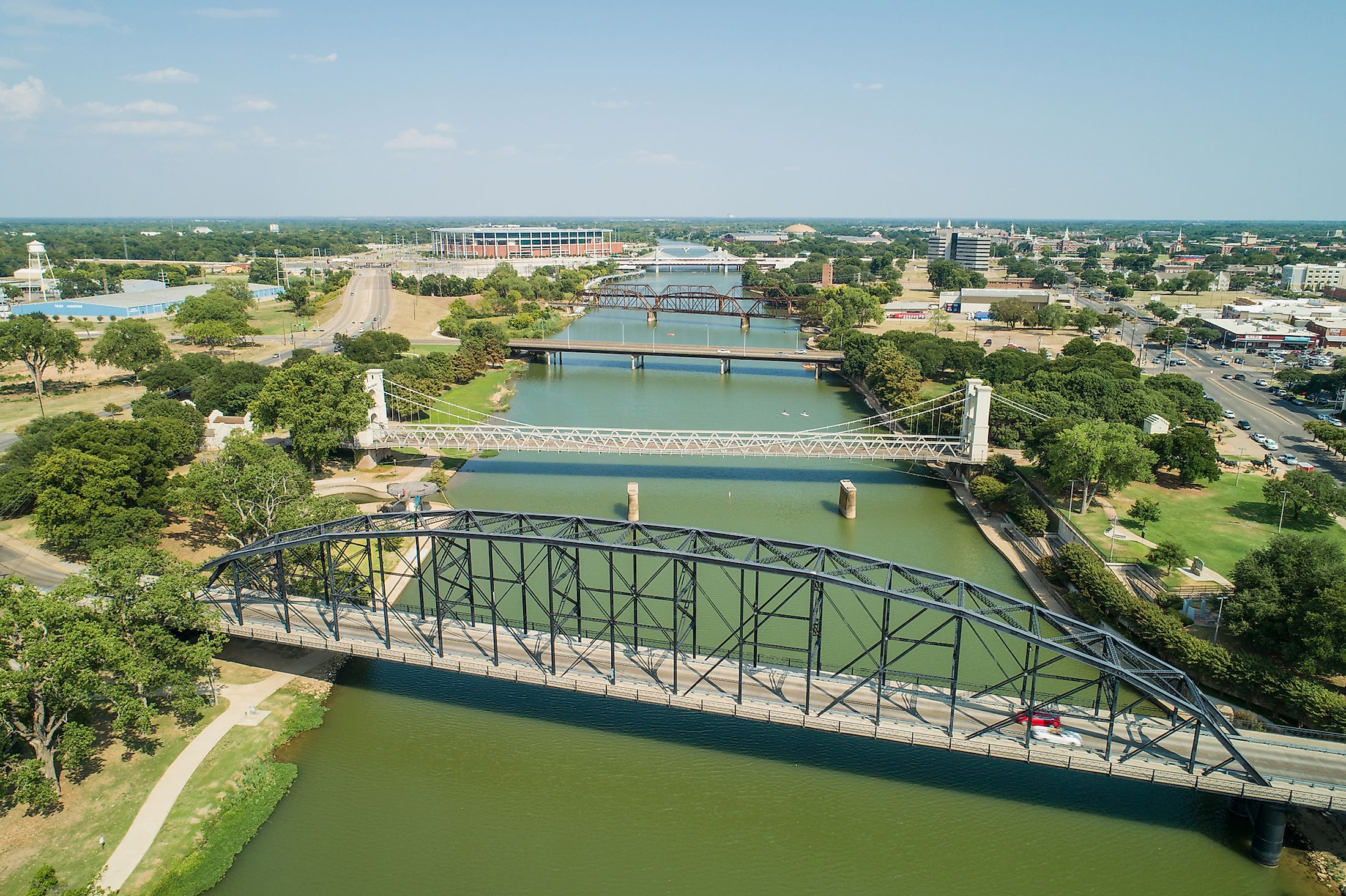
Brazos River
Also referred to as “Río de los Brazos de Dios” by the early Spanish explorers, the Brazos River is considered as the United States’ 11th longest river and the longest river that flows within the State of Texas. The headwaters of the 2,060km long Brazos River originates from the beginning of the Blackwater Draw stream in the Roosevelt County of the State of New Mexico. The river then flows through Texas and finally drains into the Gulf of Mexico. As one of the largest rivers in Texas, the Brazos River is used to mark the border between West and East Texas.
