Maps of Turks and Caicos
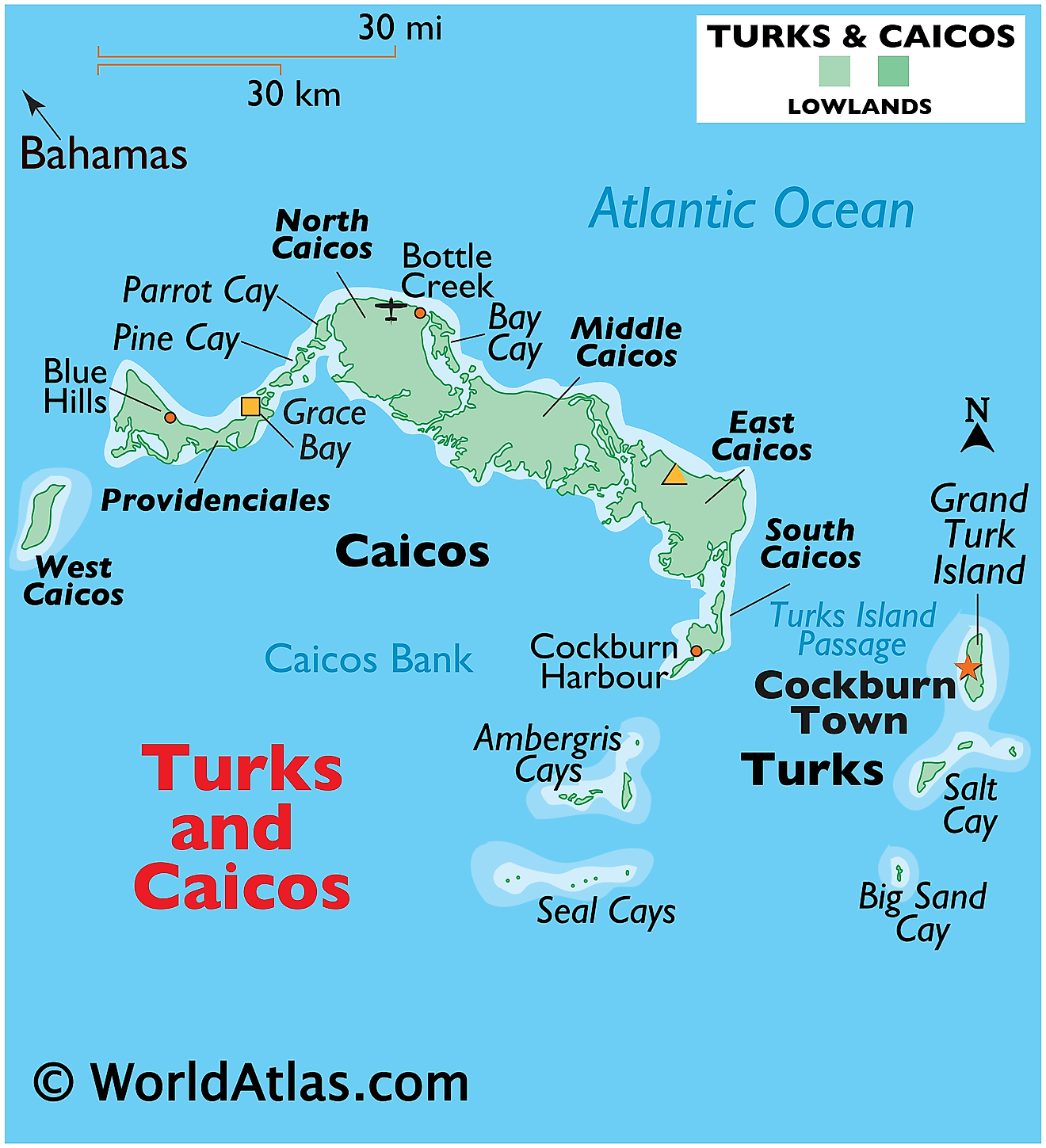
Turks and Caicos Islands, a British Overseas Territory, is located in the Atlantic Ocean. Its geographical coordinates place it southeast of the Bahamas, north of Hispaniola, and approximately 575 miles (926 kilometers) southeast of Miami, Florida. With a total area of 238 square miles (616 square kilometers), the archipelago consists of two island groups, the Turks Islands and the Caicos Islands, separated by the Turks Island Passage.
