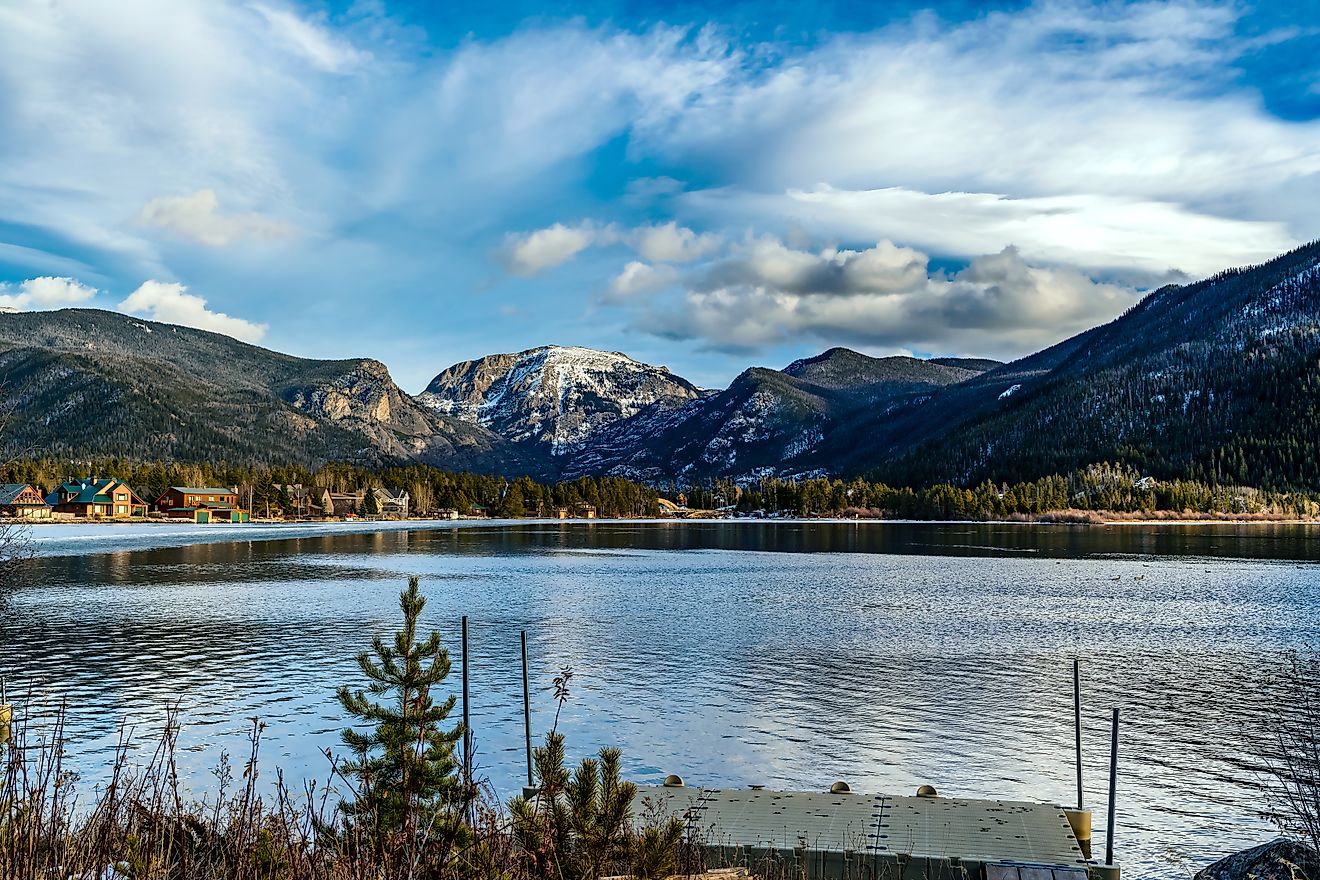
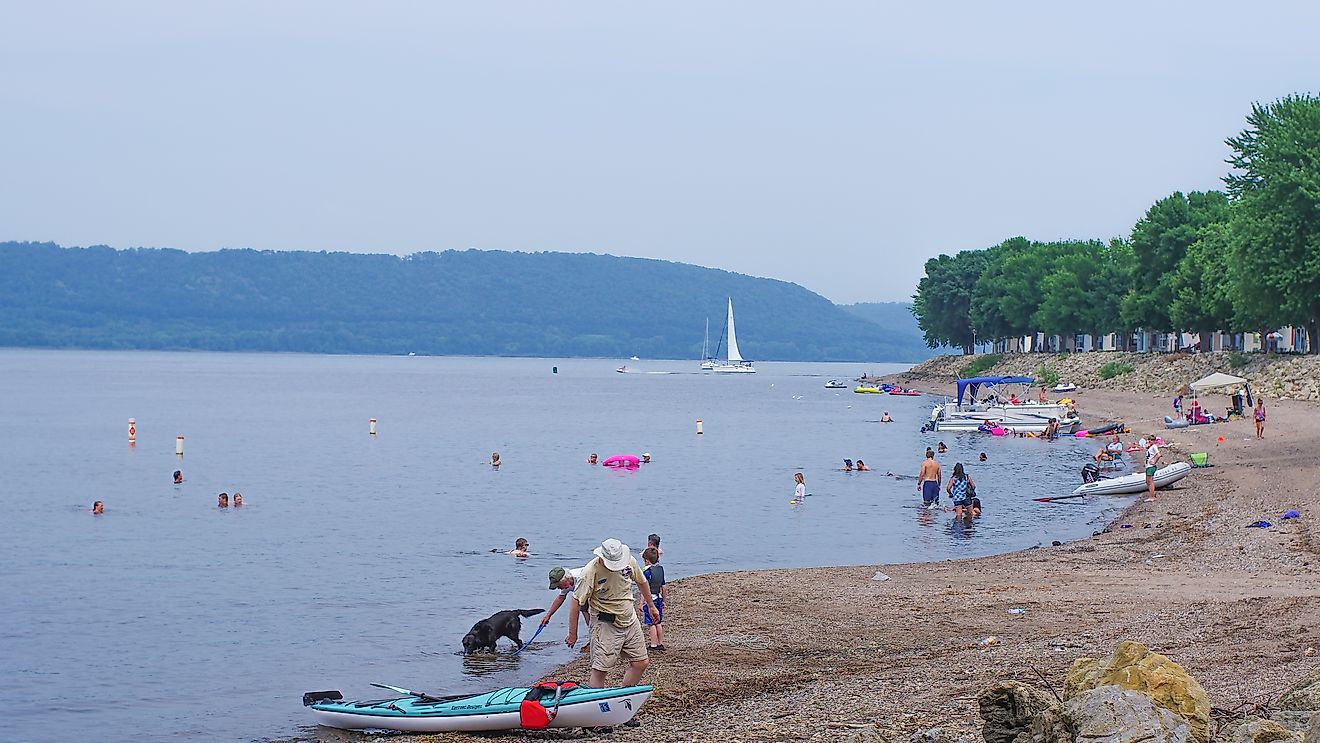Seneca Lake, New York
Seneca Lake is located in the Finger Lakes region of upstate New York and is the largest and deepest of the glacial lakes that make up this area. It is a popular spot for boating, fishing, camping, and other recreational activities and for observing the local wildlife. A long-standing feature of the landscape, Seneca Lake has been used by humans for centuries, from indigenous tribes to settlers from Europe who arrived in the late 18th century. Its waters are steeped in folklore, including tales of dragons, spirits, and sunken ships. Presently, it boasts a diverse range of species that occupy its banks or swim through its depths. Seneca Lake is also a major economic resource, with tourism being particularly important to local businesses. In recent years there have been efforts to protect its shoreline from development while using it sustainably; as such, it continues to be an important cultural and environmental destination.
Geography Of Seneca Lake

