Maps of Djibouti
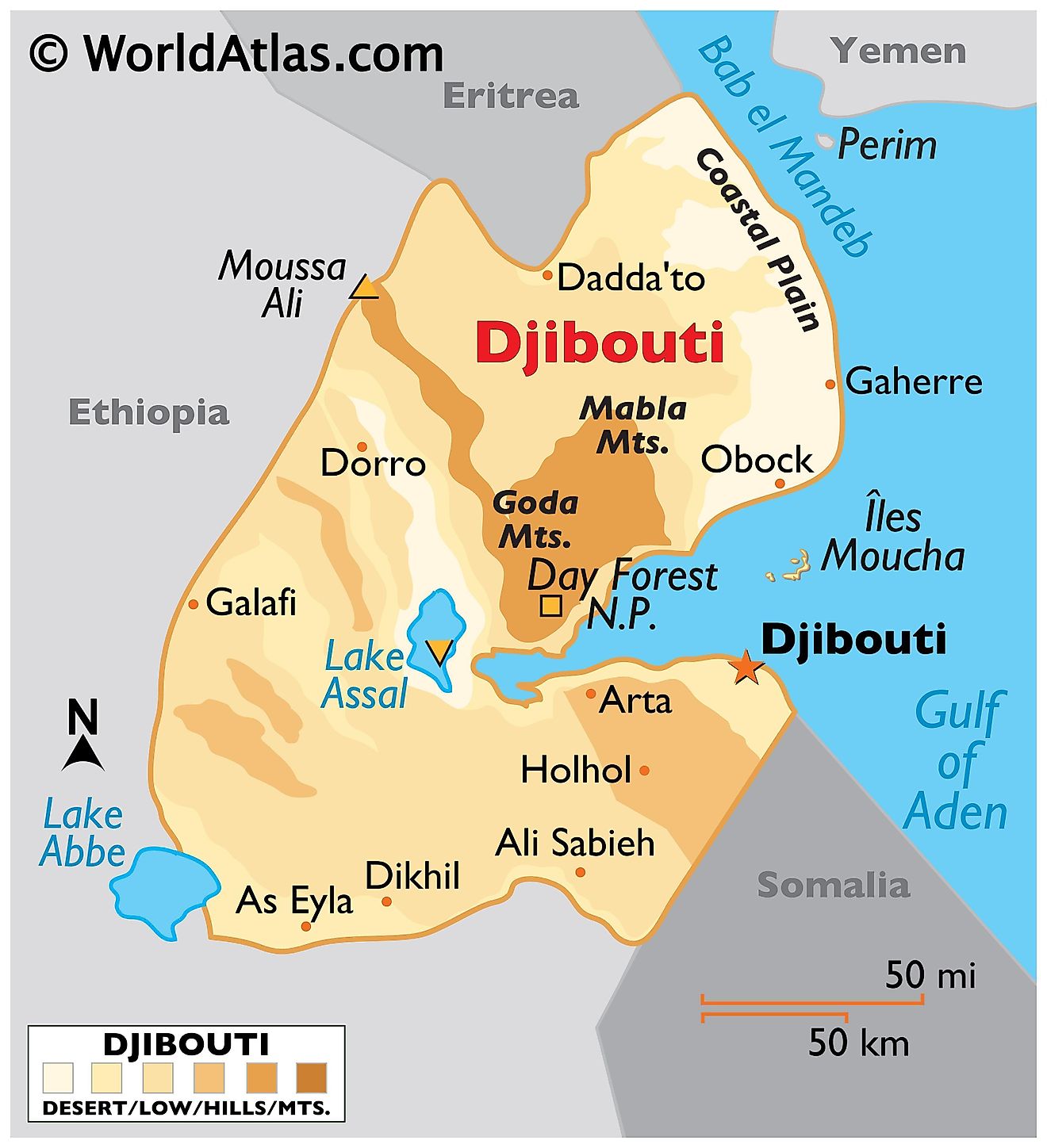
Djibouti, located in the Horn of Africa, shares its borders with Eritrea to the north, Ethiopia to the west and south, and Somalia to the southeast. Its eastern boundary is formed by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. The country's total area encompasses approximately 23,000 km2 (8,880 mi2).
The Coastal Plain stretches along the eastern edge of Djibouti, flanked by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. This region is characterized by its narrow, sandy beaches and steep, rocky cliffs. The coastal plain gives way to a series of salt flats and shallow bays, most notably the extensive salt flats at Lake Assal.
The Mountain Ranges of Djibouti are primarily located in the north and central parts of the country. The Goda Mountains, with their forested highlands, stand out as the most significant range. This region's highest point is Mount Moussa Ali, reaching an elevation of about 2,028 meters (6,654 feet), marking the highest point in the country. These ranges are characterized by rugged terrain, with steep slopes and narrow valleys.
