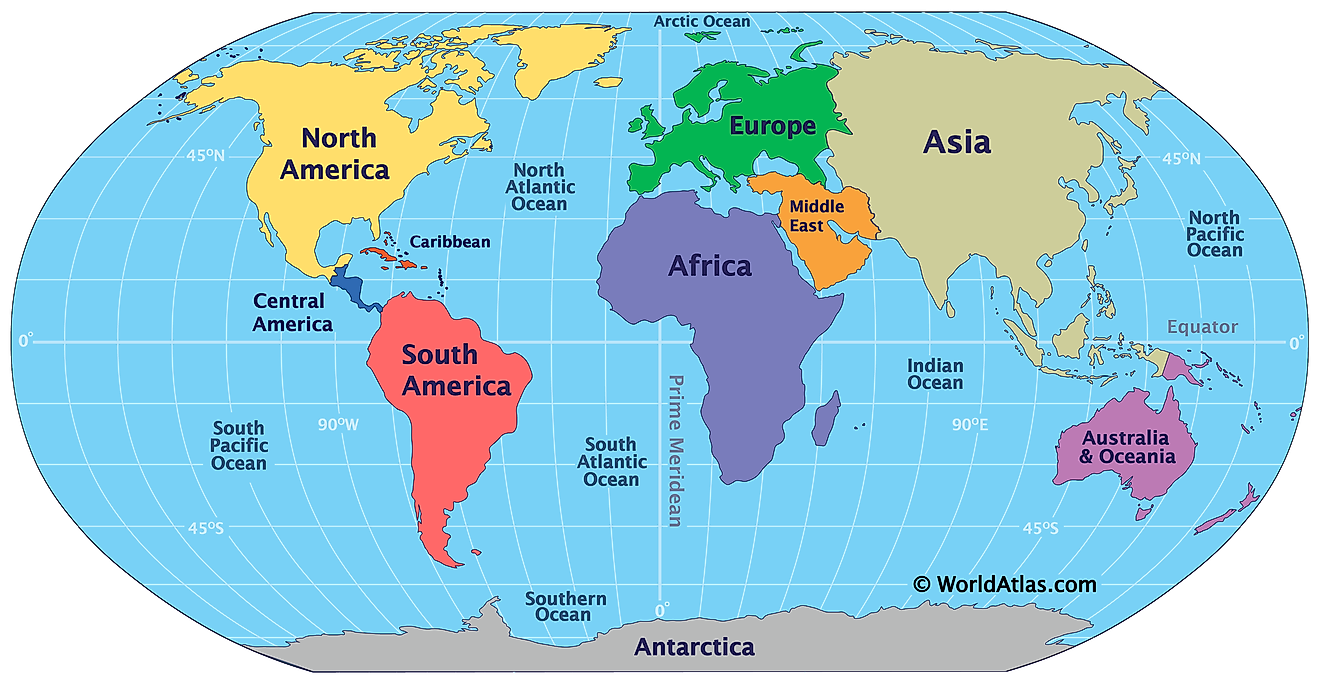
Moraine Lake
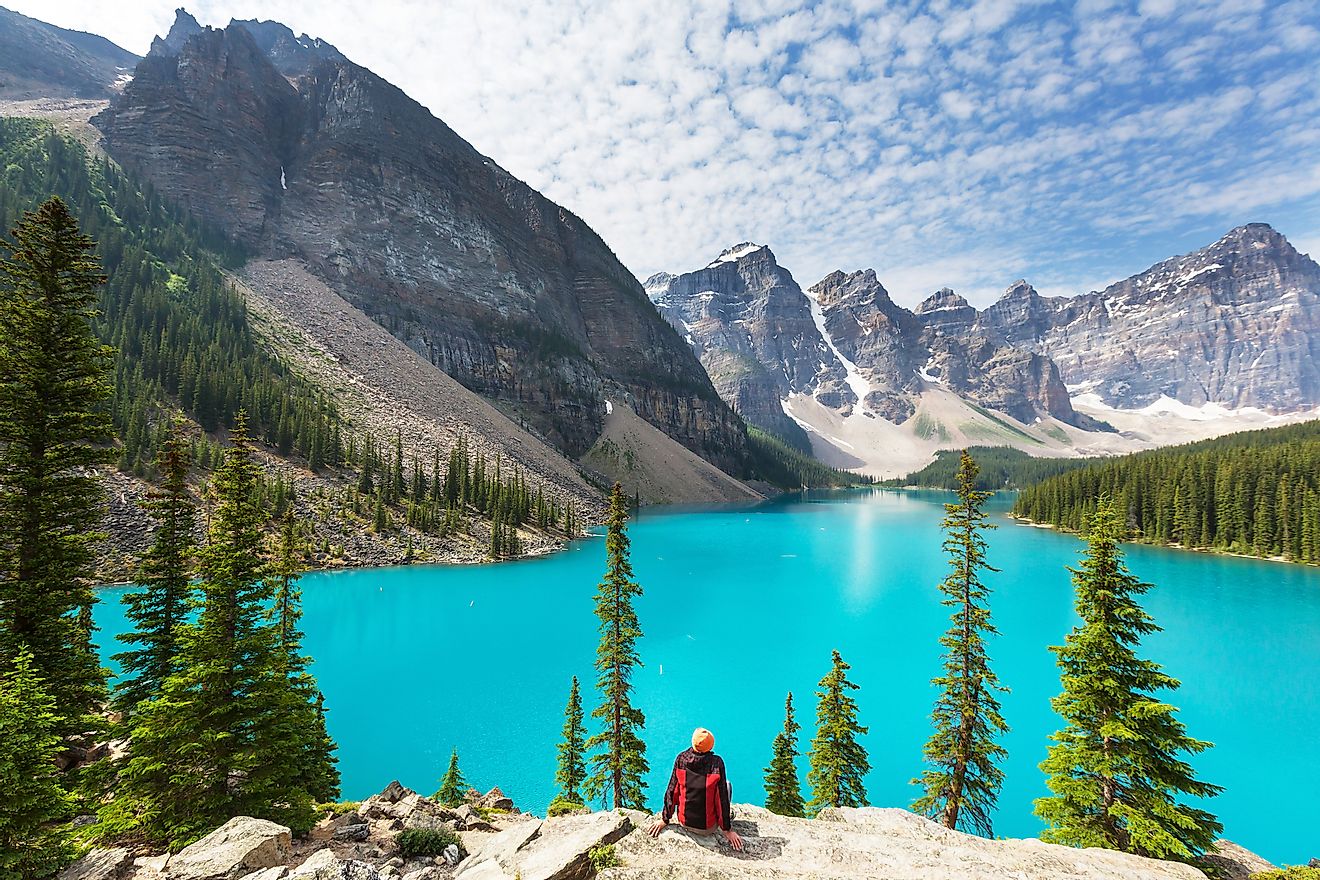

Lake Moraine is located in Banff National Park, in the province of Alberta, Canada. It is situated more specifically within the Valley of the Ten Peaks, at an elevation of 1,885 meters, or 6,183 feet. The lake has a surface area of 50 hectares, or 120 acres, and a depth of approximately 14 meters, or 46 feet.
