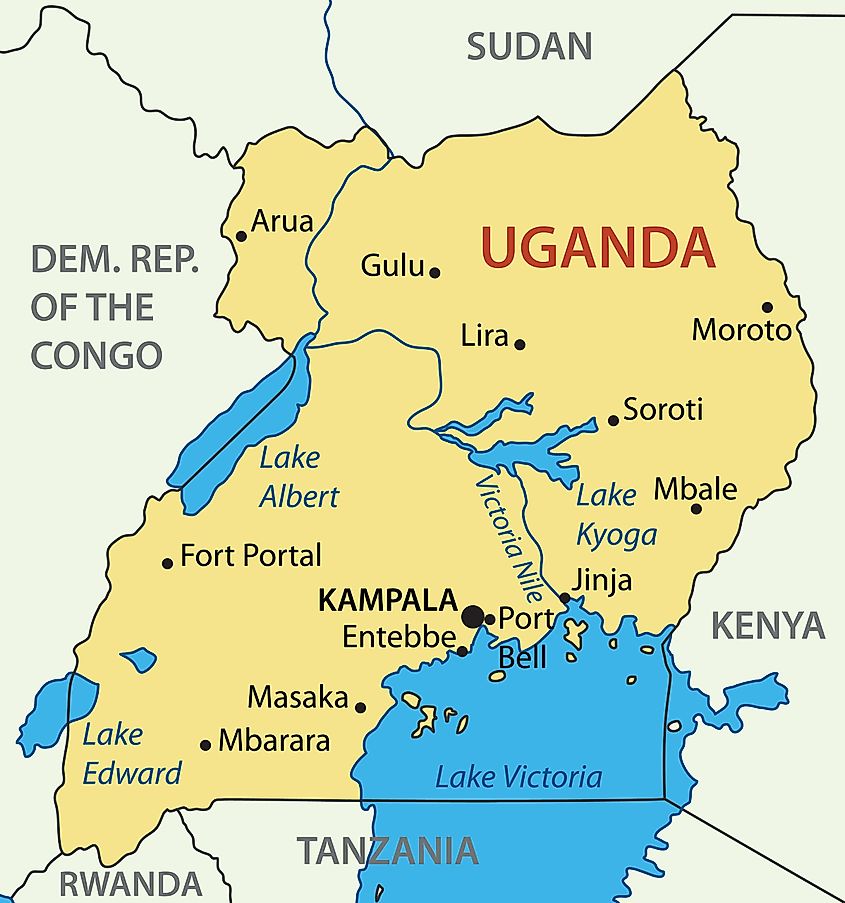
As the country's second-largest lake, surpassed only by the neighboring Lake Victoria, Lake Kyoga assumes a pivotal function in regulating water flow. One distinctive aspect of Lake Kyoga lies in its maximum depth, measuring approximately 18.7 ft (5.7 meters), with the majority of its expanse maintaining depths of less than 13 ft (4 meters). Nestled within the East African Rift Valley, this expansive freshwater lake showcases diverse geography, surrounded by wetlands, marshes, and papyrus swamps. Its shores are adorned with verdant vegetation, establishing a habitat that supports a myriad of plant and animal species.
In Uganda, the highest temperatures range from 20 to 27 degrees Celsius, with minimum temperatures between 12 and 18 degrees Celsius. Lake Kyoga gets replenished during its two distinct rainy seasons, from October to December and March to May.
