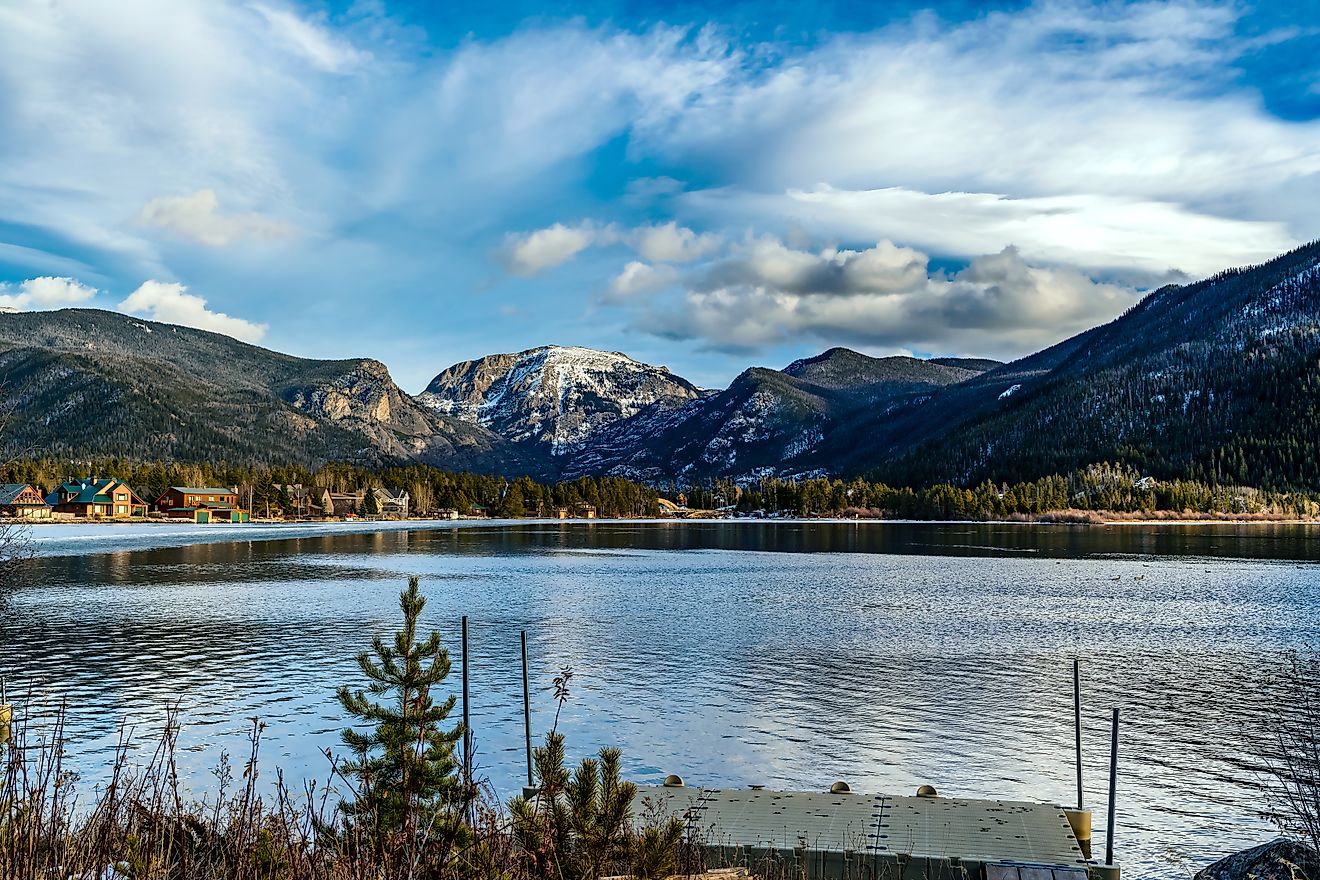
Utah Lake, Utah
Utah Lake is a shallow freshwater lake situated within the Utah Valley at the heart of Utah County in the north-central portion of the US State of Utah. The lake is slightly saline, as evaporation accounts for about 42% of the lake's outflow. In recent years, however, the water levels of Utah Lake have been lowered by drought. Utah Lake is cooperatively managed by the Utah Lake Commission and the Utah Division of Forestry, Fire & State Lands. The Division manages the lake's public use and gives necessary permission for the lakebed and shoreline's commercial use. The Utah Lake Commission facilitates the development of the lake and its surrounding areas. During summer, fishing, water skiing, picnicking, and boating are some of the most popular activities, whereas ice fishing and ice skating are offered at the Utah Lake State Park during winter.
Geography Of Utah Lake

The Utah Lake covers a total area of about 380 sq. km. The lake is about 39 km long and has a maximum width of 21 km. The lake sits at an elevation of about 1,368 m and has an average depth of 3.2 m, reaching a maximum depth of 4.3 m. The lake holds a water volume of 870,000 acre-ft and has a catchment area of 9,960 sq. km. Utah Lake receives inflows from American Fork, Provo River, Spanish Fork, Hobble Creek, Dry Creek, Current Creek, and Mill Race Creek. In addition to this, several hot springs and small creeks flow into the lake. The lake's primary outflow is the Jordan River, which starts at the lake's northern end and finally empties into the southeastern part of the Great Salt Lake. Owing to the lake's shallow average depth, large surface area, and the surrounding area's semi-arid climate, constant evaporation also accounts for about 42% of the outflow of the Utah Lake.
It is believed that the Utah Lake is a remnant of the ancient Lake Bonneville. The Utah Lake is situated on the Utah Valley's western edge, covering over 25% of the valley's floor. The Utah Valley is surrounded by several mountains, such as the Wasatch Range, Traverse Mountains, Lake Mountains, Mount Nebo, and Mount Timpanogos. Two big shallow bays, namely Goshen Bay and Provo Bay, are connected to the main body of the lake. The West Mountain, which juts into the southern portion of the lake, divides Lincoln Beach and Goshen Bay. Located close to the lake's southern end, about 3.62 km north of the Lincoln Beach boat ramp, is a small island called Bird Island. Placed between the Wasatch Range and the lake's eastern shore are the cities of Provo and Orem.
History Of Utah Lake

The first known European settler in the area was the Spaniard Silvestre Velez de Escalante in 1776. The Timpanogot Utes inhabited the area before the Europeans. Many members of the Ute Tribe were expelled and killed by European and Mormon settlers in the ensuing century. The fish of the lake was eventually overharvested and replaced with new, non-native species. The lake has also faced several issues, like pollution and harmful algal blooms. The Utah Lake is at present cooperatively managed by the State's Division of Forestry, Fire, and State Lands, as well as the Utah Lake Commission. There have been recent calls to change the name of Utah Lake to Lake Timpanogos.
Ecology Of Utah Lake

The lake area is home to many mammals, such as the big brown bat, the mule deer, and the desert woodrat. At present, several species of fish inhabit Utah Lake. These fish species include the black bullhead, white bass, blue gill, goldfish, yellow perch, and many more. The only native fish species left in Utah Lake are the Utah and June Suckers, the latter of which is endangered. The Utah Lake wetland ecosystem serves as a crucial breeding ground and a stopover for several migratory birds. Some of the avian species commonly seen in the lake include double-crested cormorant, golden eagle, mallard duck, great horned owl, sandhill crane, and many more.