Maps of Guatemala
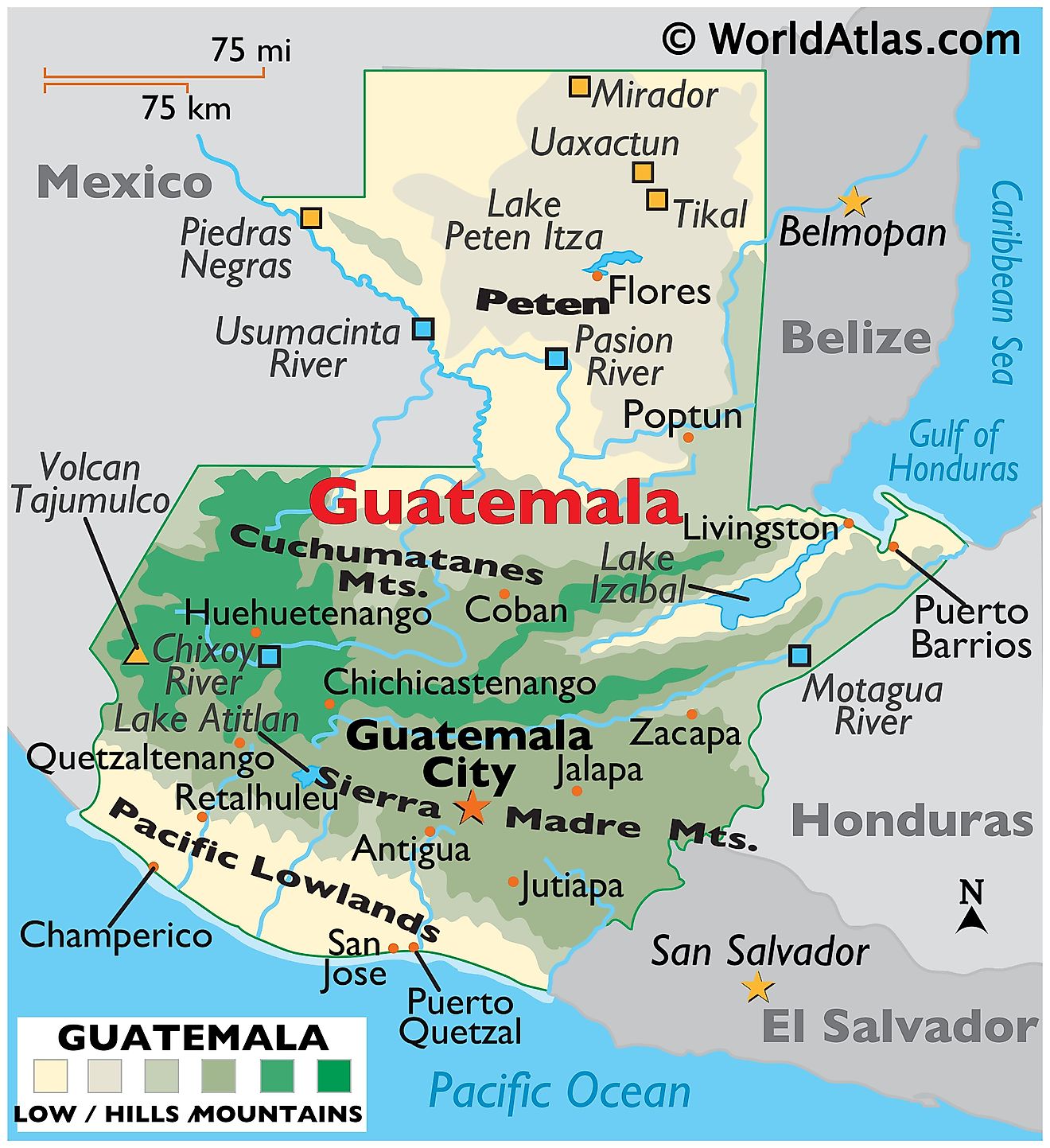
Guatemala, officially known as the Republic of Guatemala, shares its borders with four countries: Mexico to the north and west, Belize to the northeast, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast. To the south, it also borders the Pacific Ocean, while the eastern part of the country lies near the Caribbean Sea. The country extends over a total area of approximately 42,042 square miles (108,889 square kilometers).