The Central Plateaus cover much of the country's interior. This region is predominantly semi-desert or desert, featuring stony plains, plateaus, and highlands. The terrain here is generally flat but punctuated by occasional volcanic formations. The Hanle Plain and the Grand Bara Desert are notable features within this area.
The Danakil Depression, located in the central and southern parts of Djibouti, is a stark and harsh landscape. It includes the lowest point in the country, Lake Assal, situated at approximately 157 meters (515 feet) below sea level, one of the lowest points on the earth's surface. This area is renowned for its hot, dry climate and its saline lakes and salt pans.
While Djibouti does not have significant rivers, the presence of temporary watercourses or wadis is notable, especially during the rainy seasons. These wadis are crucial for the limited agricultural activities in the country.
Regions of Djibouti Map
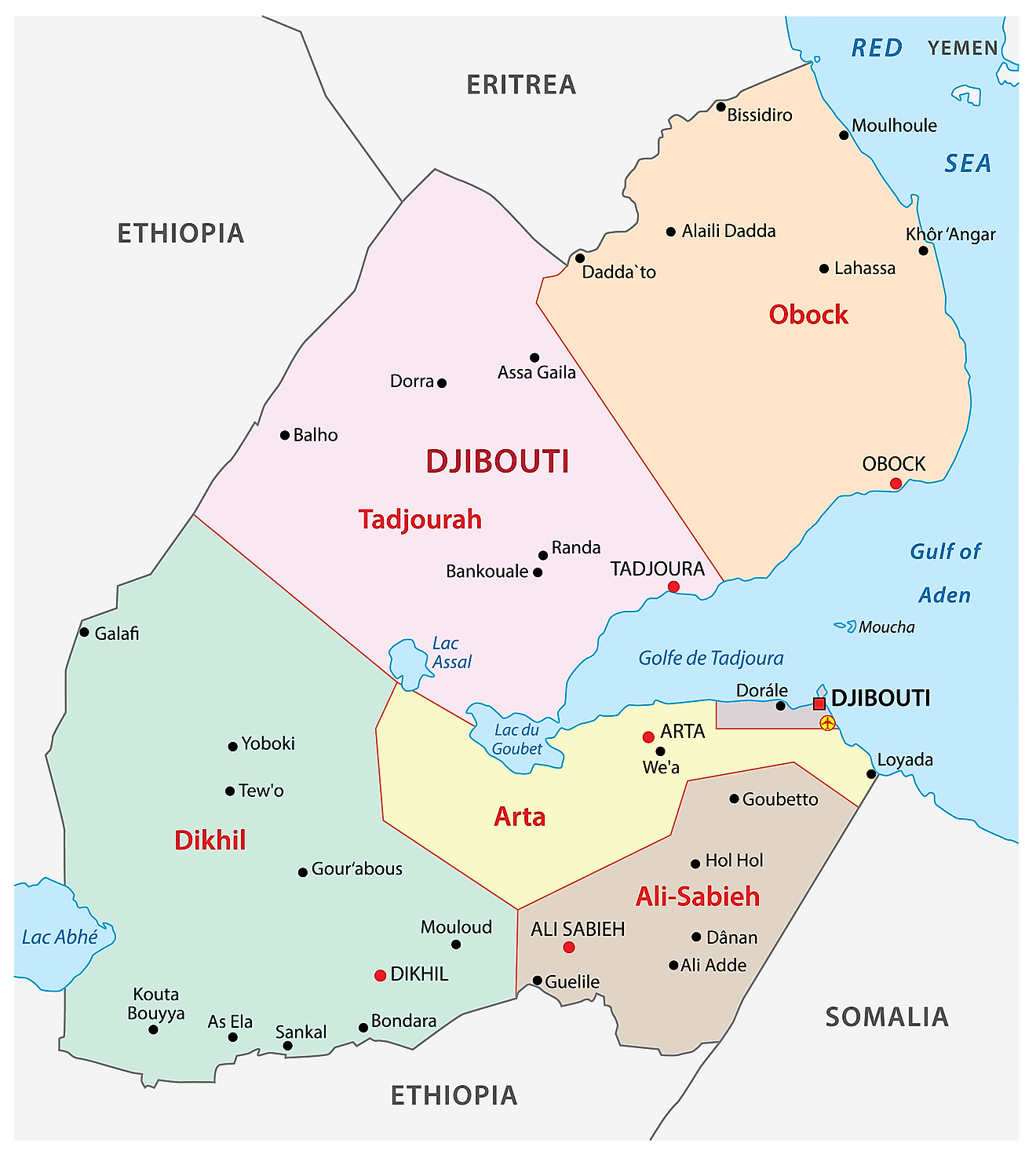
Djibouti is divided into 6 regions. These are Ali Sabieh, Arta, Dikhil, Djibouti, Obock, and Tadjourah. These regions are further subdivided into 20 administrative districts.