Biodiversity Of Lake Kyoga
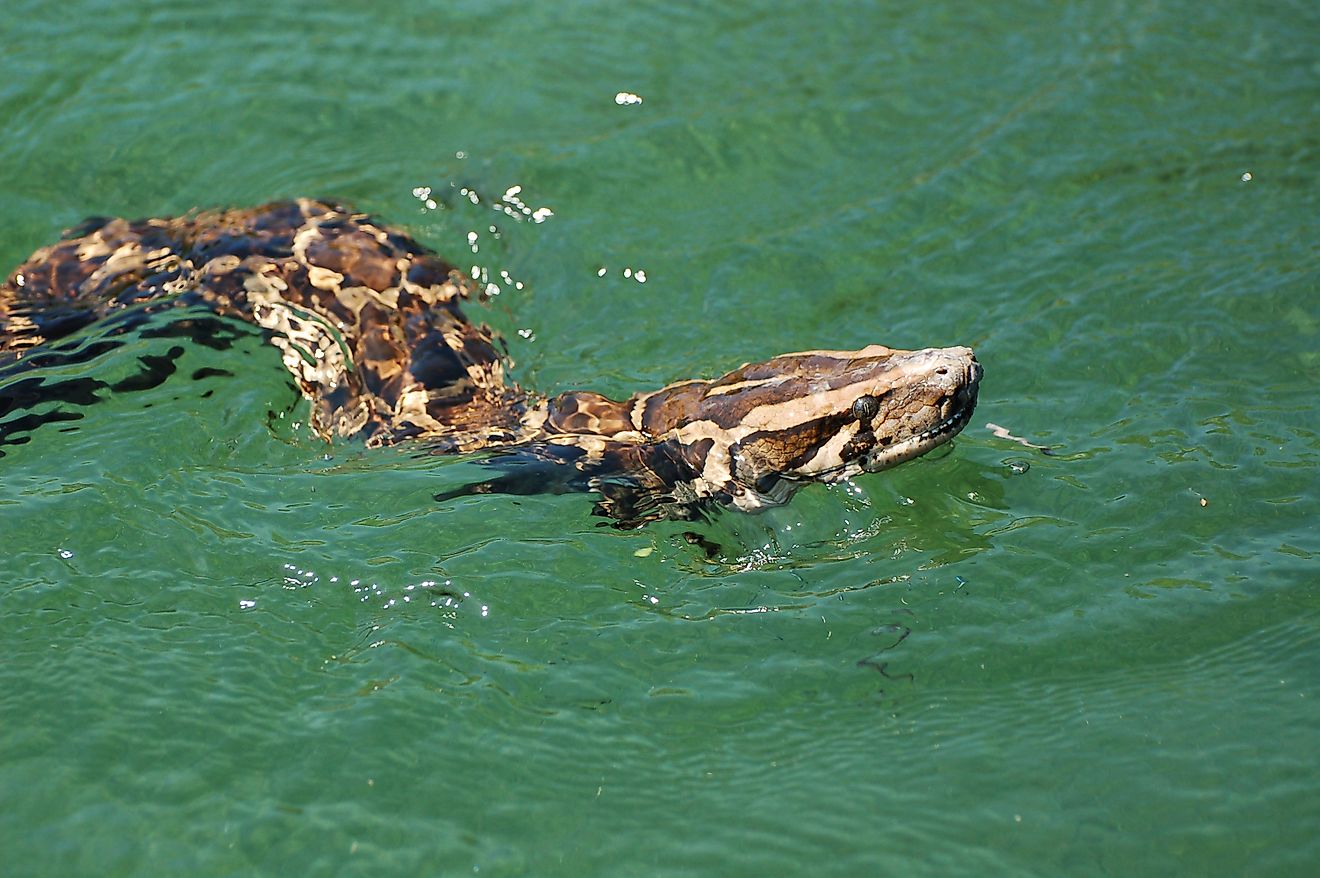
Its integration with adjacent wetlands significantly enhances overall biodiversity, rendering it a crucial element of Uganda's geographical and ecological composition. Encompassed by wetlands, marshes, and papyrus swamps, the lake forms a mosaic of habitats that sustain a diverse array of plant and animal species. Forty-six different fish species live in Lake Kyoga, some of them are endemic. The Nile Perch was introduced into Lake Kyoga in the late 1950s to increase the fish production. The varied aquatic environments create optimal conditions for numerous fish species, underlining the lake's importance as a critical fishery resource. Lake Kyoga is also home to various wildlife, including hippos, crocodiles, and otters.
