US States By Size
The United States of America is an immense federal republic spanning from the southern half of Northern America to Alaska and Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a total of 50 states, with 49 located within mainland North America and one situated in the Pacific Ocean. One can rank these states from smallest to largest based on their total area, water area, or land area. Since a state may have a larger overall size, its actual land area can often be much smaller due to its associated territorial waters. As such, ranking depends on the metric used. The following US states are listed from greatest to smallest by total area because marine environments are just as crucial to civilization as those on land.
US States Ranked By Total Area
| Rank | State | Total Area (mi²) | Land Area (mi²) | Water Area (mi²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alaska | 665,384 | 570,641 | 94,743 |
| 2 | Texas | 268,596 | 261,232 | 7,365 |
| 3 | California | 163,695 | 155,779 | 7,916 |
| 4 | Montana | 147,040 | 145,546 | 1,494 |
| 5 | New Mexico | 121,590 | 121,298 | 292 |
| 6 | Arizona | 113,990 | 113,594 | 396 |
| 7 | Nevada | 110,572 | 109,781 | 791 |
| 8 | Colorado | 104,094 | 103,642 | 452 |
| 9 | Oregon | 98,379 | 95,988 | 2,391 |
| 10 | Wyoming | 97,813 | 97,093 | 720 |
| 11 | Michigan | 96,714 | 56,539 | 40,175 |
| 12 | Minnesota | 86,936 | 79,627 | 7,309 |
| 13 | Utah | 84,897 | 82,170 | 2,727 |
| 14 | Idaho | 83,569 | 82,643 | 926 |
| 15 | Kansas | 82,278 | 81,759 | 520 |
| 16 | Nebraska | 77,348 | 76,824 | 524 |
| 17 | South Dakota | 77,116 | 75,811 | 1,305 |
| 18 | Washington | 71,298 | 66,456 | 4,842 |
| 19 | North Dakota | 70,698 | 69,001 | 1,698 |
| 20 | Oklahoma | 69,899 | 68,595 | 1,304 |
| 21 | Missouri | 69,707 | 68,742 | 965 |
| 22 | Florida | 65,758 | 53,625 | 12,133 |
| 23 | Wisconsin | 65,496 | 54,158 | 11,339 |
| 24 | Georgia | 59,425 | 57,513 | 1,912 |
| 25 | Illinois | 57,914 | 55,519 | 2,395 |
| 26 | Iowa | 56,273 | 55,857 | 416 |
| 27 | New York | 54,555 | 47,126 | 7,429 |
| 28 | North Carolina | 53,819 | 48,618 | 5,201 |