The Turks Islands comprise smaller landmasses, with the two primary ones being Grand Turk and Salt Cay. The Caicos Islands, on the other hand, are larger and contain six primary islands: Providenciales, North Caicos, Middle Caicos, East Caicos, South Caicos, and West Caicos. Providenciales, often referred to as "Provo," is the most developed island in the group and houses the majority of the territory's population.
The topography of Turks and Caicos is predominantly low-lying limestone terrain, characterized by marshes, salt pans, and long stretches of white sandy beaches. The highest point in the territory is on Blue Hills on Providenciales, standing at a modest 161 feet (49 meters) above sea level.
One of the most distinctive geographical features of the territory is the Caicos Bank, a large underwater plateau that lies south of the Caicos Islands. It covers an area of approximately 1,700 square miles (4,400 square kilometers) and is comprised mostly of shallow water and numerous small cays. Furthermore, The islands also feature an extensive system of limestone caves, with Conch Bar Caves on Middle Caicos being one of the largest above-ground cave systems in the Caribbean.
Another notable feature is the Turks and Caicos Barrier Reef, the third-largest coral system in the world. It lies to the north and east of the Caicos islands, and it significantly contributes to the diversity of marine life in the surrounding waters.
Turks and Caicos lack significant bodies of freshwater. The islands do not have any rivers, and they rely mainly on rainfall and desalinated seawater for their freshwater supply. There are numerous small ponds and marshes throughout the islands, many of which are saltwater bodies.
The territory's climate is tropical, moderated by the trade winds. Turks and Caicos typically experience warm, dry winters and hot, humid summers. Despite the potential for hurricanes, which are most common between June and November, the archipelago enjoys approximately 350 sunny days each year.
Districts of Turks and Caicos Map
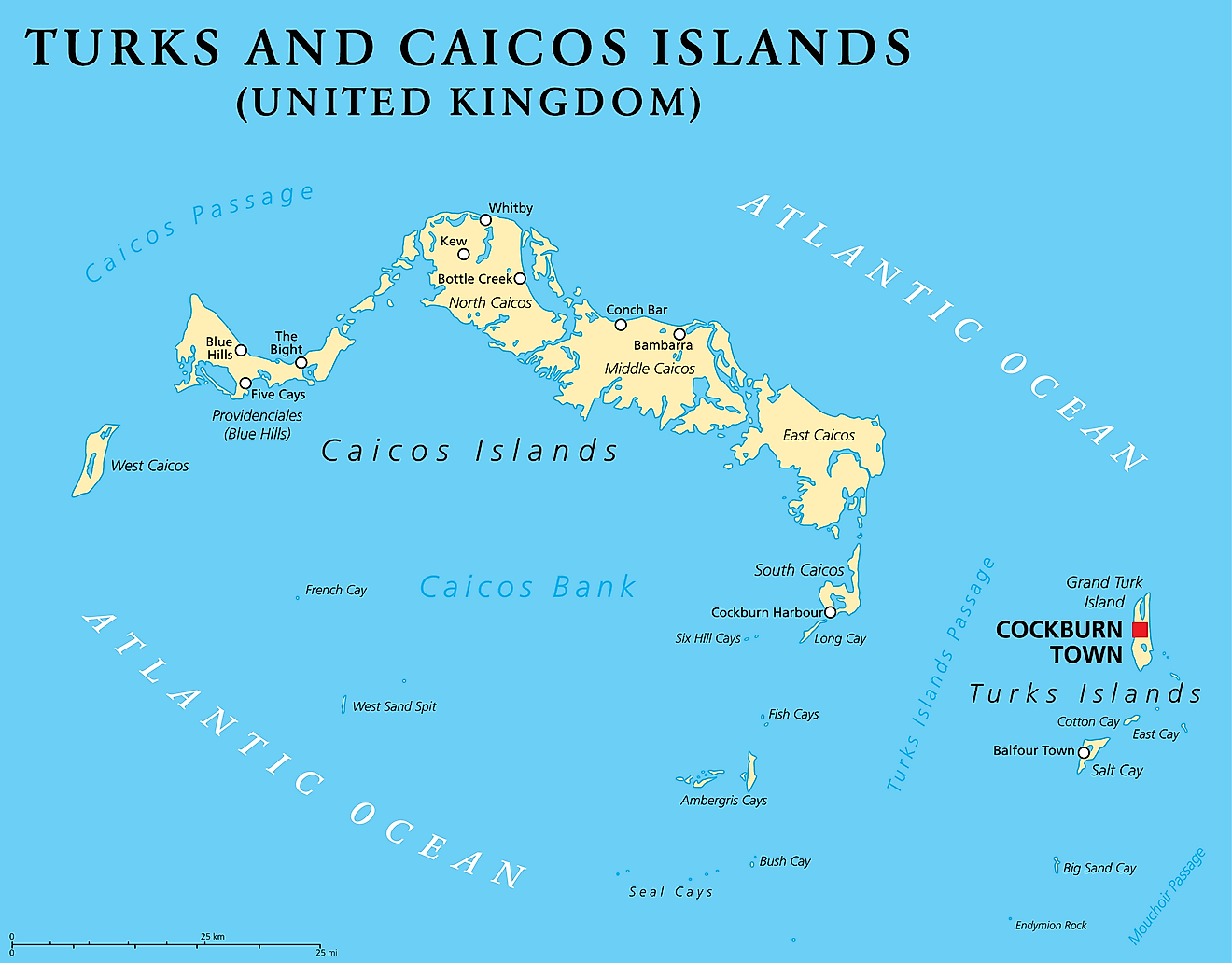
Turks and Caicos has five administrative divisions called districts including four in the Caicos Islands and one in the Turks islands. The island of Grand Turk in the Turks Islands is also a separate division. The four divisions in the Caicos Islands are Providenciales, North Caicos, Middle Caicos, and South Caicos. The district in the Turks Islands is named Salt Cay.
Located in the Grand Turk Island, Cockburn Town is the capital of Turks and Caicos. Providenciales, an island in the Caicos archipelago, is the most populated island.
Where is Turks and Caicos?