The country's geography is divisible into three distinct regions: the Highlands, the Pacific Coast, and the Petén region.
The Highlands, home to the Sierra Madre mountain range, extends across the western and central parts of Guatemala. This region contains the country's highest peak, Volcán Tajumulco, which reaches an elevation of 13,789 feet (4,203 meters). The Highlands also include many of Guatemala's most significant population centers, such as the capital city, Guatemala City, and Quetzaltenango, the country's second-largest city.
The Pacific Coast lies south of the Highlands, a narrow lowland strip that stretches along the country's southern boundary. Here, the terrain mainly consists of fertile soil, the result of centuries of volcanic activity, making it an agriculturally rich region. The main crops grown in this area are sugarcane, cotton, coffee, and various fruits.
The Petén region, covering the northern third of Guatemala, contrasts significantly with the Highlands and the Pacific Coast. It features low, flat, and dense tropical rainforest terrain, much of which remains undeveloped. This region is also home to the Maya Biosphere Reserve, one of the largest protected areas in Central America.
Guatemala's two primary bodies of water are Lake Izabal and Lake Atitlán. Lake Izabal, located near the Caribbean coast, is the largest lake in the country. Lake Atitlán, on the other hand, nestled in the Highlands, is famous for its depth and the surrounding volcanoes, which give it a distinct scenic value.