| 29 | Arkansas | 53,179 | 52,035 | 1,143 |
| 30 | Alabama | 52,420 | 50,645 | 1,775 |
| 31 | Louisiana | 52,378 | 43,204 | 9,174 |
| 32 | Mississippi | 48,432 | 46,923 | 1,509 |
| 33 | Pennsylvania | 46,054 | 44,743 | 1,312 |
| 34 | Ohio | 44,826 | 40,861 | 3,965 |
| 35 | Virginia | 42,775 | 39,490 | 3,285 |
| 36 | Tennessee | 42,144 | 41,235 | 909 |
| 37 | Kentucky | 40,408 | 39,486 | 921 |
| 38 | Indiana | 36,420 | 35,826 | 593 |
| 39 | Maine | 35,380 | 30,843 | 4,537 |
| 40 | South Carolina | 32,020 | 30,061 | 1,960 |
| 41 | West Virginia | 24,230 | 24,038 | 192 |
| 42 | Maryland | 12,406 | 9,707 | 2,699 |
| 43 | Hawaii | 10,932 | 6,423 | 4,509 |
| 44 | Massachusetts | 10,554 | 7,800 | 2,754 |
| 45 | Vermont | 9,616 | 9,217 | 400 |
| 46 | New Hampshire | 9,349 | 8,953 | 397 |
| 47 | New Jersey | 8,723 | 7,354 | 1,368 |
| 48 | Connecticut | 5,543 | 4,842 | 701 |
| 49 | Delaware | 2,489 | 1,949 | 540 |
| 50 | Rhode Island | 1,545 | 1,034 | 511 |
Source: US Census Bureau
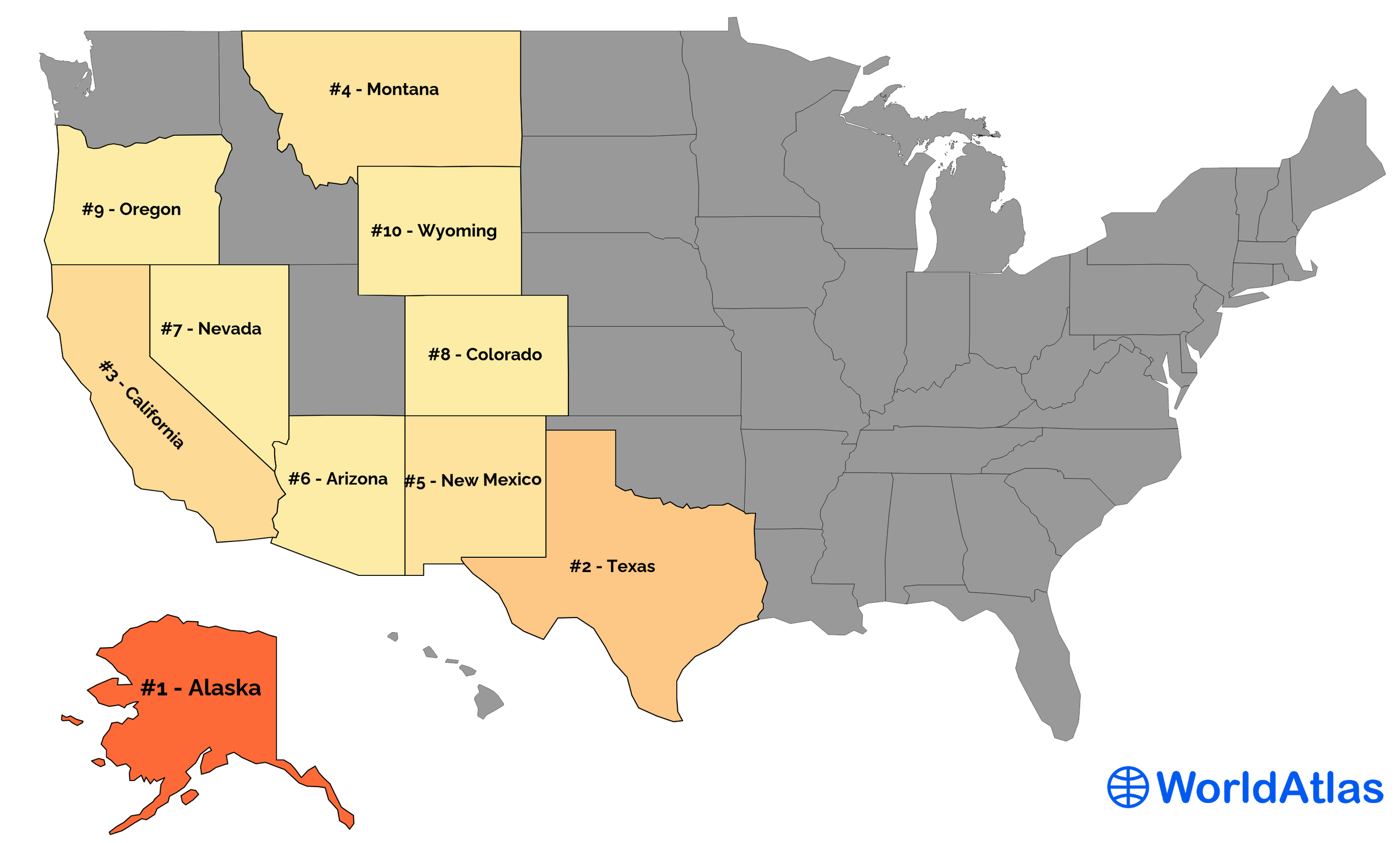
Ten Largest US States by Total Area
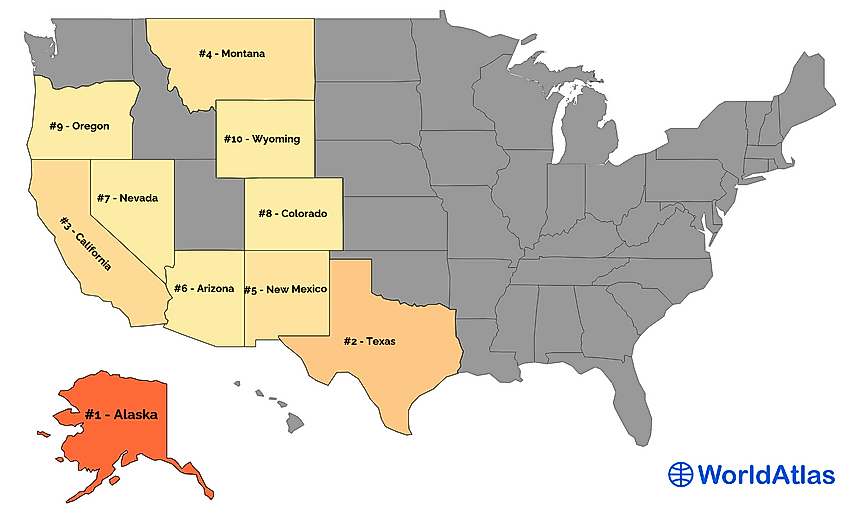
1. Alaska - 665,384 mi²
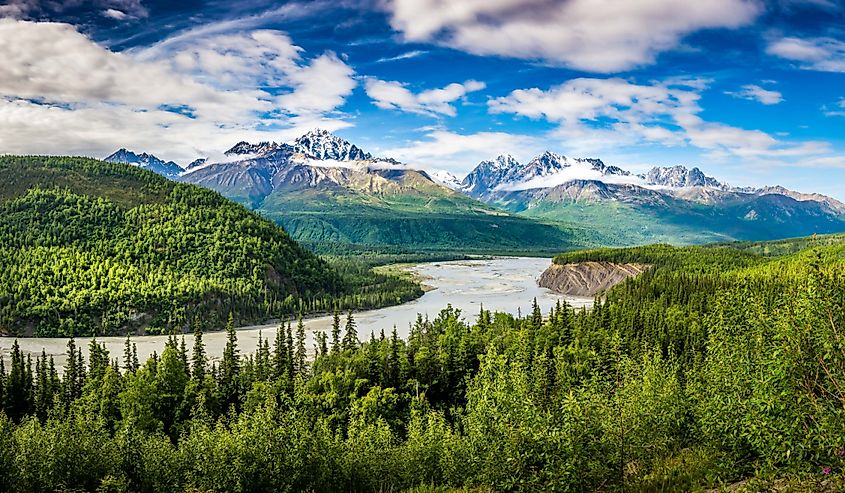

Alaska is the largest state in the United States. Spanning over 665,384 square miles, it is near twice the size of Texas and accounts for one-fifth of the US's total land area. Over half of its terrain comprises mountainous regions, while glaciers cover over 5 percent of its total geography. The two primary mountain chains are the Brooks Range, which spans across the northern part of the state, and the Alaska Range, which runs through the southeastern portion.
Regarding borders, Alaska shares a boundary with Canada, extending between Ivvavik National Park and southeast of the Gulf of Alaska. To its east lies Yukon Territory, British Columbia to its southeast, and Chukotka Autonomous Okrug (Russia) to its West across the Bering Strait.
