Lake Naivasha

Lake Naivasha is located in Kenya, roughly 35 miles southeast of Nukuru. It is situated along the eastern arm of the East African Rift, a forking rift valley which marks a continental rift that occurred within the tectonic African Plate. To the west of the lake is the Mau escarpment, which rises sharply westward from Naivasha. On the eastern side of the lake is the Ilkinopop Plateau, which is an open flat land.
Also just to the east of the lake is to town of Naivasha which has a population of just under 200,000 people. The outlying areas, and immediate vicinity of the lake are home to a few other national parks and game ranches. These include Kingono Game Ranch, which is situated along the Northern edge of lake Naivasha, the Hells Gate National Park which is located to the south, and Mount Longonot National Park which is just southeast of Hells Gate.
Dimensions Of The Lake

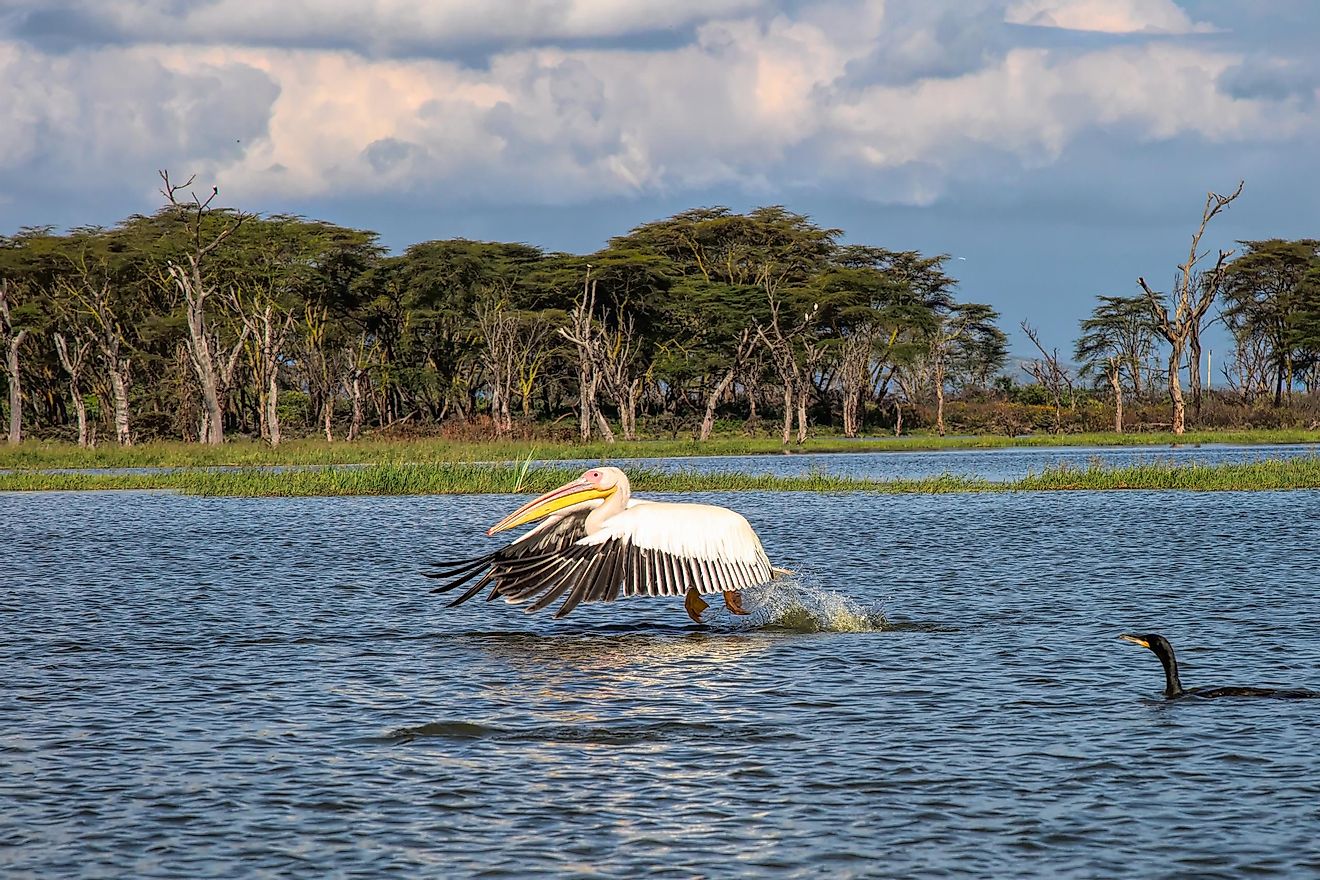
Lake Naivasha is also the highest within the Rift Valley, at a height of 1884 meters above sea level. Its water sources are the Malewa and Gilgil rivers, and there is presumed to be an outflow below ground which allows for drainage and water circulation. Naivasha measures roughly 139 square kilometers on its surface, although there is an additional 64 square kilometers of swamp land surrounding the lake itself. The marshy areas do vary in size, however, depending on the season and amount of rainfall that has occurred. On average, the lake measures around 6 meters, or 20 feet in depth, although it does get as deep as 30 meters at its deepest point (98 feet). The deepest part of the lake is the area surrounding Crescent Island, which is on the south east edge of the island.
Plant And Wildlife
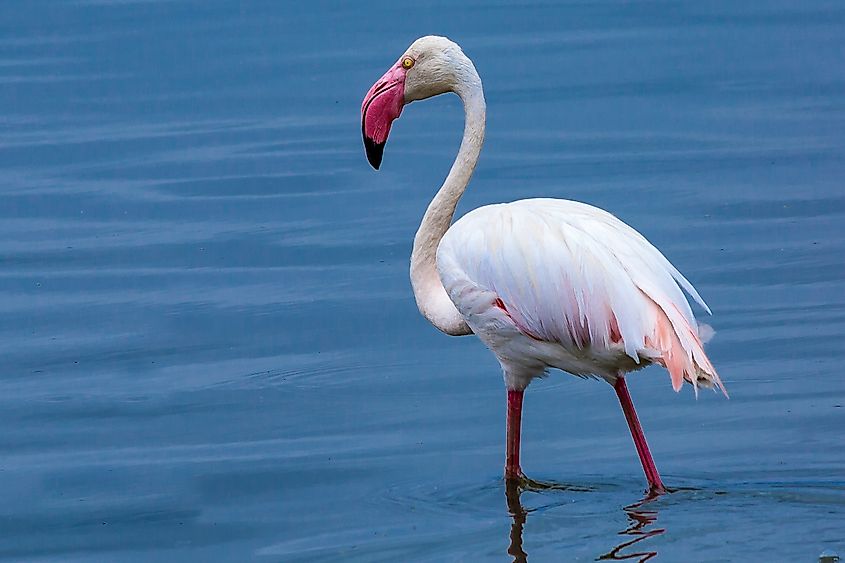

