Colorado River
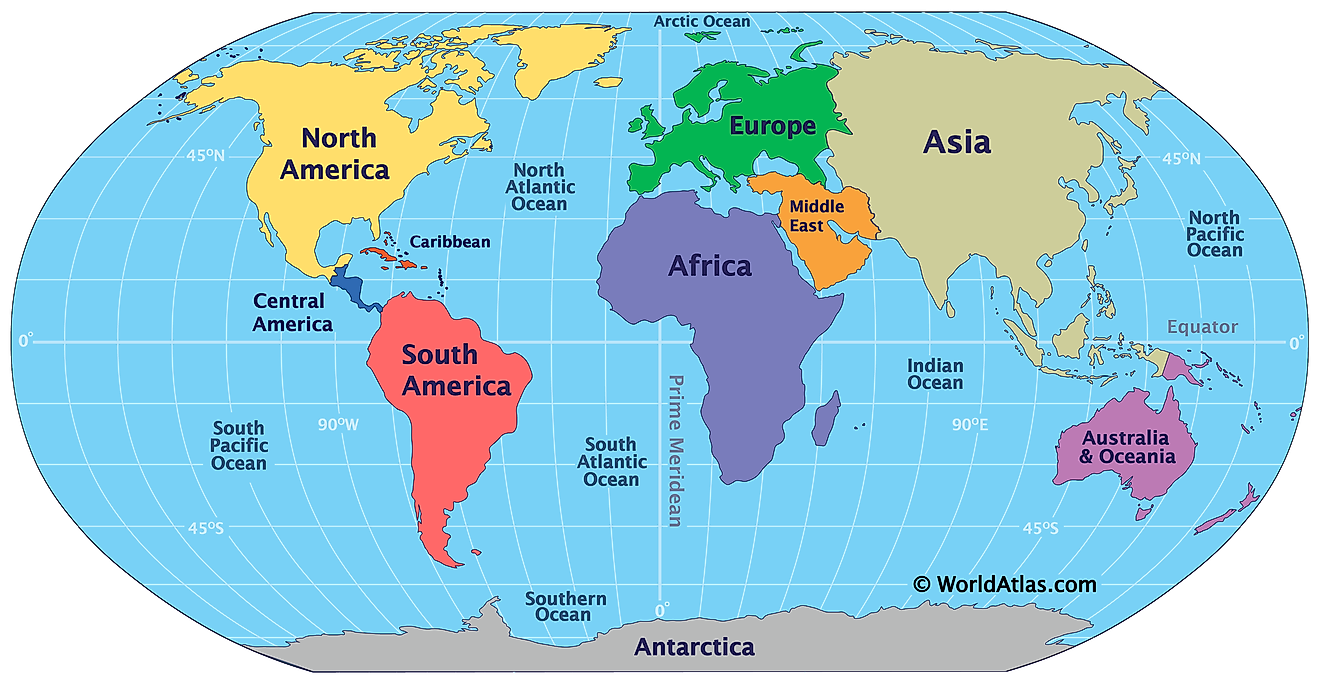
The Colorado River is both a scenic wonder and a source of water for over 40 million people. At 2,330 kilometers, the Colorado River is the United States's fifth-longest river from its source in the Rocky Mountains to its mouth in the Gulf of California. It flows through the US states of Colorado, Utah, Arizona, Nevada, and California, and Mexican states of Baja California and Sonora. Colorado forms an international boundary between Arizona (US) and Mexico for about 29 kilometers and drains North America’s vast semi-arid and arid area. The intensive development along the river has earned it the name “Lifeline of the Southwest.”
