Salton Sea
It's not often that you come across a place as eerily beautiful as the Salton Sea. With its water dyed a deep, murky green and its salt-covered shores, the sea is a photographer's dream. But don't let its beauty fool you - this place is full of secrets and surprises. If you're brave enough to explore it, here are some things you should know about the Salton Sea.
Formation Of Salton Sea

The modern Salton Sea was created in 1905 when heavy rains and a high spring tide caused the Colorado River to flood, breaching an engineering project intended to contain it. The outflow overwhelmed the canal's capacity for carrying away the water and led to the creation of the present-day lake.
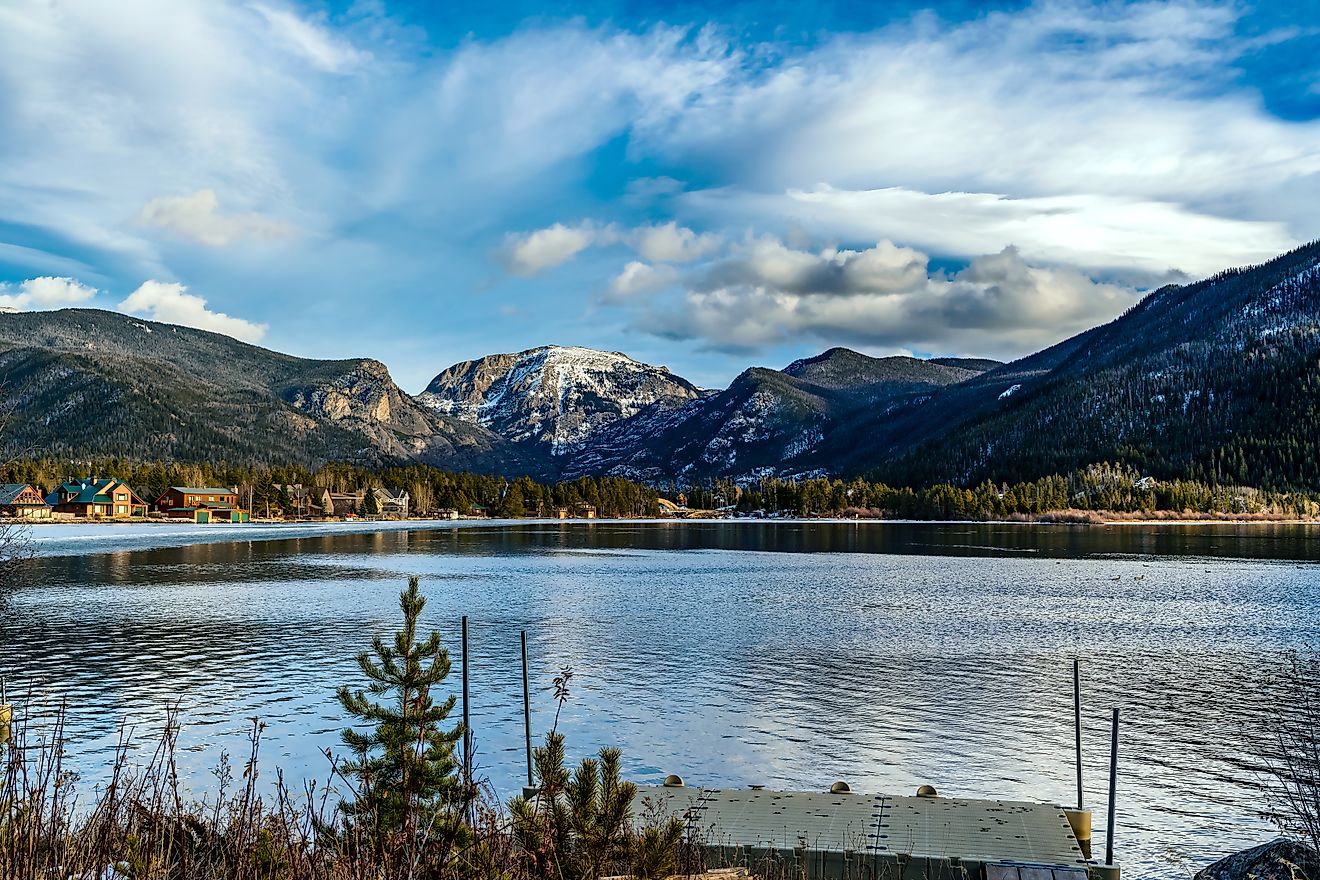
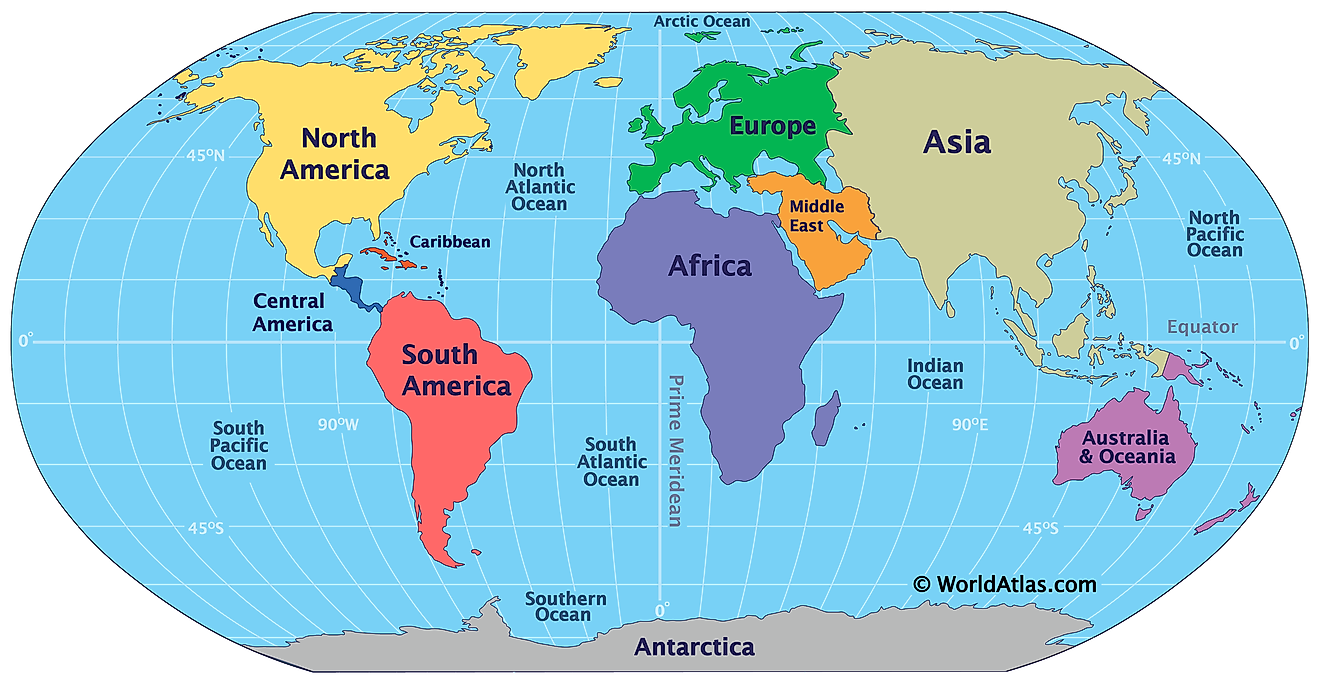
The Salton Sea is a large, saline, endorheic rift lake that is in Southern California's Imperial and Coachella valleys. The sea is fed by the New and Alamo Rivers, which flow into it from the Colorado River in the north. It lies above a basin off the San Andreas Fault; associated with this fault is a linear belt of hot springs that extends north into Washington state.
Facts About The Salton Sea

