Maps of Georgia
In the southeastern region of the United States, Georgia shares its borders with five states: Tennessee and North Carolina to the north, South Carolina to the northeast, Alabama to the west, and Florida to the south. At its southeast, Georgia has about 110 miles of coastline along the Atlantic Ocean, featuring a number of barrier islands and marshlands. The state is entirely in the Eastern Time Zone.
Atlanta, Georgia's capital, doubles as its most populous city, with a population of 510,823.
Admitted as the fourth state to the Union in early 1788, Georgia’s history stretches back to its founding as a British colony in 1732. Today, the state blends its historical legacy with modern industries such as tech, transportation, and tourism. Georgia is nicknamed "The Peach State," an ode to its thriving agricultural sector renowned for its world-class peach orchards.
Georgia is home to several well-known attractions. The historic city of Savannah showcases its preserved antebellum architecture, while Stone Mountain Park offers a view of Georgia's hills and forests near the southern reaches of the Appalachian Mountains.
Visitors also flock to the Martin Luther King Jr. National Historical Park to honor the civil rights leader, and nature lovers tend to explore the Appalachian Trail, which actually starts right on Springer Mountain near the northern border of Georgia.
Size
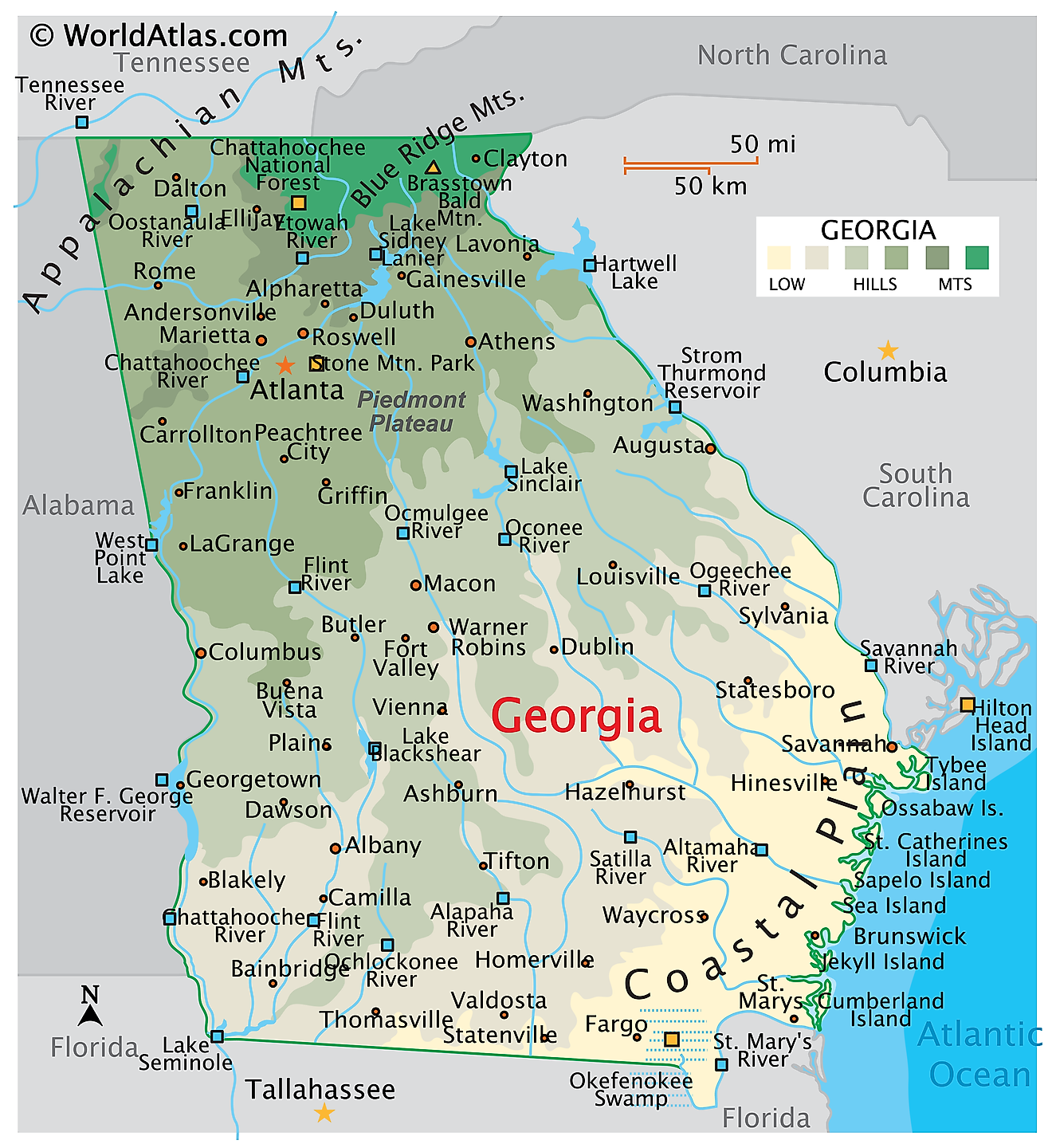
Georgia spans a total area of about 59,425 square miles, making it the 24th largest state in the United States by landmass. Its land area covers 57,906 square miles, while its water area accounts for 1,519 square miles.