In terms of rivers, the most prominent one is the Motagua River. It is the longest in the country, flowing across Guatemala from the western Highlands to the Caribbean Sea in the east. Other significant rivers include the Usumacinta River, which forms part of the boundary with Mexico, and the Sarstún River, which acts as a portion of the boundary with Belize.
Departments of Guatemala Map
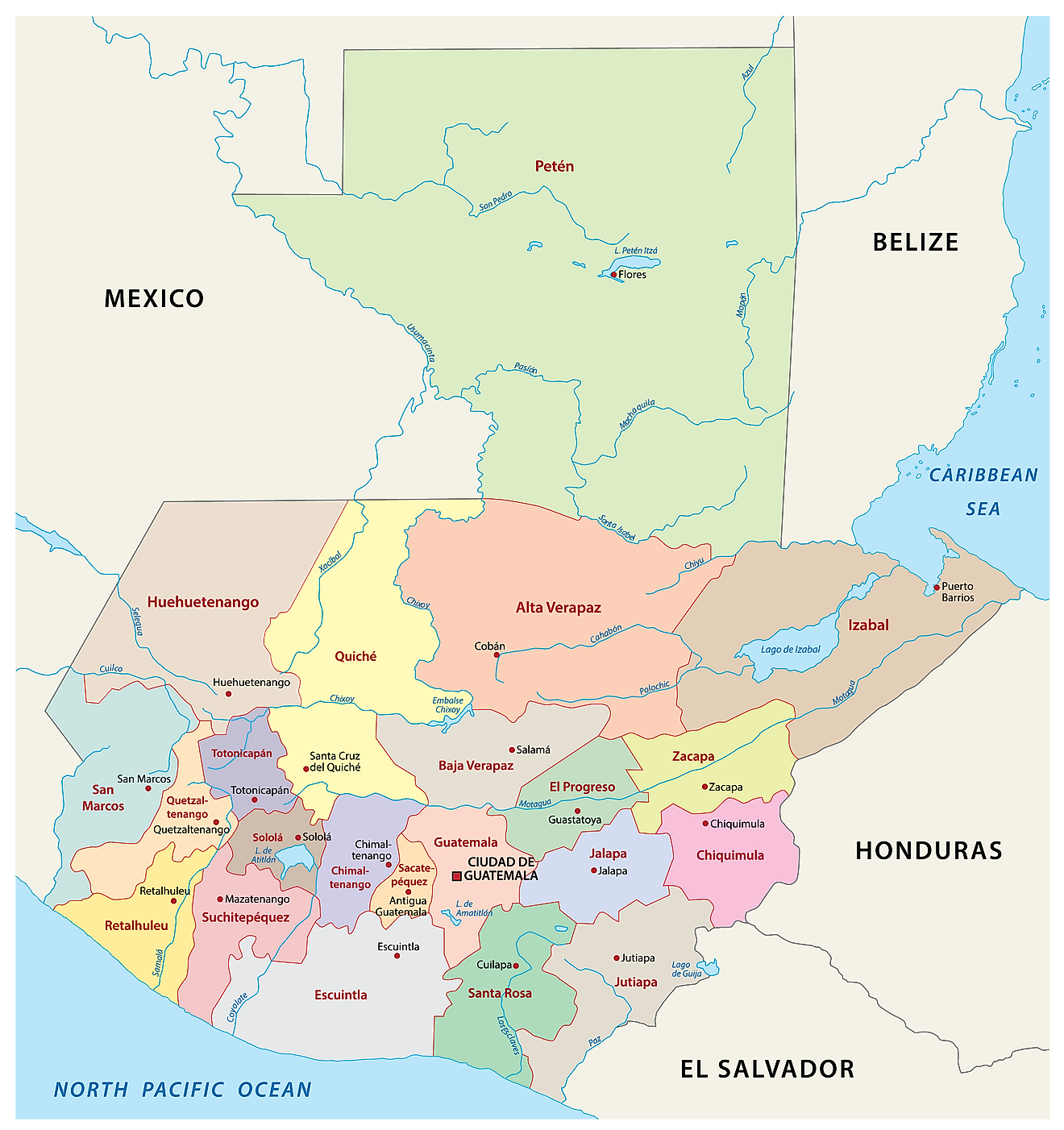
Guatemala (officially, the Republic of Guatemala) is divided into 22 departments (departamentos, sing. departamento). In alphabetical order, the departments are: Alta Verapaz, Baja Verapaz, Chimaltenango, Chiquimula, El Progreso, Escuintla, Guatemala, Huehuetenango, Izabal, Jalapa, Jutiapa, Peten, Quetzaltenango, Quiche, Retalhuleu, Sacatepequez, San Marcos, Santa Rosa, Solola, Suchitepequez, Totonicapan and Zacapa. These departments are further subdivided into 340 municipalities.
Located in the south-central region of the country, in Valle de la Ermita of the Central Highlands is Guatemala City (Nueva Guatemala de la Asuncion) – the capital, the largest and the most populous city of Guatemala. It is also the administrative, cultural and economic center of the country. Guatemala City is the largest city in Central America and also Central America’s most highly populated urban area.
Where is Guatemala?
