Geography Statistics of Middle East
- Size: 8,804,395 sq km, 3,596,959 sq miles
- Percent of Earth's Land: 6.2%
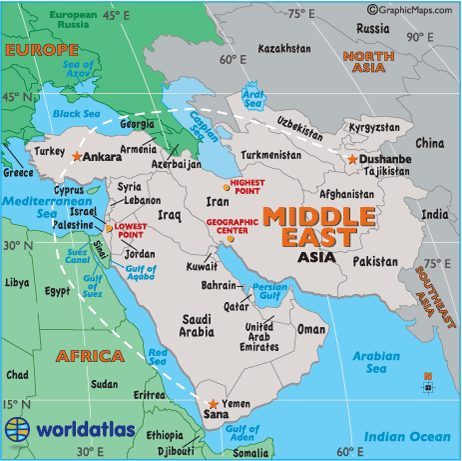
- Highest Point: Mount Damavand, Iran, 18,406ft (5,610m) (see map)
- Lowest Point: Dead Sea, 423 m (1,388 ft) below sea level (see map)
- Geographic Center: 21 miles, 33.7 km northwest of Shiraz, Iran (see map)
- Largest Country: Saudi Arabia, 1,960,582 sq km, 756,985 sq miles
- Smallest Country: Bahrain, 665 sq km, 257 sq miles
- Horizontal Width: (as the crow flies) From Ankara, Turkey to Dushanbe, Tajikistan: 1,931 miles (3,107 km) (see map)
- Vertical Length: (as the crow flies) From Ankara, Turkey to Sana, Yemen: 1,796 miles (2,890 km) (see map)
Note: Lengths and widths above are point-to-point, straight-line measurements and will vary some using other map projections. They are curved slightly here to make the map text more readable.
Note: Some sources still consider Egypt, Libya, Ethiopia, and Sudan as part of the Middle East. Here we attempt to show the modern definition of the Middle East, but in the world of geography, there are often many answers (or personal or political opinions) to what appears to be a simple question, so consider this a guide, not absolute law.
As a point-of-interest, Armenia and Azerbaijan have long been associated with the Middle East, but in recent years, some sources now consider them to be more closely aligned with Europe based on their modern economic and political trends. We have moved in that direction, and the same applies for the island country of Cyprus as it does for Georgia, the former Russian republic.