To put its size into perspective, Georgia is roughly comparable to England in total area and slightly smaller than the state of Wisconsin.
Its substantial land area supports agriculture, forestry, and urban development, and its strategic placement in the south has made way for a productive shipping and logistics industry, too.
Bodies of Water
Georgia is home to a vast network of bodies of water, including about 860 lakes, 70,150 miles of rivers, and many notable wetlands.
The Chattahoochee River, the longest river in the state at 430 miles long, begins in the Blue Ridge Mountains and flows southwest, serving as a key water source for Atlanta and forming part of Georgia’s border with Alabama. Other major rivers include the Savannah River, which creates the eastern border with South Carolina, and the Altamaha River, one of the largest free-flowing rivers in the Southeast.
Among Georgia’s lakes, Lake Lanier is the largest, covering over 38,000 acres in northern Georgia. Created by the Buford Dam on the Chattahoochee River, it serves as a major recreational and water supply resource. Other significant lakes include Lake Oconee, Lake Hartwell, and Lake Allatoona, which are popular for boating, fishing, and tourism.
In addition to lakes and rivers, Georgia contains vital wetlands and swamps within its borders. The Okefenokee Swamp, one of the largest freshwater wetlands in North America, spans 438,000 acres in the southeastern part of the state. It is a critical ecosystem for wildlife, including alligators and rare birds.
Climate
Georgia’s climate varies across its regions, with the state generally experiencing a humid subtropical climate. The northern mountainous areas tend to have a cooler, more temperate climate, while the south is warmer, with long, hot summers and mild winters.
In January, the average temperature in Georgia ranges from 40°F in the north to around 50°F in the south. By July, average temperatures soar to around 80°F statewide, with southern areas reaching into the 90s°F, accompanied by high humidity.
The state receives about 50 inches of rainfall annually, though this can also vary significantly between regions.
Georgia is susceptible to hurricanes, especially in its coastal and southern regions, typically from June to November. While not as often directly impacted as states like Florida or Louisiana, Georgia can experience heavy rains, flooding, and wind damage from these powerful storms.
Other forms of severe storms and wind patterns, including thunderstorms and tornadoes, are also common across Georgia, particularly in spring and summer months.
Topography
The state of Georgia's terrain is generally divided into five regions: the Appalachian Plateau, Ridge and Valley, Blue Ridge, Piedmont, and Coastal Plain.
The highest point in Georgia is Brasstown Bald, a mountain standing at 4,784 feet above sea level. In the northeastern part of the state, within the Blue Ridge Mountains, visitors can see the states of North Carolina and Tennessee from its top. The Blue Ridge Mountains themselves are part of the larger Appalachian Mountain range, known for their rugged terrain and huge amounts of biodiversity across both flora and fauna.
In contrast, the lowest point in Georgia is at sea level (0 feet) along the Atlantic coastline. The Coastal Plain region is characterized by flat, low-lying land and includes marshes, estuaries, and barrier islands such as Saint Simons Island and Tybee Island.
While Georgia is not known for having many dramatic canyons like some other states, it does feature some very notable geological formations, such as the Tallulah Gorge, a 750-foot-deep canyon in the northeastern part of the state.
Geology
Georgia’s geology is shaped mainly by ancient rock formations, including a variety of economically useful mineral deposits.
The northern part of the state, particularly in the Blue Ridge Mountains, features some of the oldest rocks in North America, dating back over 500 million years. These areas are rich in metamorphic rocks like granite and gneiss, formed under high pressure and temperature conditions. Additionally, Georgia’s Piedmont region is known for its crystalline rocks, such as schist and slate, which were once part of ancient landmasses that collided and formed the Appalachian Mountains.