Because the freshwater lake is at such a high altitude, it provides a unique setting for birds and other wildlife. Over 400 different species of bird live in and around the lake, many of which are fish-eating species. Some of the more common species in Lake Naivasha are the great cormorant, fish eagles, pelicans, grey-backed fiscals, herons, and a variety of different kingfishers. These birds live mostly on fish and other freshwater creatures from within the lake, such as tilapia, crayfish, carp and black bass.
Smaller high-elevation birds also live here, or emigrate through the area, including species such as the red-billed firefinch, grey-capped warblers and spectacled weavers, all of which prefer the high cliff areas around the lake.
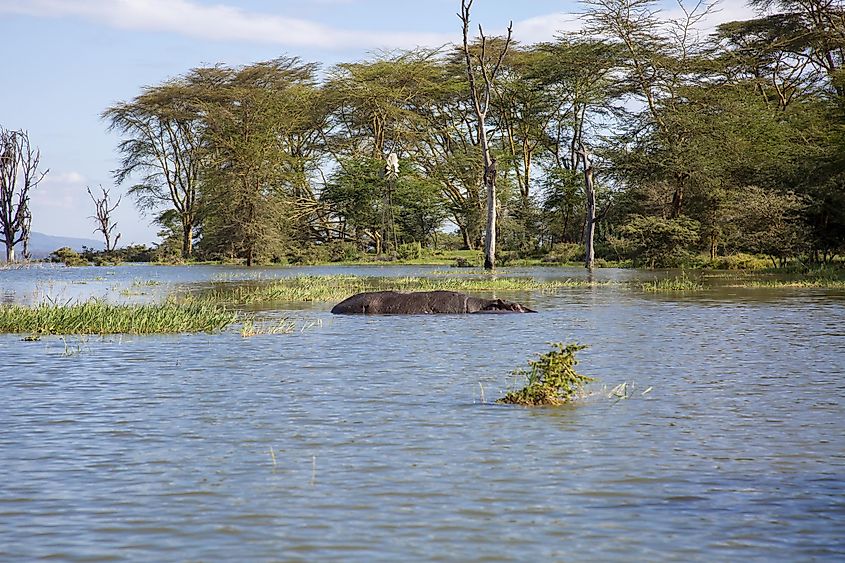