Geography and Climate
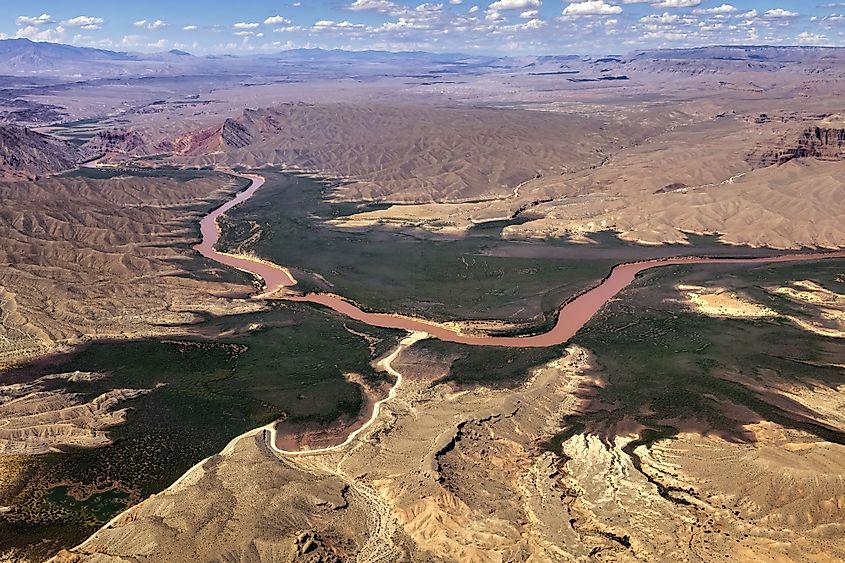

The Colorado River is 2,330 kilometers long from its source in the La Poudre Pass in Colorado’s Rocky Mountains to its mouth at the Gulf of California. The river and its tributaries drain approximately 640,000 square kilometers of southwestern North America. It discharges an average of 640 cubic meters of water per second, amounting to 20.1 cubic kilometers per second annually, and a maximum discharge of 10,900 cubic meters per second. The Colorado River has several tributaries, including Green, Gunnison, San Juan, Dolores, Little Colorado, Gila, and Virgin Rivers. The Green River is the longest river feeding into the Colorado River, discharging about 171 cubic meters per second.