As mentioned, this state is also home to significant mineral deposits. Among the most notable are kaolin, a type of clay that has been used for centuries in ceramics, paper, and other industries. Georgia is one of the world’s largest producers of kaolin, particularly in the central and eastern parts of the state. Other minerals found in Georgia include gold, which was historically mined during the Georgia Gold Rush of the 1830s.
While Georgia is not in a major earthquake zone, the state does experience occasional seismic activity, primarily along the northern and central regions.
Natural Environment
Georgia’s natural environment is highly diverse and is spread across a number of ecosystems.
The longleaf pine, one of the state's most common trees, is widespread in its coastal plain regions. It is a key species that supports other wildlife, including the endangered red-cockaded woodpecker. The Southern live oak is also a common tree in Georgia and is the official state tree. Another notable plant is the flowering dogwood, which is native to the state and usually blooms white or pink flowers in the spring.
In terms of fauna, the white-tailed deer is one of the most abundant mammals, commonly found in Geogia's numerous forests and meadows. The eastern indigo snake, one of the largest snakes in the U.S., is also native to Georgia, though it is listed as a species. It plays an important role in controlling rodent populations.
Bald eagles can be found nesting along Georgia's rivers and coasts, although species like red-winged blackbirds and various kinds of ducks are far more common.
Natural Attractions
Georgia contains a number of state and national parks, along with other significant protected natural lands that are popular attractions for visitors and residents:
Stone Mountain Park
Stone Mountain Park, just outside Atlanta, is known for its granite dome and the largest bas-relief carving in the world, depicting historic Confederate figures. From its base, visitors can take a cable car or hike to the summit for views of the Atlanta skyline and surrounding areas.
This park also houses a variety of attractions, including a train that offers scenic tours, a number of lakes, and a network of hiking trails.
Cumberland Island National Seashore
Cumberland Island National Seashore, accessible by ferry, is known for its beaches, wild horses, and historic ruins.
The island offers over 50 miles of hiking trails, including paths through its maritime forests and along its coastline. Visitors can also tour the Dungeness Ruins, once the home of industrialist Thomas Carnegie, and spot wildlife such as sea turtles and numerous sea birds.
Okefenokee Swamp
The Okefenokee Swamp is a large freshwater wetland in southeastern Georgia. It is known to biologists and tourists for its diverse ecosystems, blackwater channels, cypress forests, and floating peat islands.
Designated as a National Wildlife Refuge, it is a popular spot for kayaking, fishing, and guided boat tours. The Okefenokee's name, meaning "Land of the Trembling Earth," refers to the significant peat deposits that shift underfoot in many areas of the refuge.
Tourist Attractions
This southern state has a prominent tourism industry, with many historic, cultural, and urban attractions drawing in millions of visitors each year. These are some of the most popular destinations in Georgia:
The Georgia Aquarium
In Atlanta, the Georgia Aquarium is one of the largest aquariums in the world, housing over 500 species. Its major exhibits include the Ocean Voyager, where visitors can view whale sharks and manta rays, and the Cold Water Quest, which features sea otters and beluga whales.
The aquarium also houses several interactive experiences, such as behind-the-scenes tours and up-close encounters with some of the animals, making it popular with families and animal lovers alike. It is one of the most popular attractions in Atlanta, drawing up to 3 million visitors per year.
Savannah Historic District
Originally established in 1733, the Savannah Historic District, one of the largest and oldest in the U.S., allows exploration of famous sites like Forsyth Park, with its iconic fountain, and historic homes such as the Owens-Thomas House & Slave Quarters. Savannah's downtown streets include boutiques, art galleries, and various restaurants.
The city is known for its ghost tours and museum, which provide insights into its history. The Mercer Williams House Museum, housed in a home dating back to the 1860s, is a particularly popular spot to tour around.
World of Coca-Cola
The World of Coca-Cola, located in downtown Atlanta, is a museum dedicated to the history and legacy of the iconic beverage that was first made in this city. Visitors can explore its exhibits, taste over 100 Coca-Cola products from around the world, and view memorabilia spanning the brand's history since its creation in 1886.
Other highlights include the Vault of the Secret Formula, where the brand's recipe is kept, and a 3D theater experience. The museum also features a behind-the-scenes look at Coca-Cola’s bottling process.