Larger animals that call the lake home include hippopotami, which reside in the lakes as well as the swampier surrounding areas. These hippos feast on lake vegetation, usually found on the bottom of the lake floor.
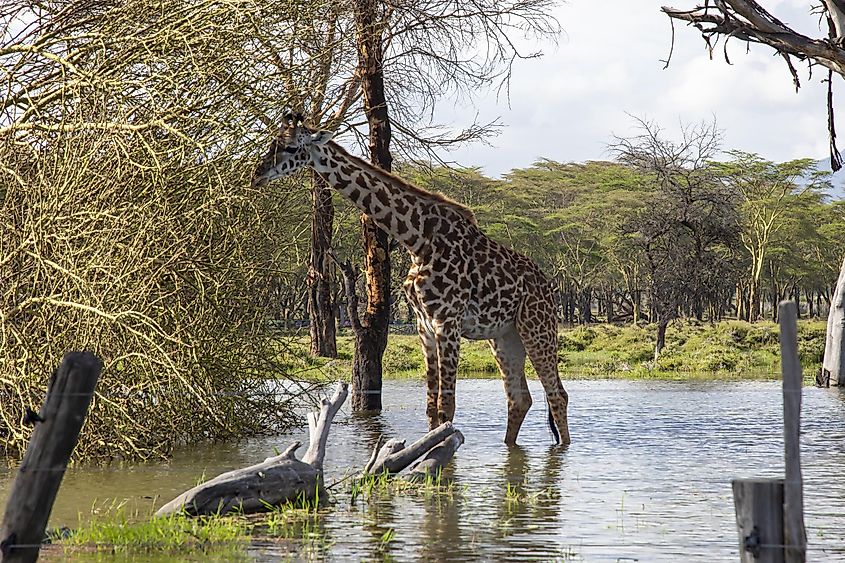

