Maps of Puerto Rico
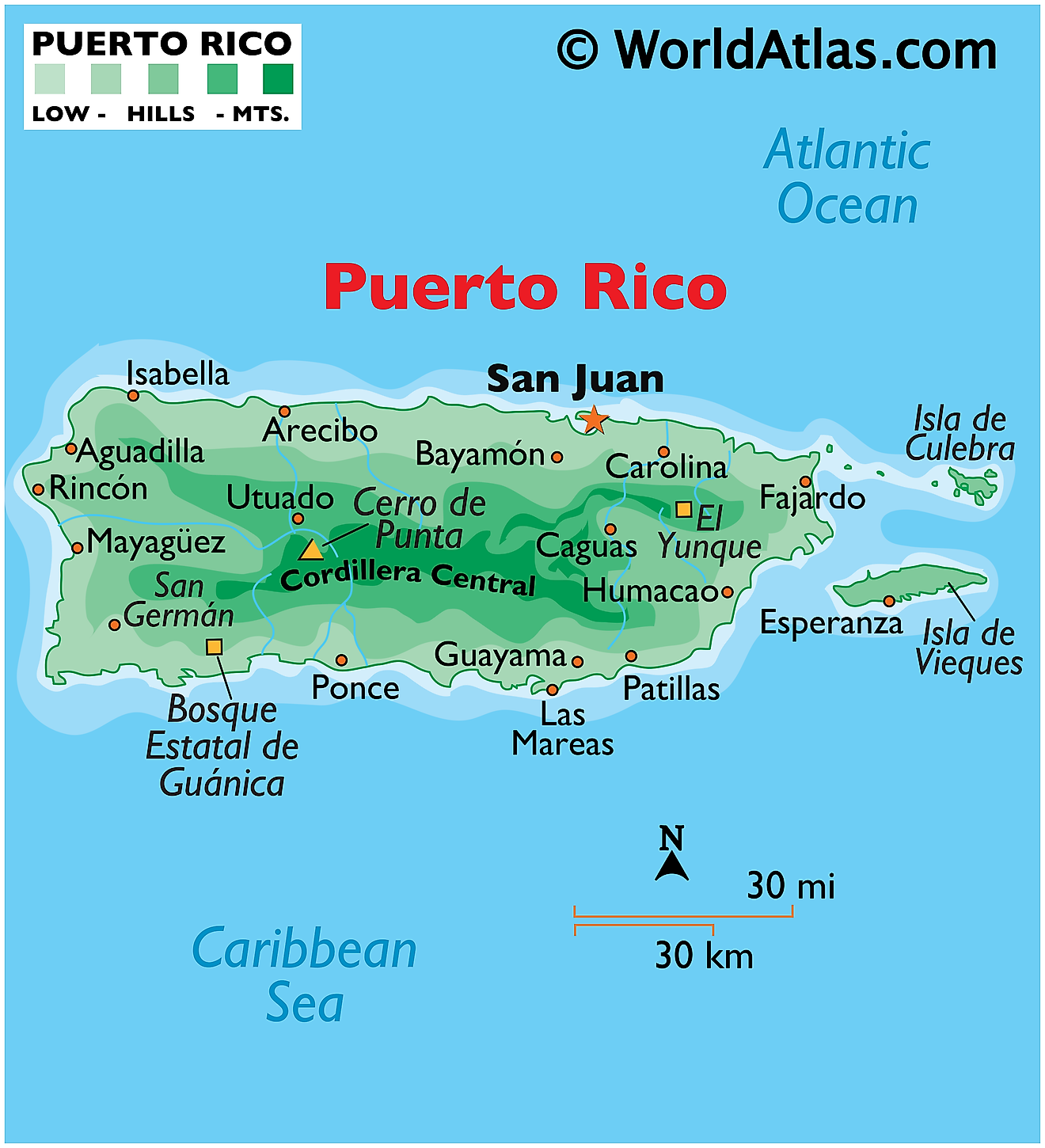
Puerto Rico, a Caribbean island and unincorporated territory of the United States, borders the Atlantic Ocean to the north and the Caribbean Sea to the south. The island occupies a total area of about 3,435 square miles (9,000 square kilometers), which includes the main island and a group of smaller islands, collectively known as the Spanish Virgin Islands. Puerto Rico is divisible into three main geographical regions: the mountainous interior, the coastal plains, and the northern karst area.
La Cordillera Central - The Mountain Interior
The mountainous interior of Puerto Rico, also known as "La Cordillera Central," bisects the main island from east to west. Its peaks, some reaching an elevation of more than 4,000 feet (1,200 meters), are the highest points in the territory. The most notable peak is Cerro de Punta, standing at 4,390 feet (1,340 meters). This region is characterized by steep slopes, dense vegetation, and rich soil, making it a major center for coffee production.
The Coastal Plains
The coastal plains surround the mountainous region, with the most extensive plains found in the north and south. The southern coastal plain, also known as the Ponce-Patillas alluvial plain, is notable for its dry climate and flat terrain. It supports many crops, such as sugarcane, and fruit cultivation. Conversely, the northern coastal plain experiences a more humid climate, suitable for various crops, including coffee, tobacco, and fruits.