Geographic Regions
The state of Georgia is mainly split up into these five distinct geographic regions, from its hilly, forested interior to its Atlantic coast:
Appalachian Plateau
In the far northwest corner of Georgia, the Appalachian Plateau is the state's smallest geographic area. It is characterized by flat-topped mountains and deep valleys. This area includes Lookout Mountain and the town of Dalton. The region is also near the Chickamauga and Chattanooga National Military Park, a historic site from the Civil War straddling the border of Georgia and Tennessee.
Ridge and Valley
The Ridge and Valley terrain stretches across the northern part of Georgia and is known for its alternating ridges and valleys formed by eons of erosion. These valleys are fertile areas for agriculture, particularly in crops like apples and corn. The area includes the town of Ellijay, as well as the city of Rome. The mountains here are part of the larger Appalachian range and are a hotspot for hiking and other outdoor activities.
Blue Ridge
The Blue Ridge region lies in the northeastern corner of Georgia and is part of the larger Appalachian Mountains. This area is known for its steep mountains, deep gorges, and abundance of streams and other flowing waterways. The terrain includes Brasstown Bald, Georgia’s highest point, and is a popular outdoor tourist destination. The Appalachian Trail notably starts or ends here at Springer Mountain. It also features towns like Blairsville and Blue Ridge.
Piedmont
The Piedmont region covers much of central Georgia and is exemplified by its gently rolling hills, clay-rich soils, and scattered forests. It serves as the state's heartland, with major cities such as Atlanta, the state capital, and Augusta, the second-largest city. The Piedmont is also important for agriculture, producing crops like cotton, peanuts, and peaches.
Coastal Plain
The Coastal Plain covers many of the southern parts of Georgia, extending from the fall line (an ancient shoreline that stretches from the city of Columbus, Georgia, to Augusta) down to the Atlantic Ocean. It is mostly flat, with fertile soil and numerous rivers, including the Savannah and Altamaha. This region is also known for its agricultural output, including crops like tobacco and pecans. It also features Georgia’s coastal barrier islands, including Jekyll Island, St. Simons Island, and Cumberland Island, which are highly sought-after spots for tourism.