Landscape
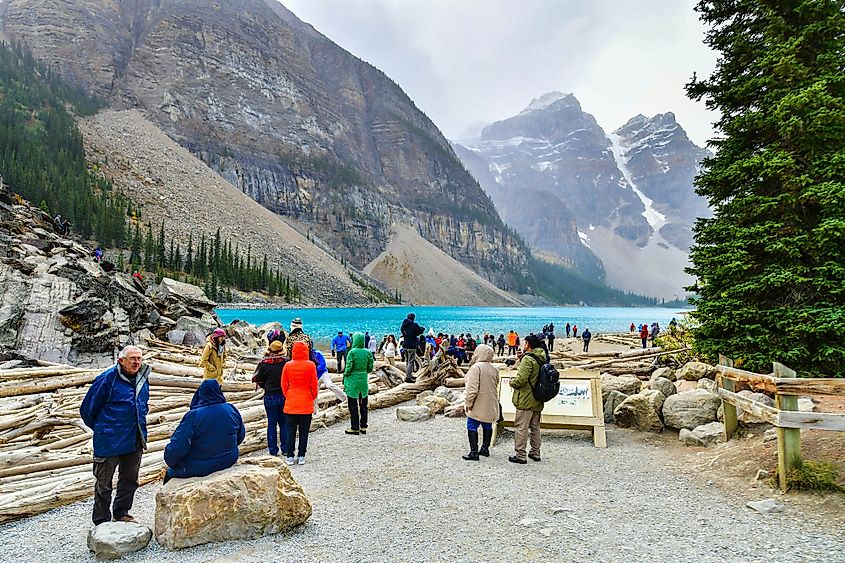

Lake Moraine is part of the larger National Park in Banff, Alberta. As such, it is a protected area popular for outdoor-loving tourists and naturalists. The region around the lake features mountains, cliffs, and rocky terrain; as well as glaciers, rivers and waterfalls.