The climate of the Colorado River basin varies, with a mean monthly temperature (high) of 25.3°C in the upper basin and 33.4°C in the lower basin. The basin receives an average of 164mm in precipitation, with the upper basin receiving snow and rain during winter and early spring and the lower basin in summer. However, some areas, especially around the Rocky Mountains, receive up to 1,000mm, while other areas receive as low as 15mm.
Course
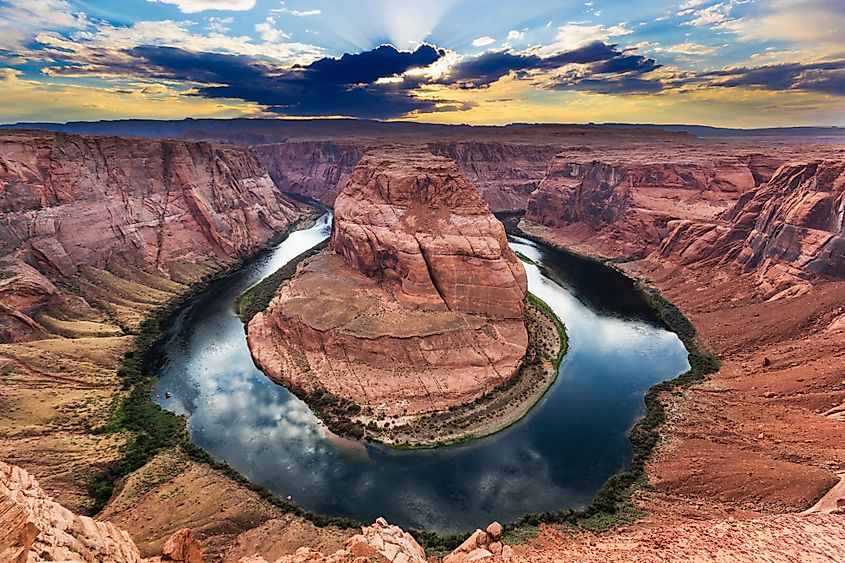

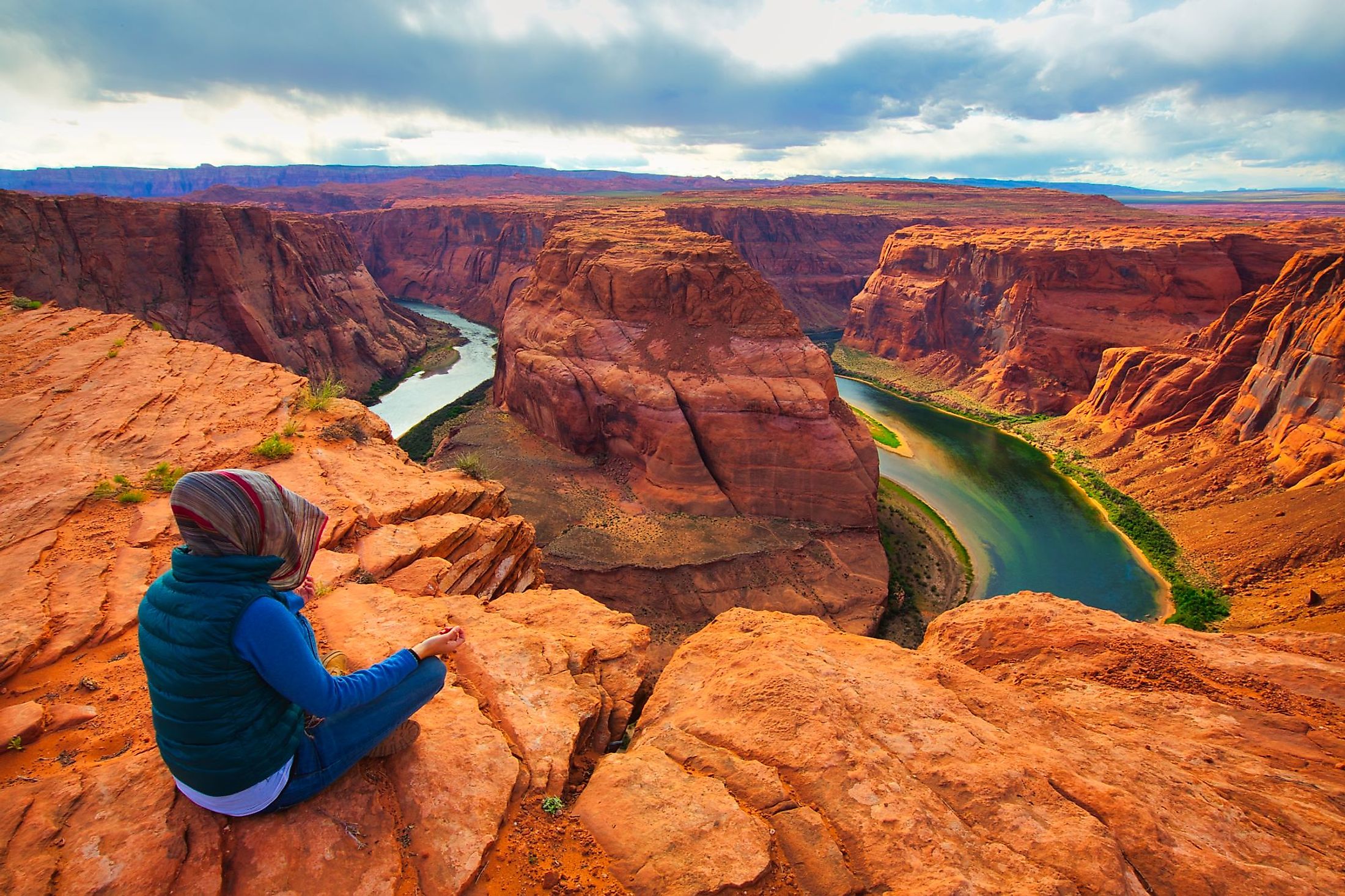
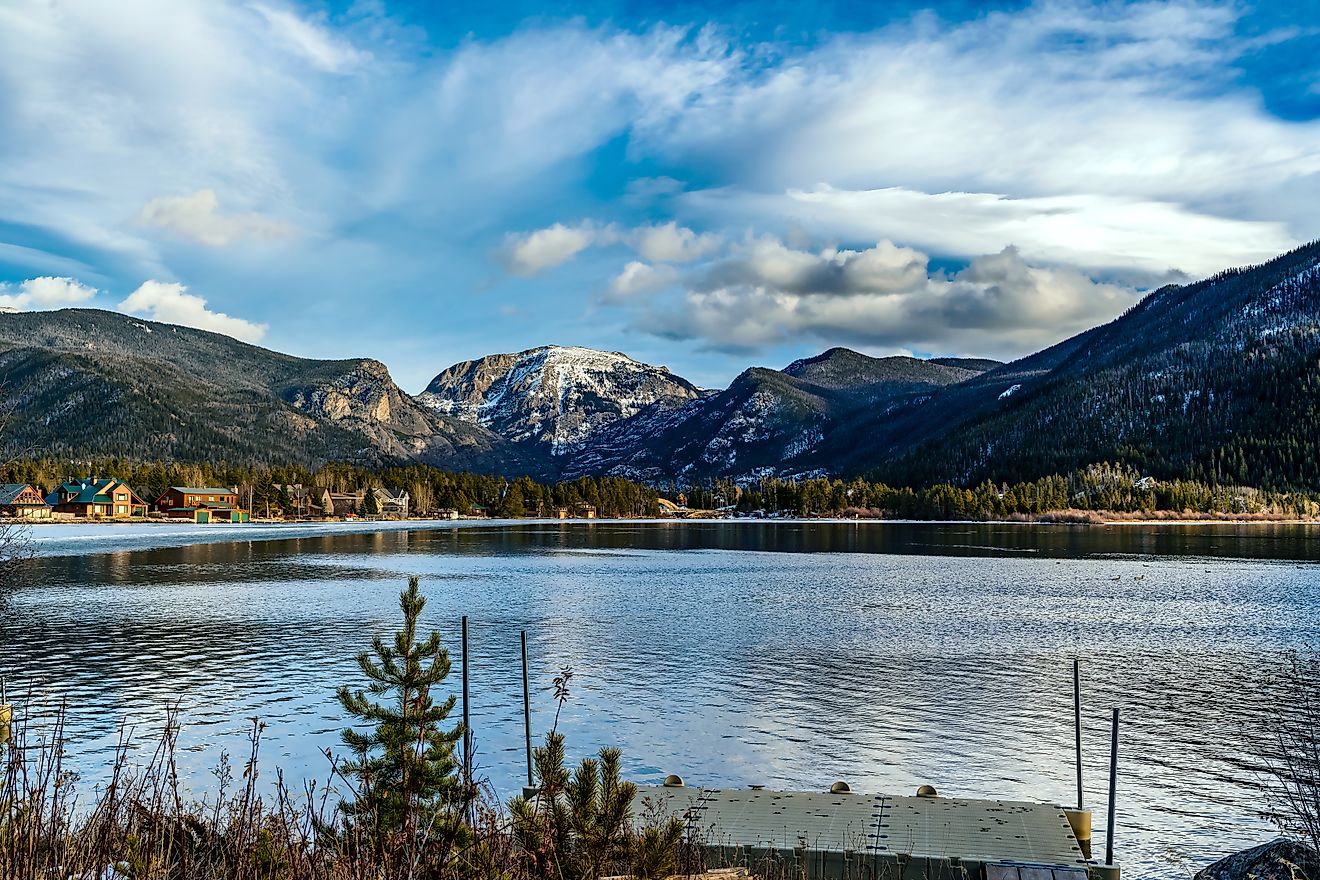
The Colorado River has its headwaters at the La Poudre Pass in Colorado’s Rocky Mountain National Park, about 40 kilometers from Lake Granby. The headwater is located at an altitude of 3,104 meters above sea level. The river flows southwards from its source for a short distance then turns west towards Grand Lake (Colorado’s largest natural lake). After about 1.5 kilometers, the Colorado River cuts through its first canyon, known as the Little Yellowstone Canyon, then through Kawuneeche Valley and exits the Rocky Mountain National Park.
From the national park, the Colorado River flows into Lake Granby through Shadow Mountain Lake. The river leaves Lake Granby and flows parallel to Highway 40 to Kremmling Town, Colorado. Fraser River joins the Colorado River downstream from Lake Granby, while the Blue River joins it at Kremmling. The river then flows through the Gore Canyon until the State Bridge, where it forms a confluence with the Piney River on the left. The Eagle River feeds into the Colorado River at Dotsero, from where the river runs parallel to Interstate 70 until Utah through the Glenwood Canyon. The Roaring Fork River, Colorado’s second major tributary, joins it at Glenwood Spring.