Counties Map
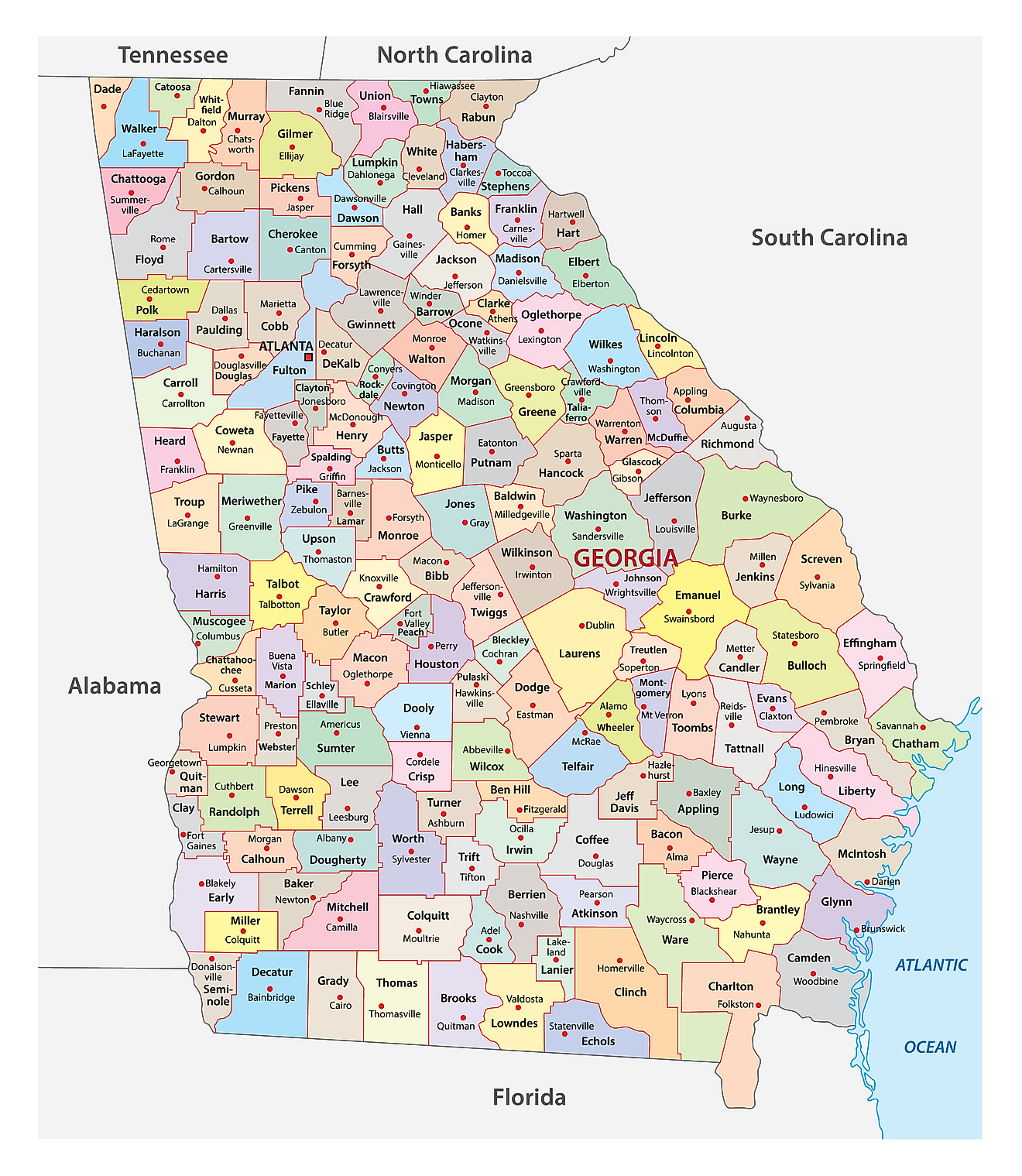
The State of Georgia is divided into 159 counties. In alphabetical order, these counties are: Appling, Atkinson, Bacon, Baker, Baldwin, Banks, Barrow, Bartow, Ben Hill, Berrien, Bibb, Bleckley, Brantley, Brooks, Bryan, Bulloch, Burke, Butts, Calhoun, Camden, Candler, Carroll, Catoosa, Charlton, Chatham, Chattahoochee, Chattooga, Cherokee, Clarke, Clay, Clayton, Clinch, Cobb, Coffee, Colquitt, Columbia, Cook, Coweta, Crawford, Crisp, Dade, Dawson, Decatur, DeKalb, Dodge, Dooly, Dougherty, Douglas, Early, Echols, Effingham, Elbert, Emanuel, Evans, Fannin, Fayette, Floyd, Forsyth, Franklin, Fulton, Gilmer, Glascock, Glynn, Gordon, Grady, Greene, Gwinnett, Habersham, Hall, Hancock, Haralson, Harris, Hart, Heard, Henry, Houston, Irwin, Jackson, Jasper, Jeff Davis, Jefferson, Jenkins, Johnson, Jones, Lamar, Lanier, Laurens, Lee, Liberty, Lincoln, Long, Lowndes, Lumpkin, Macon, Madison, Marion, McDuffie, McIntosh, Meriwether, Miller, Mitchell, Monroe, Montgomery, Morgan, Murray, Muscogee, Newton, Oconee, Oglethorpe, Paulding, Peach, Pickens, Pierce, Pike, Polk, Pulaski, Putnam, Quitman, Rabun, Randolph, Richmond, Rockdale, Schley, Screven, Seminole, Spalding, Stephens, Stewart, Sumter, Talbot, Taliaferro, Tattnall, Taylor, Telfair, Terrell, Thomas, Tift, Toombs, Towns, Treutlen, Troup, Turner, Twiggs, Union, Upson, Walker, Walton, Ware, Warren, Washington, Wayne, Webster, Wheeler, White, Whitfield, Wilcox, Wilkes, Wilkinson, and Worth.
With an area of 153,909 sq. km, the State of Georgia is the 24th largest and the 8th most populous state in the USA. Located in Fulton County (also partly in DeKalb County), at the foothills of the Appalachian Mountains, in the northwestern part of the state is Atlanta – the capital, the largest, and the most populous city of Georgia. Atlanta is the commercial, financial, technology, and education center of Georgia. It also serves as the major trade and transportation center of the southeastern United States.
Where is Georgia?