Geography
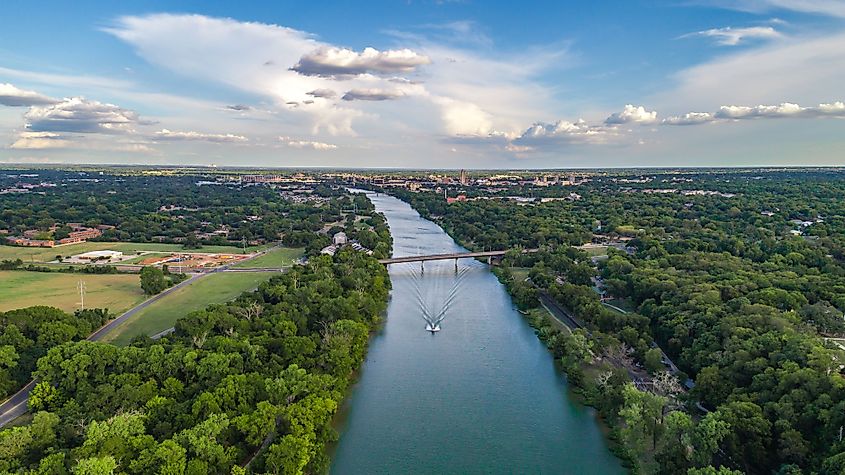

The two Upper Brazos tributaries namely the Double Mountain Fork and Salt Fork rises on the high plains of Llano Estacado. The Brazos River originates at the confluence of these two tributaries in the Stonewall County of Texas. The river then flows for 1,350km in the southeast direction, through the heart of Texas before joining with the Clear Fork River close to the city of Graham to form the Lower Brazos River.
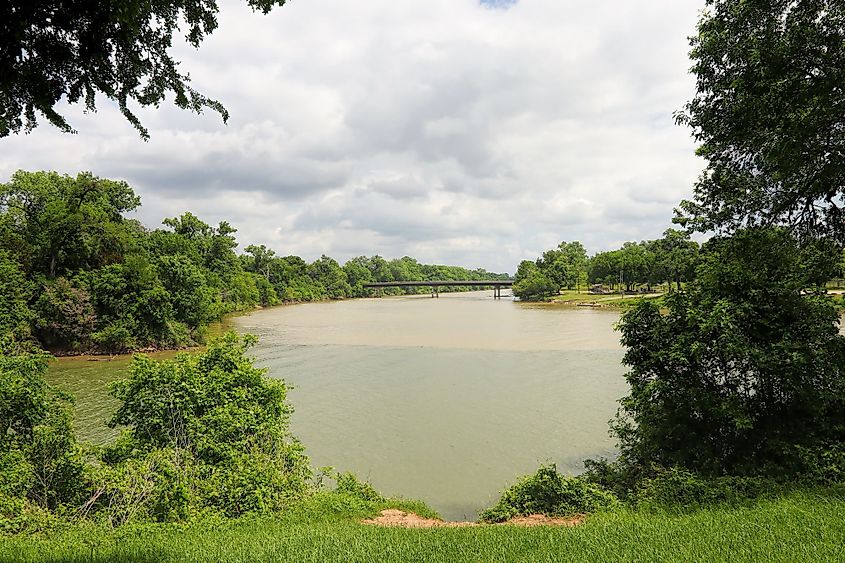

Some of the major tributaries of the Lower Brazos River include the Bosque River, Leon River, Little River, Lampasas River, Nolan River, Navasota River, Paluxy River, San Gabriel River, and the Yegua Creek. The Brazos River then flows eastwards towards the large cities of Dallas and Fort Worth, before turning in the southward direction and flowing through the campus of Baylor University and the city of Waco. The river continues its southward journey and flows past the cities of Calvert, Bryan, and College Station into the city of Richmond. The Brazos River finally drains into the Gulf of Mexico near the southern part of the city of Freeport.
