Yarra River
Also referred to as Yarra Yarra, Birrarung and Wongete, the Yarra River is a perennial river that flows in the south-central part of Victoria, Australia and is one of Melbourne’s major attractions. The river flows for about 242 kilometers from the Yarra Ranges of the Great Dividing Range to Port Philip at Hobsons Bay. Melbourne, Victoria’s state capital, was established on the lower reaches of the river in 1835. Several Aboriginal Australians have lived along the river for thousands of years, using it as their meeting place and food and water source. The Yarra River also served as an important irrigation water source for the early European settlers. Currently, it accounts for about 70% of Greater Melbourne’s drinking water supply.
Natural Features Of Yarra River

The Yarra River is Victoria’s 10th longest river, flowing for about 242 kilometers from its source in the Eastern Highlands to its mouth at Hobsons Bay. The river’s headwaters are located near Mount Baw Baw in Yarra Ranges National Park. It rises at an elevation of 792 meters above sea level and drops to sea level at Port Philip. The Yarra River drains an area of approximately 4,078 square kilometers and discharges an average of 37 cubic meters of water per second at the mouth.
The river flows through different habitats, including large pristine forests, dense urban areas, and agricultural land. The upper river section flows through mountainous and forested areas that have been protected for more than 100 years to ensure the river provides quality drinking water. Agriculture and industrial development takes place in the middle and lower portions. The lowest section is an estuary where ocean water and salt travel upstream for about 10 kilometers. The section of the Yarra River between Warrandyte and Warburton is a Victoria Heritage River.
Course Of The Yarra River

The river's upper portion is a swampy area in the Yarra Ranges National Park. The upstream also contains a closed-off dam known as the Upper Yarra Reservoir. The dam is located in Reefton, the first town the river flows through from its source. From Reefton, the river flows through the temperate forests to Warburton. From Warburton, farms begin to emerge on the banks of the Yarra River, including dairy and beef farms. Then the river turns northwards at Woori Yallock and flows through the Yarra Valley wine region. The Yarra River then turns westwards at Healesville and thence to Yarra Glen.
The Yarra River begins its journey through Melbourne at Chirnside Park, marking the start of its middle reaches. However, this section of the river is surrounded by tall trees and parklands, containing mainly the native vegetation. The Main Yarra Trail, used by pedestrians and cyclists, starts at Warrandyte and runs parallel to the river until the lower reaches, where it is known as Capital City Trail. Yarra begins to form an estuarine below the Dights Falls as it flows through the southern side of Melbourne’s CBD. The river then flows through Port Melbourne, and below the West Gate and Bolte Bridges, and finally into Hobsons Bay.
Flora And Fauna Of The Yarra River