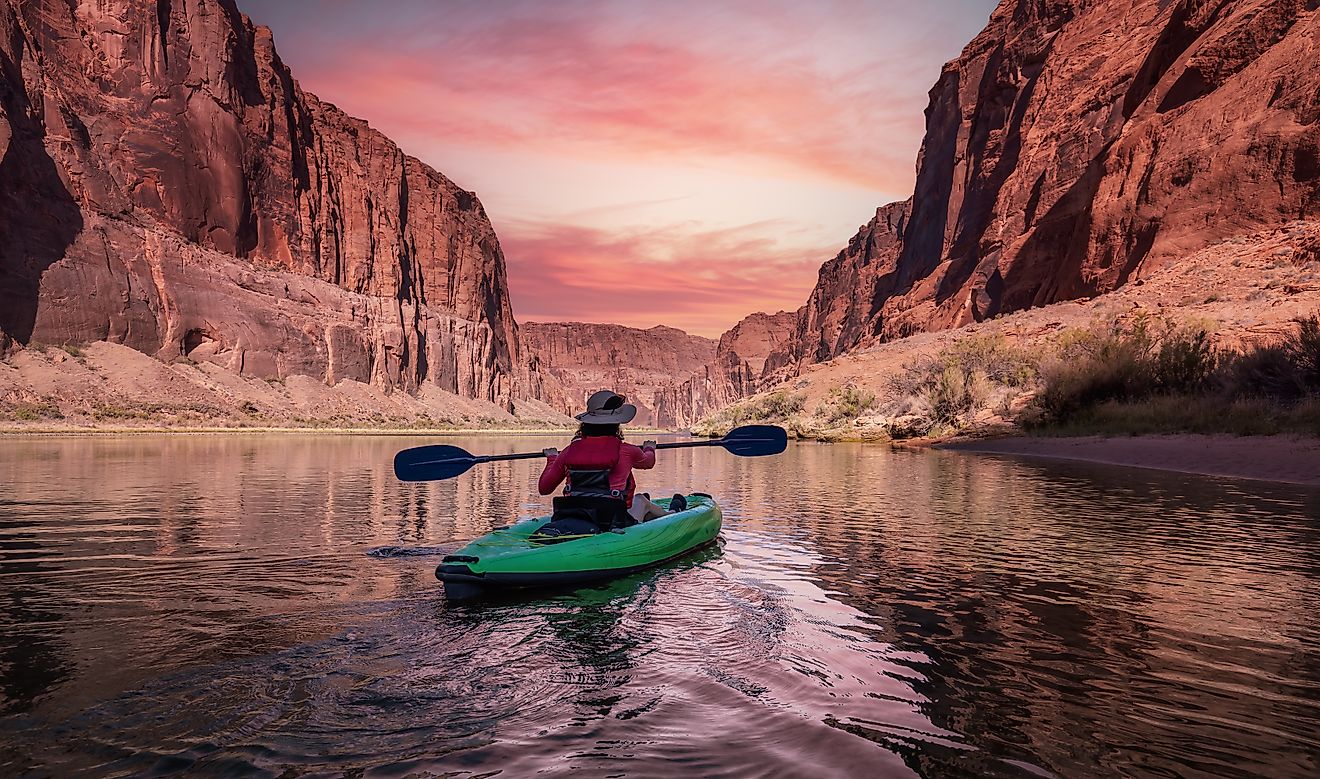
In Utah, the river flows mainly through the Colorado Plateaus, running through the Westwater Canyon. The Dolores River and San Miguel join the Colorado River near Dewey, from where it flows past Fisher Towers to Arches National Park. From the park, Colorado enters the Moab Valley and cuts through The Portal. It then flows through the Dead Horse Point State Park and Canyonlands National Park where it receives water from the Green River. From the confluence with the Green River, the Colorado River flows through the Cataract Canyon then to Glen Canyon before entering Arizona.