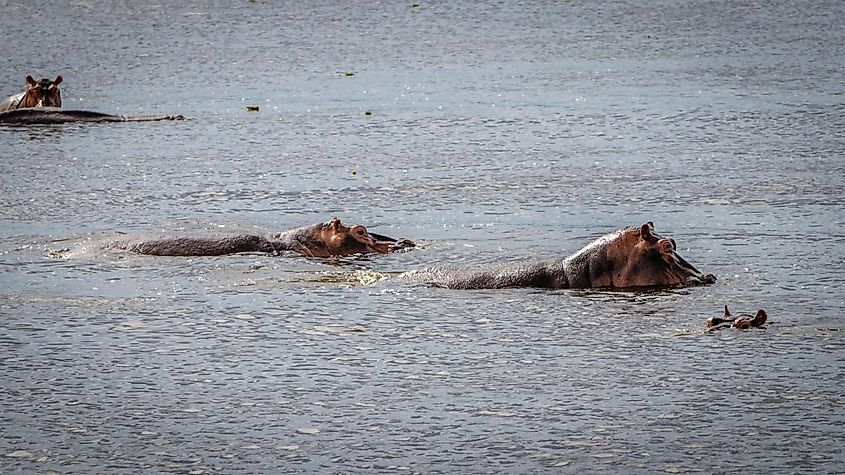

Additionaly, the wetlands and marshes play a pivotal role as essential breeding grounds for waterfowl and various avian species, establishing it as a haven for migratory birds. Hosting over 350 bird species, including the majestic African fish eagle and the elusive shoebill stork, Lake Kyoga becomes a haven for enthusiasts of birdwatching. The lake's nutrient-abundant waters sustain a intricate food web, supporting a wide array of flora and fauna. The interconnection between Lake Kyoga and its surrounding landscapes enhances biodiversity by facilitating the transfer of nutrients and species across diverse habitats. This intricate web of life not only positions Lake Kyoga as a crucial ecological focal point in central Uganda but also serves as a representative example of the significance of conserving its multifaceted ecosystems.
A primary issue related to the biodiversity of the lake is the introduction of invasive species, such as the water hyacinth, by human activities into Lake Kyoga. This disrupts the natural balance of the ecosystem, requiring collaborative efforts to maintain stability in the local environment.
Local Communities Along The Shores Of Lake Kyoga

The people living near Lake Kyoga have long-standing cultural practices linked closely with the lake. The lake holds religious and spiritual significance for the local community. Those living near Lake Kyoga use it for transportation, especially for moving goods and people between different settlements along its shores. The lake is the main source of food in the area. The locals primarily depend on fishing for their income. The diverse range of species in the lake supports the local economy and food availability, offering employment to many residing in the lake region.
The surrounding area is known for its fertile soil, creating the perfect space for agricultural lands. These lands rely heavily upon the lake as a water source for irrigation practices. The lake not only ensures food security for the local communities through its abundant resources but also as a water source for local agriculture.
Visiting Lake Kyoga
The area is renowned as an excellent spot for ecotourism. Whether you want to enjoy the calm beauty of Lake Kyoga or appreciate the diverse species in the surrounding region, there are ample opportunities for both. Different safaris provide distinctive experiences across the landscape. For those who love fishing, the lake is rich in valuable fish like Nile perch, tilapia, and catfish, making it a top fishing destination in Africa. Several chartering services are available in the lake's vicinity. Lake Kyoga remains accessible throughout the year, though weather conditions fluctuate with the seasons.
For generations, this wonder of nature has been integral to local culture, offering a vital resource for nearby communities to thrive. Lake Kyoga, celebrated for its rich and varied life, stands out with its vast expanse, diverse ecosystems, and plentiful wildlife, a true treasure of Africa. Exploring the second-largest lake in Uganda promises visitors an authentic African experience to cherish.