The Salton Sea is approximately 35 miles long and 15 miles wide at its widest point, with an area of 443 square miles, making it larger in surface area than Lake Tahoe but smaller in volume. It has a depth of 37 feet at its deepest point.
The Salton Sea has no outlet to the ocean, causing water to evaporate at a rate greater than the inflow of fresh water. The high evaporation rate leaves behind large quantities of dissolved minerals, which precipitate out to form a layer of crust around the shoreline. The resulting mineral buildup causes the water to become increasingly salty and alkaline over time.
Wildlife In The Salton Sea

The sea's increasing salinity and density make it hospitable only to a limited variety of organisms. The most common fish in the sea are tilapia, which were introduced in the 1960s for aquaculture purposes, and Corvina, which were introduced in the 1950s for the same reason. Due to the lack of predators and competition from other species, these fish have been able to flourish in the Salton Sea.
The high concentrations of dissolved minerals in the water also create perfect conditions for algae blooms. These blooms can deplete the oxygen in the water, leading to fish die-offs. The resulting increase in decomposing organic matter further reduces oxygen levels and creates an ideal environment for bacteria. These conditions can lead to the release of toxins that are harmful to human health. The lake is also in the path of a large volume of agricultural runoff, which has brought increasing amounts of fertilizers into the lake's waters. Since the Colorado River used to irrigate much of the Imperial Valley, the excess water and agriculture runoff feeds right into Salton Sea.
The Salton Sea is also home to a large population of migrating birds. The sea provides an important stopover for birds migrating between North and South America. More than 400 species of birds have been recorded at the Salton Sea, making it one of the most important birding areas in North America.
Recreation

The area around the Salton Sea has been converted into a state park and recreation area. Visitors to the park can enjoy boating, kayaking,and beach areas. The area is also popular for fishing, and has a number of hiking trails and campsites. However, activities have shifted somewhat over the last few decades as the water and air quality in the region has fallen.
In Summary
So if you're feeling brave enough to explore this strange and ethereal place, be sure to keep these things in mind. And if you have any tips or tricks of your own, be sure to share them in the comments below! We would love to hear about your experiences at the Salton Sea.