Seneca Lake is a glacial lake located in the Finger Lakes region of New York. With a surface area of nearly 70 square miles, it is the largest of the Finger Lakes and is also the second-deepest in North America. It is approximately 38 miles long and has a maximum depth of 618 feet. The shores of Seneca Lake are dotted with several small towns and villages, many of which are popular tourist destinations.
Watkins Glen State Park and other nature preserves line its banks, along with numerous wineries, cideries, restaurants, and breweries. The northern shore features several state parks that offer camping and kayaking on the lake.

Seneca Lake is renowned for its unusually clear waters due to its great depths; this clarity helps draw fish to its depths and makes it an ideal spot for swimming, boating, and paddling activities. The lake hosts several fish species, including carp, smallmouth bass, yellow perch, and channel catfish, while lake trout can be found closer to the bottom.
Development around the lake has led to increasing challenges with water quality in recent years; phosphorus levels have been drastically increasing since 1990 due to runoff from agricultural fields. This has caused heavy algal growth during the summer months in some areas, leading to restrictions that limit recreational activities such as swimming in some locations near Geneva.
Seneca Lake also boasts its own microclimate, which produces notably strong winds between 20mph-60mph (average wind speeds between 10mph-20mph). These storms are known locally as "white squalls" because they can quickly fill the sky with white foam from waves crashing against the shoreline. Although causing considerable damage on shorelines throughout history, these gusts bring much-needed nutrients out from shallow waters for wider coverage into the depths of lakes.
History
Indigenous populations dominated the area until 1779 when European settlers first arrived at Seneca Lake. The Seneca had settled along the lake's northern shore since prehistory and were displaced during this period by colonial settlement from Germany and Switzerland. These settlers brought viticulture to Seneca Lake and established it as one of the major agricultural centers in western New York state.
By 1820, several towns had developed around the central Finger Lakes. In 1848, Union Springs became one of these towns when it was incorporated on the east side of Seneca Lake's northern branch. The town flourished over time due to its proximity to nearby lake towns and transportation hubs such as railways, making it an important hub for commerce.

In modern times, Seneca Lake remains known for its agricultural culture. Vineyards have grown significantly over time, producing world-renowned wines that bring tourists from all around.
Folklore Revolving Around Seneca Lake
From time to time, mysterious distant "booms" can be heard across Seneca Lake. Some attribute the sound to cannons from long ago, while others believe it is a message from Native Americans or Revolutionary War soldiers. The Native Americans believed that the noise resulted from evil spirits, drums played by their ancestors, or a curse from the Great Spirit if sacred laws were violated. However, according to science, these sounds are actually caused by natural gas bubbles escaping from different levels of sandstone.

Then there's the infamous monster of Seneca Lake, an underwater beast described as a cross between an alligator and a snake which was first encountered by a steamboat in 1899. The passengers presumed the animal, with some describing it as being bigger than a horse and up to 25 feet long, as being dead after the boat's paddle wheel struck it.
For twelve years, the Seneca Lake Whale Watch Festival shined a spotlight on one of the lake's unsolved mysteries. They supposed that there might be a whale living in its depths if it was conceivable that the creature had followed networks of canals from the ocean.
Finally, tales abound of several sunken ships at the bottom of Seneca Lake – stories supported by archaeological evidence dating back to the 1800s. Some locals insist that these vessels carry valuable treasure within their holds, though no man has yet uncovered them.
Wildlife Of Seneca Lake
The wildlife of Seneca Lake is teeming with activity and diversity. Its freshwater has served as home to countless species over the years, from fish and amphibians like bass, perch, bullhead catfish, and salamanders to reptiles such as snapping turtles, a variety of snakes, and even rare rattlesnakes.

Birds are also abundant here; waterfowl like ducks and swans can often be seen gliding along its surface, while ospreys nest on its banks. On land, there's an array of animals including squirrels, deer, and foxes which can be spotted at times around the lake's edges or in nearby woodlands.
Anglers have long had success fishing these waters for game fish – many find success targeting trout in the spring when they move upriver for spawning season. In addition to its native species, Seneca Lake has become home to invasive species, including zebra mussels and spiny water fleas, which have caused massive disruption to its original ecosystem.
Overall, Seneca Lake is an important natural and cultural resource in the Finger Lakes region of New York State. With its rich history, diverse wildlife, and myriad recreational opportunities, it remains an integral part of the local culture and a beloved destination for visitors from all over. It is evident that Seneca Lake is a special site that should be safeguarded for future generations. Through continued efforts for protection and sustainable use of its resources, the beauty of this area can remain intact for years to come.