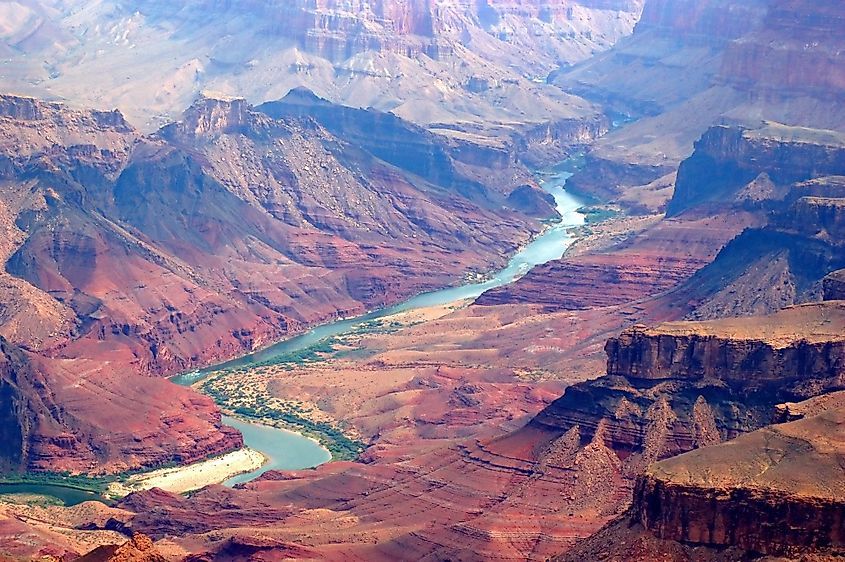

In Arizona, Colorado flows past Lee’s Ferry to the Marble Canyon and is joined by the Little Colorado River. It then flows westwards into the Granite Gorge. Colorado flows through the Grand Canyon for about 446 kilometers, of which most of its length is in the Grand Canyon National Park. The river also passes through the Black Canyon’s Lake Mead on its way to the Lower Colorado River Valley, where it widens to 150-300 meters. The Colorado River flows through Yuma and is joined by the Gila River. It then flows for about 39 kilometers along the US-Mexico border. At Morelos Dam, the river is diverted to Mexicali Valley. In Mexico, the Colorado River flows mostly along the Sonora-Baja California border on its way to the Gulf of California.
Plant and Animal Life

The Colorado River basin contains a wide range of fauna, ranging from coniferous forest and Alpine tundra to juniper and sagebrush. The watershed supports about 1,600 plant species, including saguaro cactus, Joshua trees, creosote bush, ponderosa pine, and Engelmann spruce. The arid and semi-arid areas like Canyonlands National Park support extensive grassland.
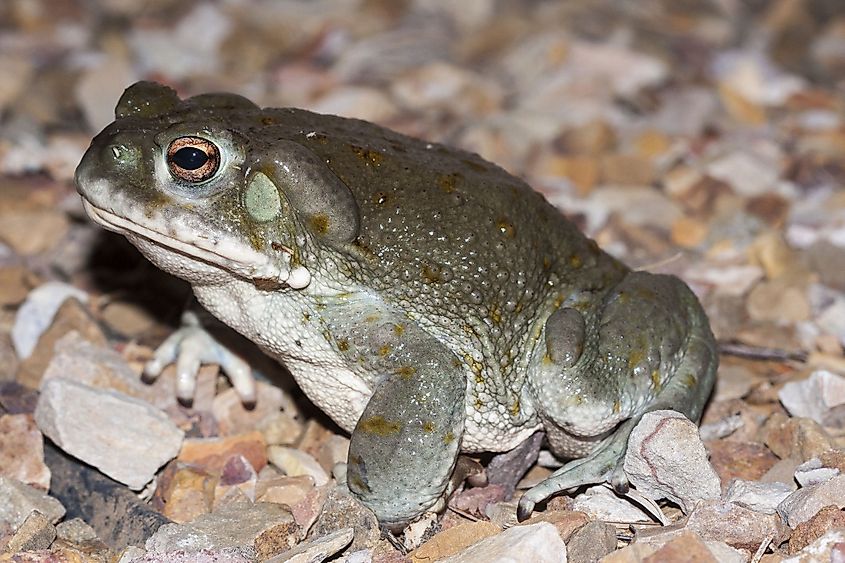
The drainage basin is home to a variety of wildlife, including large mammals like pronghorn, mountain sheep, mountain lion, coyote, and bobcat. The drainage basin is home to about 358 bird species, including bald eagles. The river itself once contained 49 fish species, of which 42 species were endemic. However, the engineering projects along the river have affected at least 40 species, whose population has decreased significantly. Some critically endangered species include razorback sucker, bonytail chub, humpback chub, and Colorado pikeminnow.