The lake itself is in a valley, known as the Valley of the Ten Peaks. It consists of a number of towering mountain peaks which circle the lake, as part of the wider mountain ranges of the Candian Rockies. The peaks themselves include Mount Fay, Mount Little, Mount Bowlen, Mount Tuzo, Deltaform Mountain, Neptuak Mountain, and Wenkchemna Peak. The Peaks range in elevation between 3,235 meters, or 10,613 feet and 3,170 meters, or 10401 feet.
Water Source
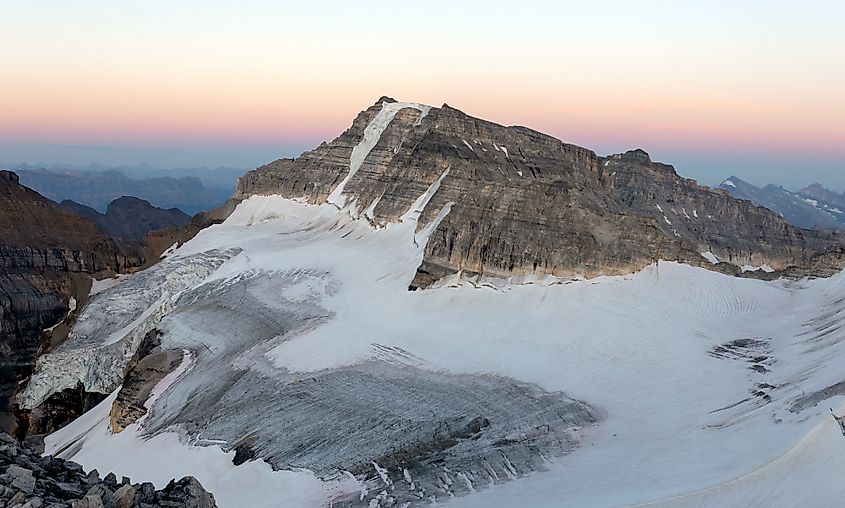

Like most lakes in Banff, Lake Moraine is glacier-fed, meaning it gets most of its water source from glacial streams and melting ice. Glacial waters tend to have a bright blue or turquoise colour, which create especially picturesque lakes and ponds. This colour variant is caused by what is called ‘rock flour’.
Rock flour is the term used for the tiny particles of rock which collect in glaciers and run-off streams. These particles cause the water to appear with a bright, crystalline blue, green, or turquoise hue, as is the case with Moraine Lake. The main inflows to Lake Moraine are from Fay Glacier, which is part of Mount Fay along the border of Alberta and British Columbia, and Larch Creek.
Wildlife
The valley that surrounds the lake ranges in vegetation. While the mountain peaks are relatively sparse, the slopes are heavily forested, featuring fir trees, spruce, and pine trees. The tree line reaches as high as approximately 2,300 meters in elevation, and runs all the way down to the rocky shores of the lake’s edge.
Moraine Lake basin is home to a range of fauna, from fish, to small mammals, and even some large predators. These animals are not specific to the lake or valley itself, but would mainly roam through Banff National Park and surrounding areas.
Grizzly bears and black bears both reside in the Banff area, and can sometimes be spotted around Moraine Lake. Similarly, cougars and lynx live in the rocky cliffs and mountain ranges, and prefer to stay ghidden and as far from human activity as possible.
Wolves and coyotes can also be found in the forest valleys, and hunt and live throughout much of the Rocky Mountain Range. Small mammals are also common in this terrain, including squirrels, porcupines, and marmots. Beavers have also been known to live in and around Moraine Lake, and spend much of their lives below the water’s surface. Fish in the lake include various species of lake trout, as well as whitefish.