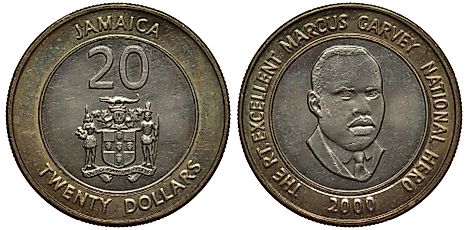Flags, Symbols, & Currency of Jamaica

The flag of Jamaica was adopted on August 6, 1962. The flag a tricolor flag consisting of a gold-colored cross shape running diagonally from corner to corner. This cross creates 4 triangular areas on the flag. The triangles above and below the cross are dark green in color, while the triangles to the left and right of the cross are black. The flag was originally designed with horizontal stripes, but this was considered too similar to the Tanganyikan flag, and so the stripes were substituted with saltire.
The flag of Jamaica is sometimes referred to as “The Cross” or as the “Black, Green, and Gold” because of its colors. It was officially adopted on August 6, 1962, when Jamaica gained its independence from the United Kingdom. The flag's design was selected through a public nationwide competition. In its original design, the bands of the flag were placed in a horizontal position, but the government soon realized the design was nearly identical to the flag of Tanganyika. The flag has a height to width ratio of 1:2.
Symbolism of the Flag of Jamaica
The flag of Jamaica is unique compared to other flags around the world in that it is the only flag that does not contain one of the following colors: red, white, or blue. Over time, the meaning behind the colors of Jamaica's flag has changed. After independence in 1962, government officials claimed the black color stood for the challenges the country faced, the green represented the island itself, and the gold color symbolized the bright sun that shines over the land. Today, however, the colors have taken on slightly different meanings. Beginning in 1996, the black color has been said to represent the people of the land, particularly their strength and resilience against hardships. The green color represents the abundance of flora found throughout the island, and the gold color symbolizes the riches found within Jamaica.
Variations of the Flag
As a former colony of the United Kingdom, Jamaica has had a number of flags throughout history. The first of these was used between 1875 and 1906. It had a blue background with a small flag of the United Kingdom in the upper left corner. In the middle of the right side, a white circle was situated with the image of a crocodile on top of a red cross. The cross was lined with 5 pineapples and circled by a gold-colored hoop. In other variations, the only part of the design that changed was the image in the white circle. Between 1906 and 1957, the image was of the same crocodile and pineapple-lined cross, but in a shield shape, and on either side stood an indigenous woman and an indigenous man. Between 1957 and 1962, the image changed only slightly, by adding a golden stand upon which stood the crocodile.
Today, a few other flags are used by various offices of the government. The Coast Guard of Jamaica, for example, flies a white flag with a red cross in its center. This cross creates 4 quadrants and in the top left quadrant is a smaller version of the Jamaican flag. The government sometimes uses a flag that is similar to the colonial design. Known as the Blue Ensign, this flag has a bright blue background with a small Jamaican flag in the top left corner.
Symbols of Jamaica
National Coat of Arms of Jamaica

The coat of arms depicts a male (viewer's right) and female (left) member of the Taino tribe standing on each side of a shield, which bears a red cross with five golden pineapples. The crest shows a Jamaican crocodile mounted on the Royal Helmet of the British Monarchy and mantling. At the base of the shield is a white and red ribbon displaying the national motto: "Out of Many, One People."
National Anthem
- Anthem Title: Jamaica, Land We Love
- Music composer: Robert Lightbourne (arranged by Mapletoft Poulle)
- Lyricist: Hugh Sherlock
- Date of Adoption: July 19, 1962
The national anthem of Jamaica, "Jamaica, Land We Love," was adopted in 1962 after a competition between September 1961 and March 31, 1962. From the competition, the House of Parliment selected lyrics written by Hugh Sherlock and set to music by Robert Lightbourne. The competition attracted over 100 entries with "Jamaica, Land We Love" being one of the two entries given to the House of Parliament to vote for on July 19, 1962. Once the winning script was chosen and set to music, the anthem was arranged by Christine Alison Poulie and Mapletoft Poulie
Jamaica, Land We Love
Eternal Father bless our land
Guard us with Thy mighty hand
Keep us free from evil powers
Be our light through countless hours
To our leaders, Great Defender,
Grant true wisdom from above
Justice, truth be ours forever
Jamaica, land we love
Jamaica, Jamaica, Jamaica, land we love.
Teach us true respect for all
Stir response to duty's call
Strengthen us the weak to cherish
Give us vision lest we perish
Knowledge send us, Heavenly Father,
Grant true wisdom from above
Justice, truth be ours forever
Jamaica, land we love
Jamaica, Jamaica, Jamaica, land we love.
The Currency of Jamaica is the Jamaican dollar
The currency of Jamaica is the Jamaican dollar. The Jamaican dollar is abbreviated as "J$”. The letter J serves the purpose of differentiating the Jamaican dollar from other dollar-dominated currencies. The international code of the Jamaican dollar is JMD. It exists in the denominations of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 500, 1000, and 5000 dollars. Jamaican currency banknotes are printed by the De La Rue Currency Company in England. The coins are minted by the British Royal Mint Company. The body which circulates the Jamaican dollar is the Bank of Jamaica.
Jamaican dollar Coins
Jamaican sterling pound coins were introduced in 1840. The first coins came in denominations of 5/-, 10/-, 1, and 5 pounds, and were struck in copper, gold, and cupronickel. The Jamaican dollar coins were introduced and circulated in 1969. Since then, they have taken various forms such as decagonal, seven sided and round shapes used in 1976, 1991, and 1994, respectively. The Jamaican dollar coins are uniquely designed so that the coat of arms appears in front of every coin. On the reverse side, portraits of Jamaican national heroes such as Marcus Garvey and the common national fruit called ackee can be found.
Jamaican dollar Banknote Issues
Jamaican dollar banknotes were introduced in 1969. The first notes came in denominations of 50 cents, 1, 2, and 10 dollars. Then in 1970, a 5 dollar banknote was introduced, followed by a 20 dollar note in 1976. In 1986 and 1988, the 50 and 100 dollar notes were issued, respectively. Six years after its introduction, the 2 dollar note was dropped. The 500 dollar note were established in 1994, and in 1999 the 20 dollar coins were replaced by notes. In addition to these changes, the 1, 5, and 10 dollar notes were replaced by coins in 1990, 1994, and 1999, respectively. There was also the introduction of a 1000 banknote in 1999. Some features of the Jamaican dollar banknote include distinct watermarks, unique serial numbers, and portraits of national heroes, like Samuel Sharpe. Other features on the notes are Doctor’s Cave Beach, Jamaica House, Dunn’s River Falls, and Montego Bay.
Historical Currencies of Jamaica
Jamaica used the sterling pound before adopting the Jamaican dollar in 1969. Subsequently, sterling pounds were exchanged for Jamaican dollars at a rate of 1 pound to 2 dollars. The dollar currency was introduced by a majority vote of members of the House of Representatives who wanted to change the currency into a decimal system. In 1960, the Bank of Jamaica was officially given the responsibility of producing banknotes and coins. Consequently, by 1969, the banknotes and coins were circulating in the economy.