The Yarra Riverbank is home to over 20 unique plant communities. Swamp scrubs dominate the wet areas in the east and west, while riparian scrubs are common on most river sections. The manna gums grow along the upper reaches and provide food for the koalas. Other trees on the riverbank include river red gums, river bottlebrushes, sedges, rushes, and prickle currant bush.
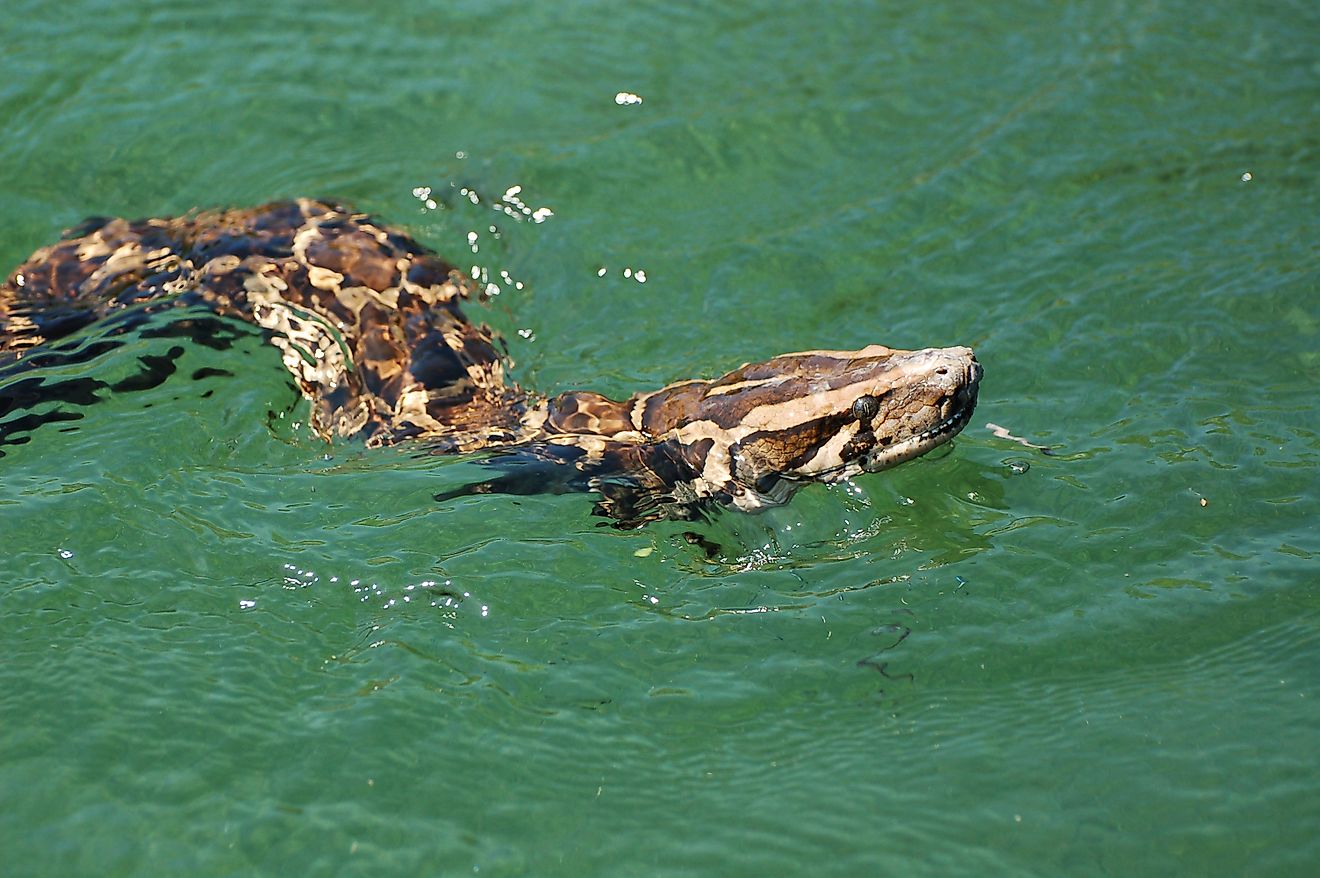
The Yarra River basin is home to almost 30% of the animal species in Victoria. The basin is home to over 190 bird species, including honeyeaters, waterbirds, birds of prey, and songbirds. The common species include Nankeen Night Heron and White-faced Heron. Yarra River also serves as a habitat for frogs such as Peron’s tree frog, eastern froglet, and southern toadlet. 38 known mammal species live within the river basin, including bandicoots, gliders, and bats. Reptiles that are common in the area include lizards, snakes, turtles, and skinks.
Brief History

The Aboriginal people belonging to the Kulin nation, particularly Wurundjeri and Boonwurrung, were the first people to settle along the Yarra River. The river provided food and water and places for spiritual activities like burial grounds and birthplaces for the indigenous groups. The Wurundjeri people named the river “Birrarung” and used it sustainably until the European arrival. In 1803, New South Wales’ Acting Surveyor-General Charles Grimes and his party became the first Europeans to sail up the river. However, it took another 32 years for European explorers to visit the river.
1835 was an eventful year in the history of the Yarra River. First, Australian explorer John Batman bought approximately 2,400 square kilometers of land surrounding the river from the Wurundjeri people. However, the Aboriginals later denied selling the land to Batman, saying they only permitted him to pass through their land. Richard Bourke, the New South Wales Governor, declared the purchase treaty (Batman’s Treaty) invalid on August 26, 1835. In the same year, a small settlement that later became Melbourne developed on the river’s lower reaches.
Gold was discovered in the suburb of Warrandyte at Anderson’s Creek, one of Yarra’s tributaries, in 1851, marking the beginning of the Victorian gold rush. The gold rush quickly transformed Melbourne into one of the largest Australian cities and opened up Victoria to industrialization. However, the increased industrialization came at a cost. The Yarra River soon became polluted with sewer and industrial waste.