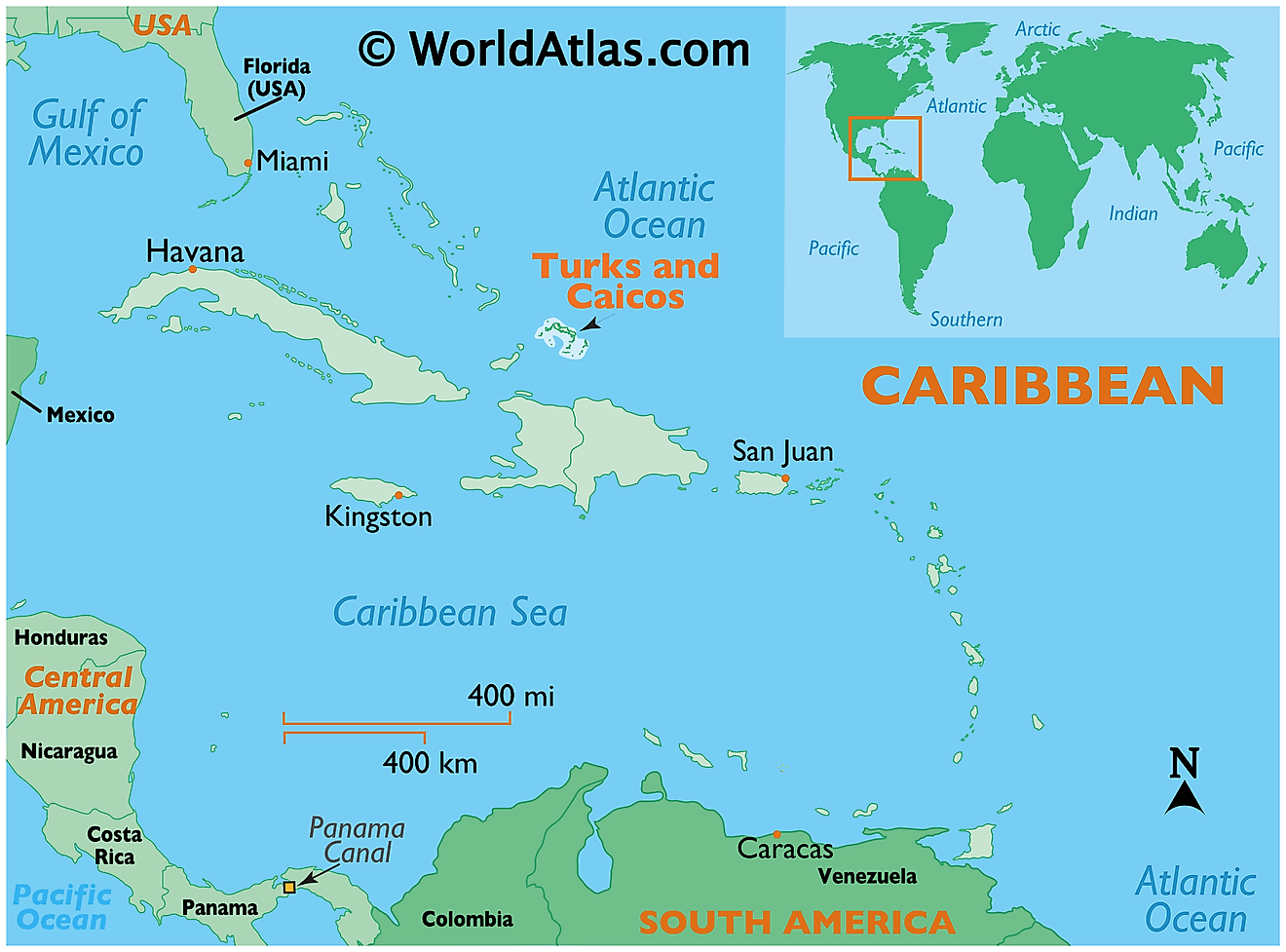
The Turks and Caicos Islands are a British Overseas Territory and comprises of two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago, to the north of the Caribbean Sea. They are positioned in the Northern and Western hemispheres of the Earth. The Turks and Caicos Islands are situated to the southeast of Mayaguana (part of The Bahamas chain of Islands); to the northeast of Cuba; and to the north of Hispaniola Islands (shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic).