The Karst Region
The northern karst region is a unique geographical feature of Puerto Rico. It extends from the western to the northeastern part of the island, characterized by its limestone formations, sinkholes, caverns, and mogotes - rounded hills with steep sides. The region is home to the Rio Camuy Cave Park, one of the largest cave networks in the world.
Bodies of Water
Water bodies in Puerto Rico include numerous rivers, lakes, and the surrounding oceanic bodies. More than 50 rivers originate from the mountainous interior, the most significant being the Rio de la Plata, the Rio Grande de Loíza, and the Rio Grande de Añasco. The rivers on the northern side are typically long, wide and slow-moving, providing vital water supplies to major metropolitan areas. In contrast, the rivers on the southern side are generally short, swift and less navigable.
There are no natural lakes in Puerto Rico; however, artificial lakes have been created due to dam construction for hydroelectric power and water supply. The largest of these is Lago de Guajataca in the western region.
Regarding the islands, beyond the main island of Puerto Rico, the archipelago includes several smaller islands and cays. The most significant are Vieques and Culebra, both to the east of the main island. Mona Island, located between Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic, is a natural reserve known for its unique flora and fauna. Furthermore, the Puerto Rico Trench, some 70 miles directly to the north, is the largest and the deepest trench in the Atlantic Ocean at 27,600ft (8,400m).
Municipalities of Puerto Rico Map
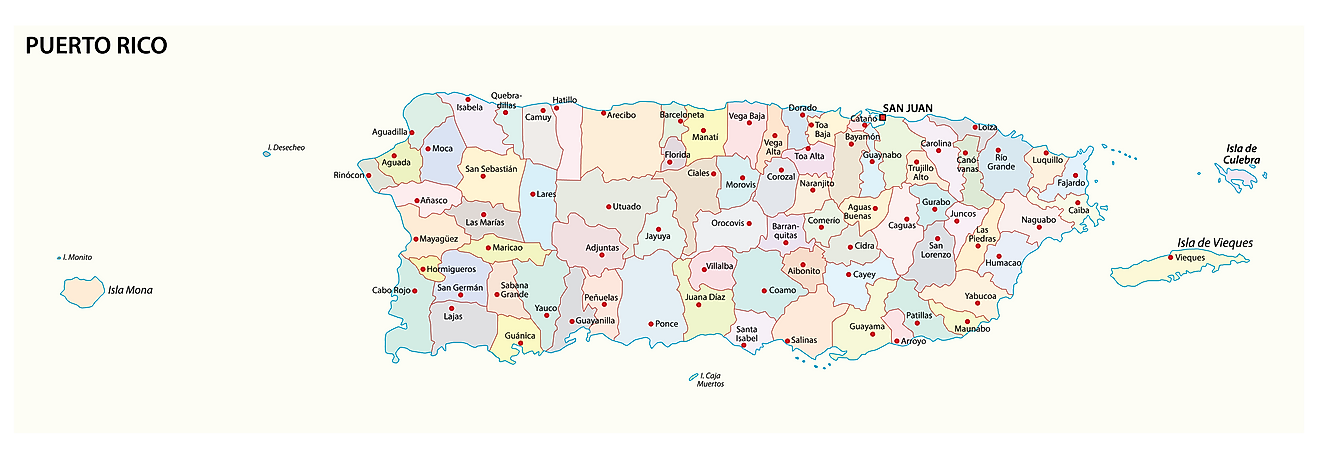
Puerto Rico (officially, the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico) has no first- order administrative divisions as defined by the US Government. There are 78 municipalities (municipios, singular – municipio), which are the 2nd order administrative divisions in Puerto Rico. In alphabetical order, the municipalities are: Adjuntas, Aguada, Aguadilla, Aguas Buenas, Aibonito, Anasco, Arecibo, Arroyo, Barceloneta, Barranquitas, Bayamon, Cabo Rojo, Caguas, Camuy, Canovanas, Carolina, Catano, Cayey, Ceiba, Ciales, Cidra, Coamo, Comerio, Corozal, Culebra, Dorado, Fajardo, Florida, Guanica, Guayama, Guayanilla, Guaynabo, Gurabo, Hatillo, Hormigueros, Humacao, Isabela, Jayuya, Juana Diaz, Juncos, Lajas, Lares, Las Marias, Las Piedras, Loiza, Luquillo, Manati, Maricao, Maunabo, Mayaguez, Moca, Morovis, Naguabo, Naranjito, Orocovis, Patillas, Penuelas, Ponce, Quebradillas, Rincon, Rio Grande, Sabana Grande, Salinas, San German, San Juan, San Lorenzo, San Sebastian, Santa Isabel, Toa Alta, Toa Baja, Trujillo Alto, Utuado, Vega Alta, Vega Baja, Vieques, Villalba, Yabucoa and Yauco. The municipalities are further subdivided into barrios.
Located in the north-eastern coast of the island country is, San Juan – the capital, the largest city and the most populous municipality of Puerto Rico. It is the cultural, tourism and financial center of the country. San Juan is also the most important seaport of Puerto Rico.