The lake also provides a useful drinking hole for other grazing animals in the area, which seek out the lake for water. Large herd animals such as zebras, buffalo, elands, and waterbucks flock to the lake to keep cool and stay hydrated.
Human Influence
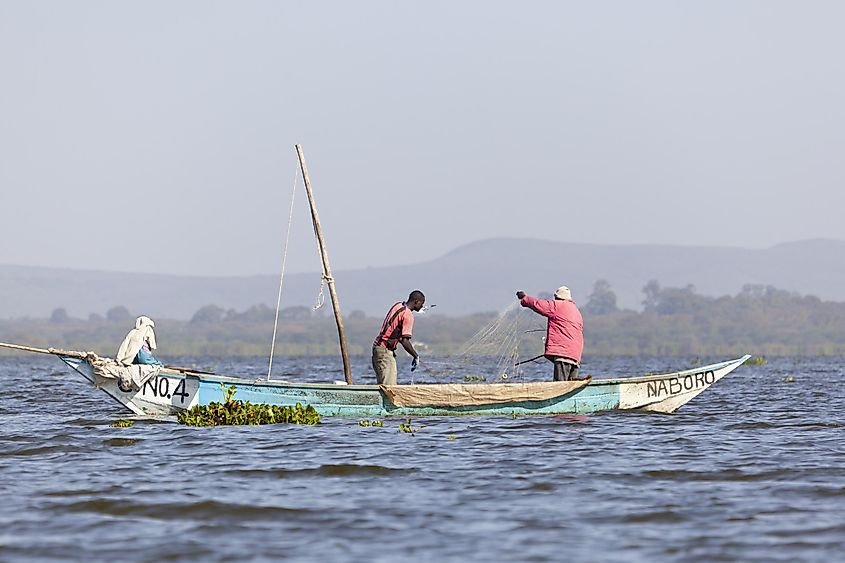

Fishing has been a major industry within Lake Naivasha. In fact, the presence of carp within the lake is a direct result of human interference. Humans introduced carp to the lake, as part of a fishing initiative, and the species then began to overpopulate. Another problem caused by humans is related to the actual water level in Lake Naivasha. Agriculture and flower farming is common in the region around the lake, and as such the lake was used as a fresh water irrigation source. This use was unregulated, and because of excessive use, the water levels in the lake dropped drastically. Though the lake does vary naturally due to changes in rainfall, this use as an irrigation source puts the lake at potential risk of drought, and threatens the habitat of wildlife that live in and around the lake.
The increase in agricultural activity and human industry have also resulted in runoff concerns. Nutrients, chemicals and natural sewage from farms have created a waste issue which seeps into the soil around the lake, or drains into the kae itself. While some of these elements are natural, they are still not naturally found in this region, and as such chemical and nutrient balances in the lake and surrounding areas are being thrown off, which in turn can cause negative effects to vegetation as well as wildlife in the area.
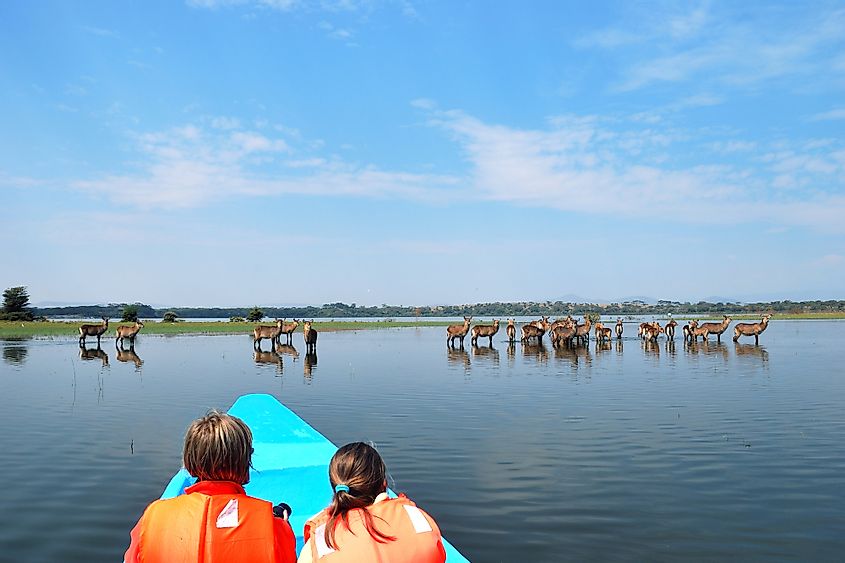

It is therefore important that parks and reserves such as that in Lake Naivasha as established and maintained, in order to preserve the natural landscape and habitats around the world. By regulating human activities, water use, and development, as well as protecting the region itself, governing bodies are better able to prevent negative human impacts, and provide a safe haven for vulnerable animals, and any wildlife that call his region home.