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Turks and Caicos
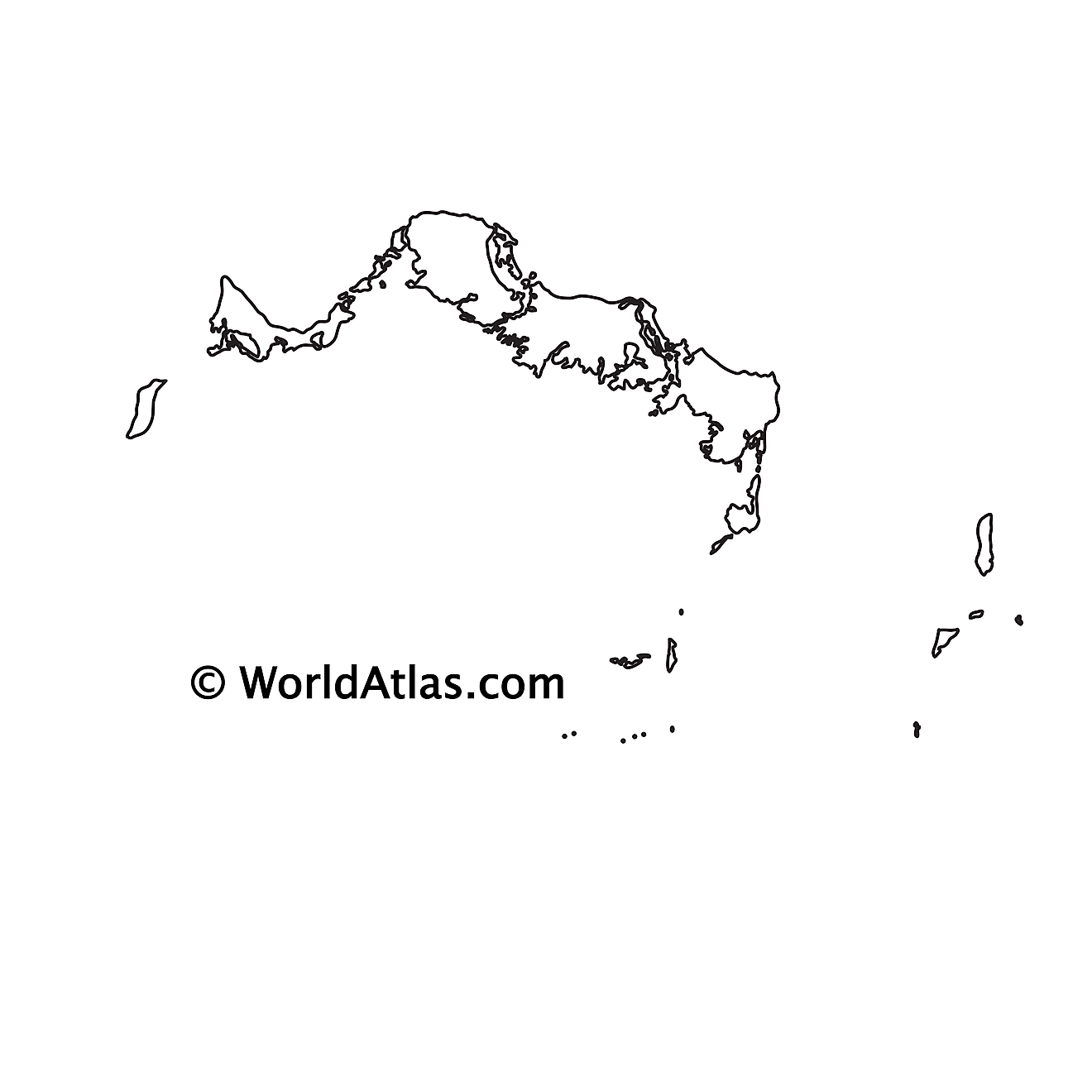
The above blank map represents The Turks and Caicos Islands - a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. The map can be downloaded, printed and used for educational purposes or coloring.