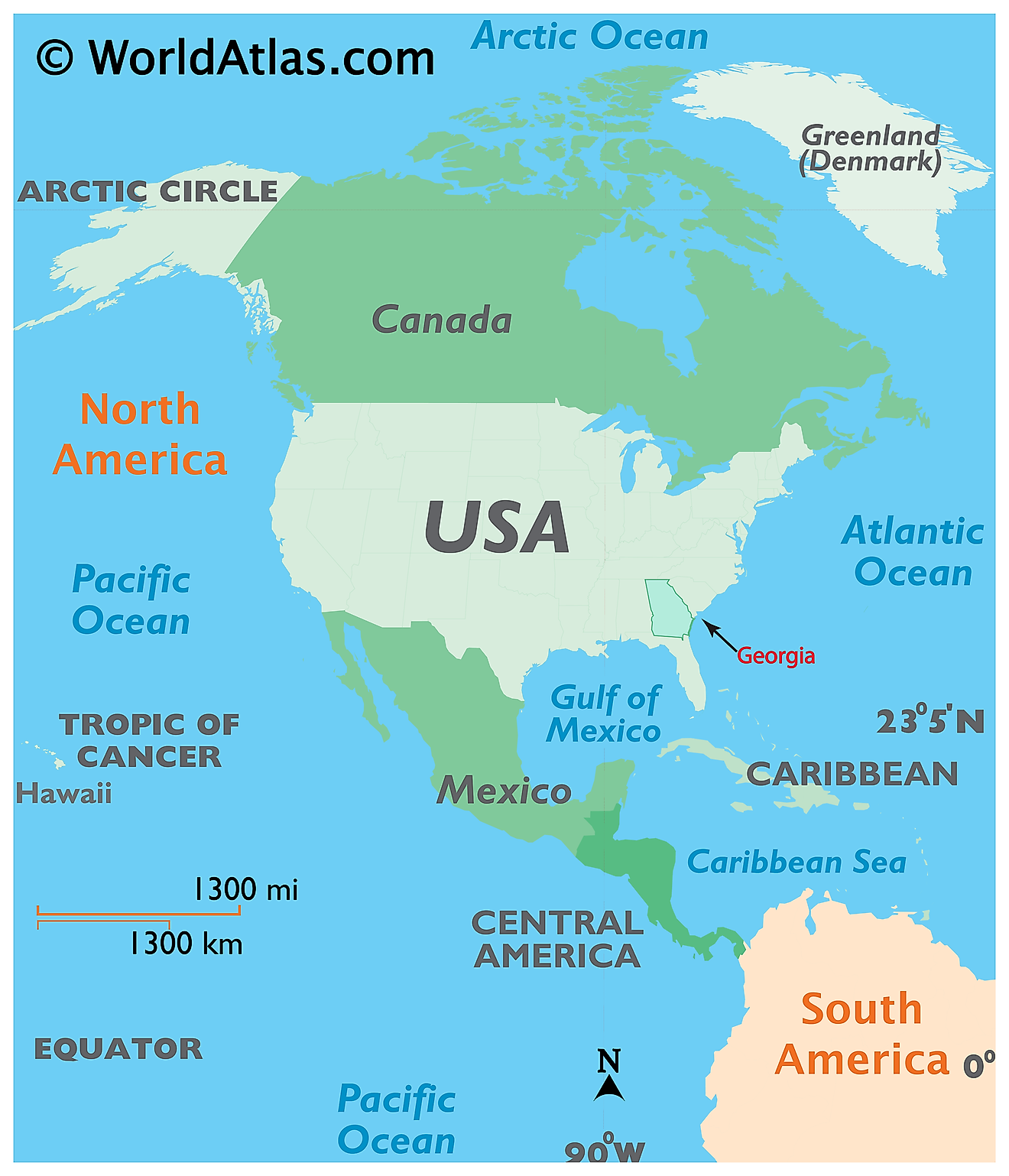
The State of Georgia is located in the south-eastern region of the United States. Georgia is bordered by the states of Tennessee and North Carolina in the north; by Alabama and Florida in the southwest; and by South Carolina in the east. It is also bordered by the Atlantic Ocean in the southeast.
Regional Maps: Map of North America
Outline Map of Georgia
The above blank map represents the State of Georgia, located in the southeastern region of the United States. The above map can be downloaded, printed and used for geography education purposes like map-pointing and coloring activities.
The above outline map represents the State of Georgia, located in the southeastern region of the United States.
Key Facts
| Legal Name | State of Georgia |
|---|---|
| ISO 3166 Code | US-GA |
| Capital City | Atlanta |
| Major Cities |
|
This page was last updated on December 19, 2024