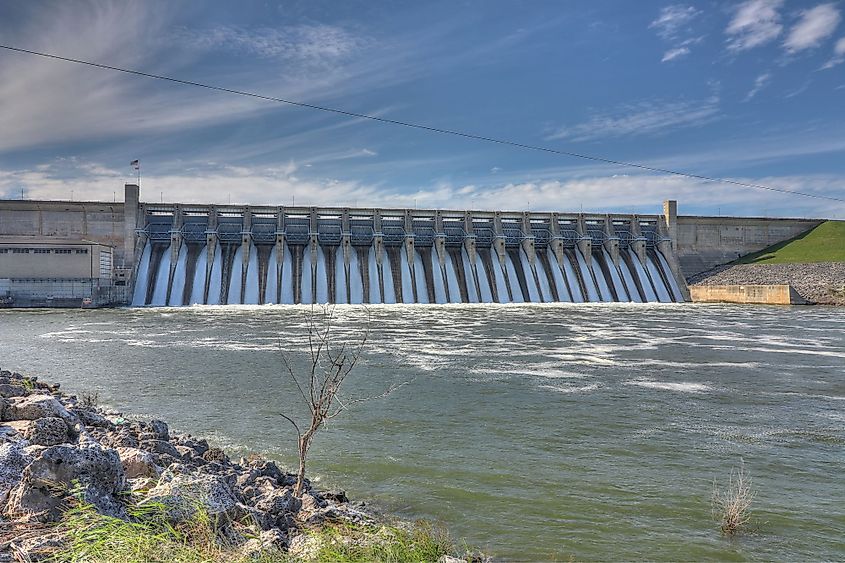

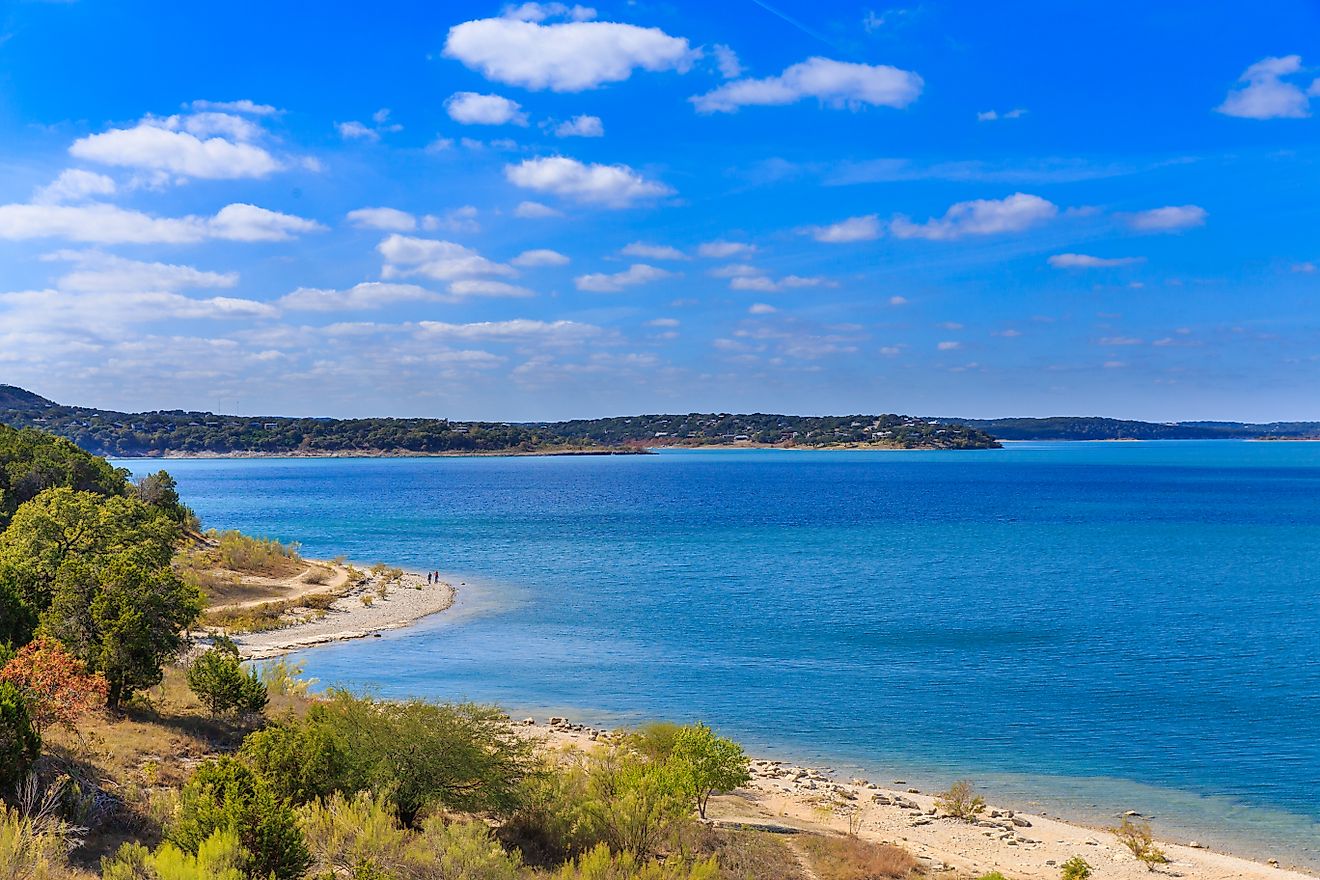
The Brazos River has been dammed thrice to form Lake Granbury, Possum Kingdom Lake, and Lake Whitney. Situated on the Upper Brazos River, the Whitney Dam is used for controlling floods, generating hydroelectric power, and for irrigating the cotton fields. Covering a vast area of 119,174 sq. km, the Brazos River watershed hosts more than 42 lakes, streams, and rivers that have a combined storage capacity of 2.5 million acre-feet. The Brazos River watershed also stores about 119,275 acre-feet per year of groundwater. It has been estimated that about 31% of the watershed is used for agriculture, 61% is grassland, 19.8% is shrubland, 11% is forest, and only 4.6% is for urban settlements. Major educational institutions in Texas such as Texas A&M University, Texas Tech University, and Baylor University are situated close to the Brazos River Basin.
Several studies have raised concerns regarding the quality of water in the Brazos River watershed due to low dissolved oxygen, high salinity and bacterial levels, and high nutrient loads. It is believed that this poor water quality is mainly because of the chemical and fertilizer runoffs and the wastes of livestock that flow into the river from the agricultural areas and industrial sites that are located along the course of the river. Researches have shown that as of 2012, the Lower Brazos River has received about 33.4 million pounds of toxic wastes. Nevertheless, the Brazos River serves as a popular tourist destination and offers many recreational activities such as canoeing, boating, fishing, sandbar camping, picnicking, etc for its visitors. Boating and canoeing are popular activities as many suitable sites for launching and recovery are located along the river, and the best paddling spots are situated just below Lake Granbury and Possum Kingdom Lake.
Brief History
In 1822, one of the major Anglo-American settlement sites in Texas was established along the lower Brazos river valley. These Anglo-American settlement sites were considered to be the first English-speaking colonies that were founded by San Felipe de Austin and Stephen F. Austin along the Brazos River. In 1836, Texas declared independence from Mexico in the unincorporated community of Washington-on-the-Brazos in the Washington County located along the Brazos River. During the Texas Revolution, the Brazos River also served as the site of a fierce naval battle between the Mexican and Texas Navy. The Brazos River is presently under the administration of the Brazos River Authority and the river serves as the principal source of water for irrigation, recreational activities, and generation of hydropower.