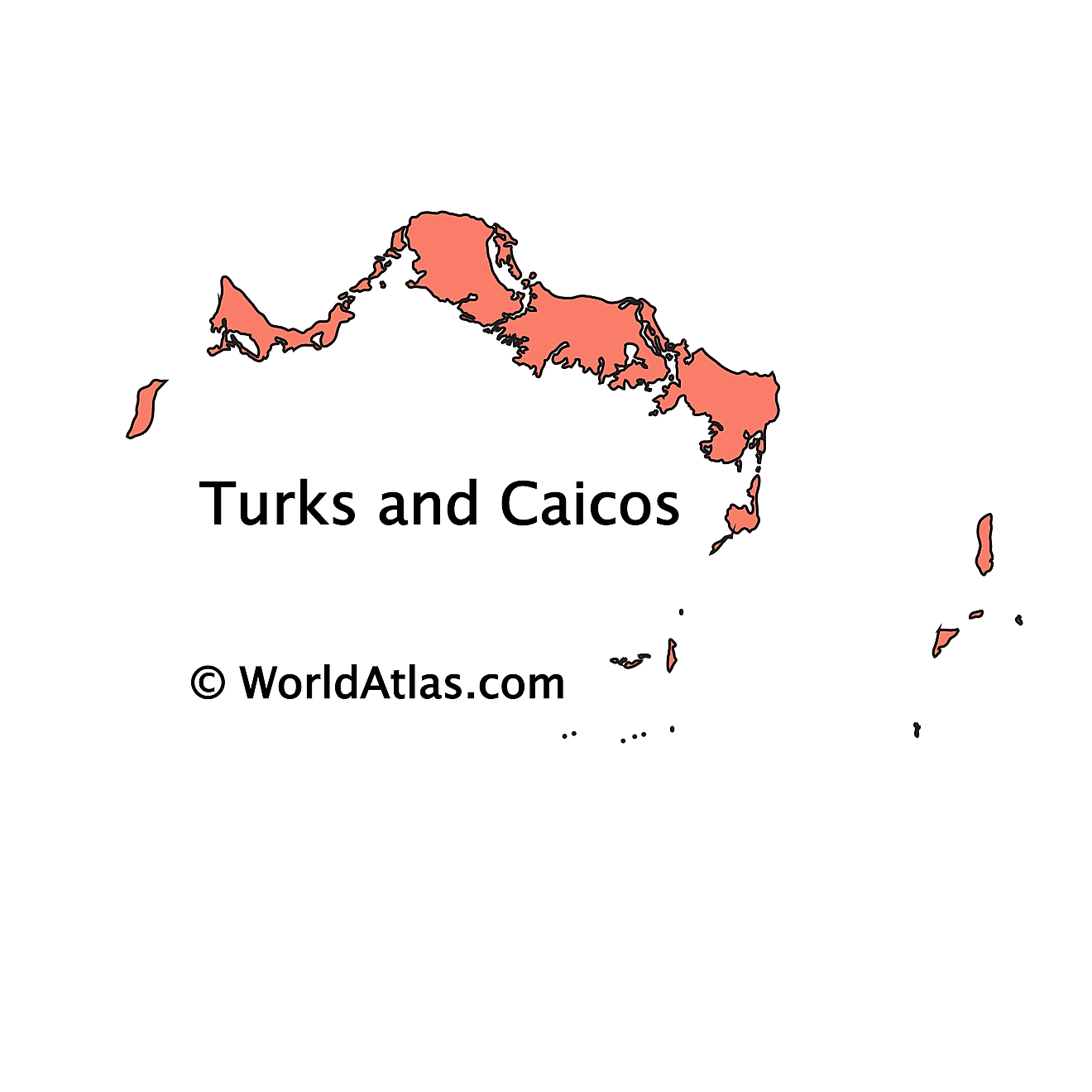
The above outline map represents The Turks and Caicos Islands - a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean, comprising of two groups of tropical islands - the larger islands of Caicos and the smaller islands of Turks.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | Turks and Caicos Islands |
|---|---|
| Flag |

|
| Capital City | Grand Turk (Cockburn Town) |
| 21 28 N, 71 08 W | |
| Total Area | 948.00 km2 |
| Land Area | 948.00 km2 |
| Water Area | N/A |
| Population | 38,191 |
| Currency | US Dollar (USD) |
| GDP | $1.02 Billion |
| GDP Per Capita | $27,142.23 |
This page was last updated on June 26, 2023