Where is Puerto Rico?
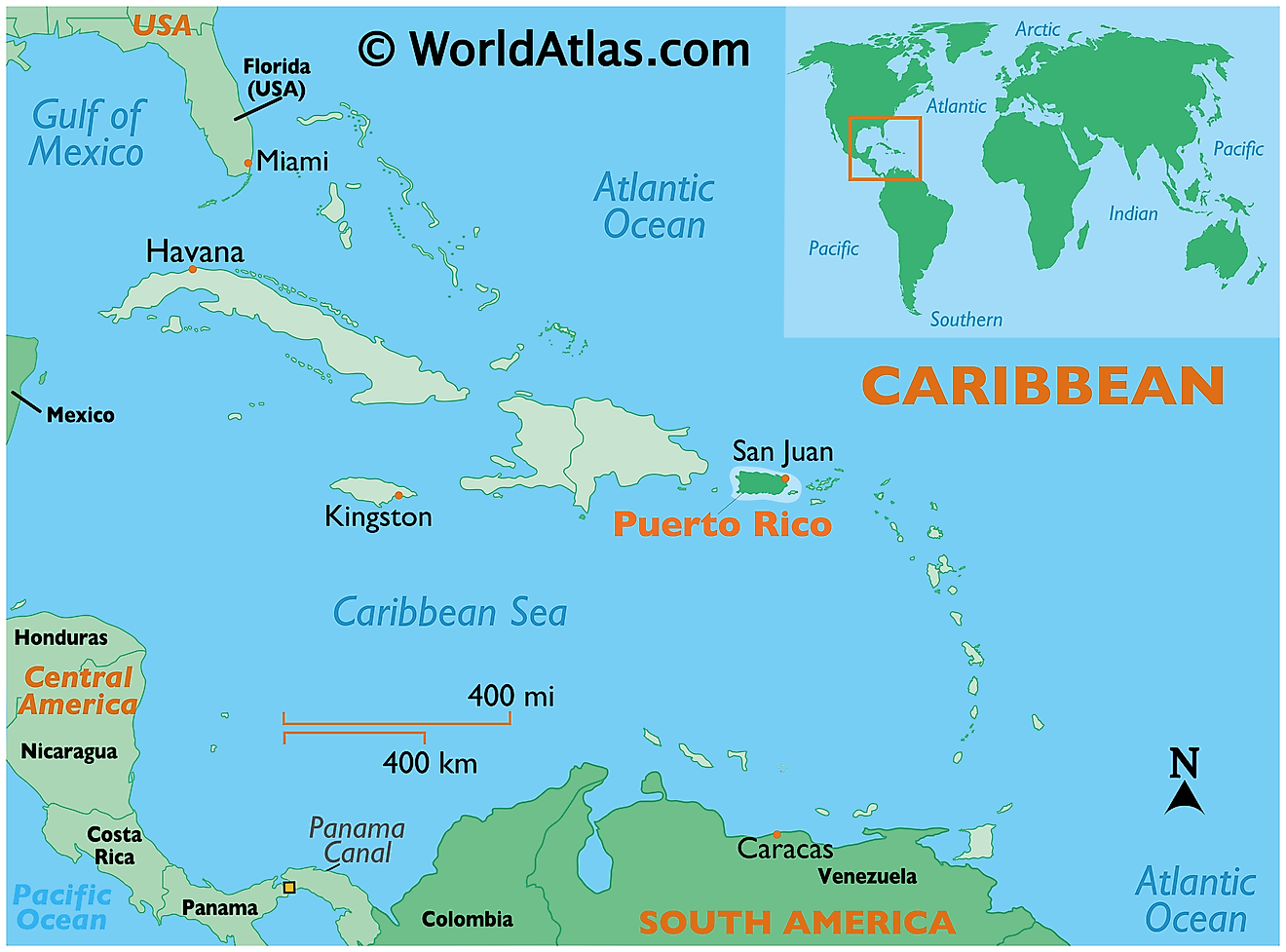
Puerto Rico is an unincorporated island territory of the United States of America, located in the north-eastern Caribbean Sea. Puerto Rico - the easternmost island nation and a part of the Greater Antilles Chain; is geographically positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. It is situated to the east of the Hispaniola Islands (shared by Haiti & the Dominican Republic); to the west of the US Virgin Islands and to the southeast of Florida. The northern shore of Puerto Rico faces the Atlantic Ocean.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Puerto Rico
The above blank map represents Puerto Rico – an unincorporated island territory of the United States of America in the Caribbean Sea. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for educational purposes or coloring.
The above outline map represents Puerto Rico, a roughly rectangular shaped island in the Caribbean Sea.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Commonwealth of Puerto Rico |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | San Juan |
| 18 28 N, 66 07 W | |
| Total Area | 9,104.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 8,959.00 km2 |
| Water Area | 145.00 km2 |
| Population | 3,193,694 |
| Major Cities |
|
| Currency | US Dollar (USD) |
| GDP | $104.99 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $32,873.72 |
This page was last updated on June 23, 2023