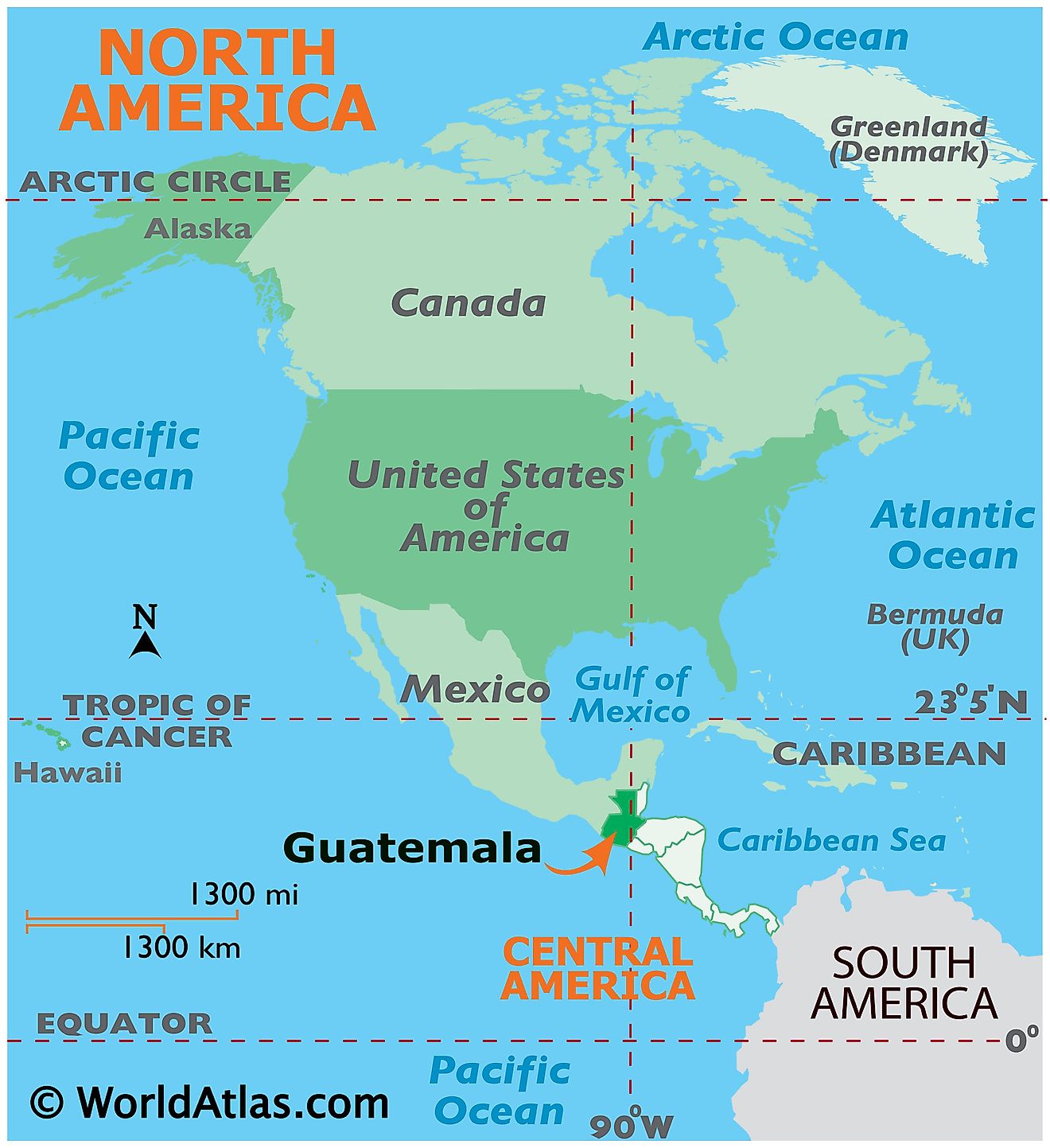
Guatemala is a country located in Central America. It is positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. It is bordered by Mexico to the north and west; by Belize and the Gulf of Honduras (Caribbean Sea) to the northeast; by Honduras to the east; by El Salvador to the southeast and by the Pacific Ocean to the south.
Guatemala Bordering Countries: Mexico, Belize, Honduras, El Salvador.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Guatemala
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Republic of Guatemala |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Guatemala City |
| 14 37 N, 90 31 W | |
| Total Area | 108,889.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 107,159.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 1,730.00 km2 |
| Population | 16,604,026 |
| Largest City |
Ciudad de Guatemala (Guatemala City) (3,095,099) |
| Currency | Quetzales (GTQ) |
| GDP | $76.71 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $4,619.99 |
This page was last updated on June 19, 2023