With an area of 7,100 sq. km, Tadjourah is the largest region by area. Djibouti Region is the smallest by area and the most populous one. Djibouti is the capital city of the country.
Where is Djibouti?
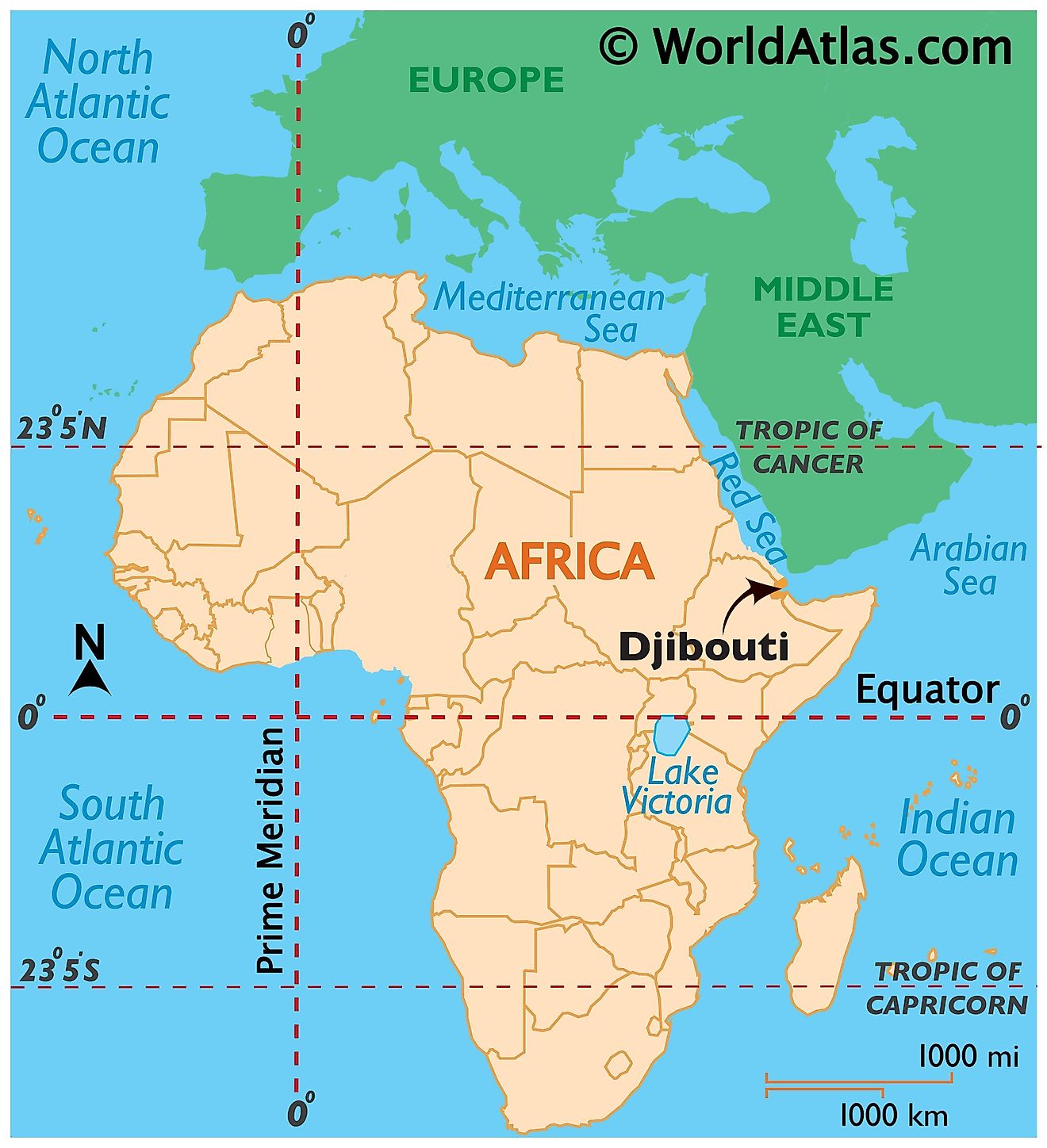
Djibouti is an East African country located in the Horn of Africa in the Northern and the Eastern Hemispheres of the Earth. Three countries border Djibouti. These are Eritrea to the north, Somalia to the south, and Ethiopia to the south and west. The country also has coastlines on the Red Sea and the Gulf of Eden to the east.
Djibouti Bordering Countries: Ethiopia, Eritrea.
Regional Maps: Map of Africa
Outline Map of Djibouti
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Republic of Djibouti |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Djibouti |
| 11 35 N, 43 09 E | |
| Total Area | 23,200.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 23,180.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 20.00 km2 |
| Population | 973,560 |
| Largest City |
Djibouti (599,504) |
| Currency | Djiboutian francs (DJF) |
| GDP | $3.32 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $3,408.85 |
This page was last updated on November 27, 2023