One historical landmark within Alaska's borders, which continues to draw numerous tourists annually from around the world, is Denali National Park & Preserve, located in south-central Alaska near Talkeetna village. This expansive national park spans over six million acres and features Mt McKinley (now known as Denali), North America's highest peak at an elevation of 20,310 feet above sea level. Additionally, visitors can experience diverse wildlife, such as bear species, moose, and Dall sheep, along with many bird species, including bald eagles.
2. Texas - 268,596 mi²

Texas is the second largest state in the United States, spanning 268,596 square miles. It was one of the original republics of Mexico until 1836, when it declared itself an independent nation, before joining the Union as a state in 1845.
The Lone Star State has been shaped by its various borders over time. When it took its place alongside other states in the United States, it had a much different shape than today, including parts of present-day Colorado, New Mexico, and Wyoming. Through a series of treaties between the U.S. government and Mexico since then, Texas' borders were eventually finalized.
Surveyors set out to create six "survey districts" throughout the state; these divisions remain intact today and are known as "empresario grants." Their purpose was and is to help establish population density. The Old San Antonio Road, which stretches from San Antonio to Nacogdoches, is also included within this survey district framework.
For Texans, landmarks like the Great Plains have come to represent their unique spirit and culture over time. However, one of the largest deserts exists in Texas: the Chihuahuan Desert. This gigantic desert stretches over 200,000 square miles and is larger than the state of California, which is why Mexico shares access to it. This area is characterized by its hot and dry climate with sparse vegetation and a variety of diverse habitats from rocky mountains to grasslands. The region also hosts an array of unique species adapted to survive in this arid environment, such as the black-tailed jackrabbit and the Texas horned lizard. Furthermore, this desert provides an important source of groundwater for humans in southwestern parts of the United States and Mexico, making it an ecologically significant area.
3. California - 163,695 mi²
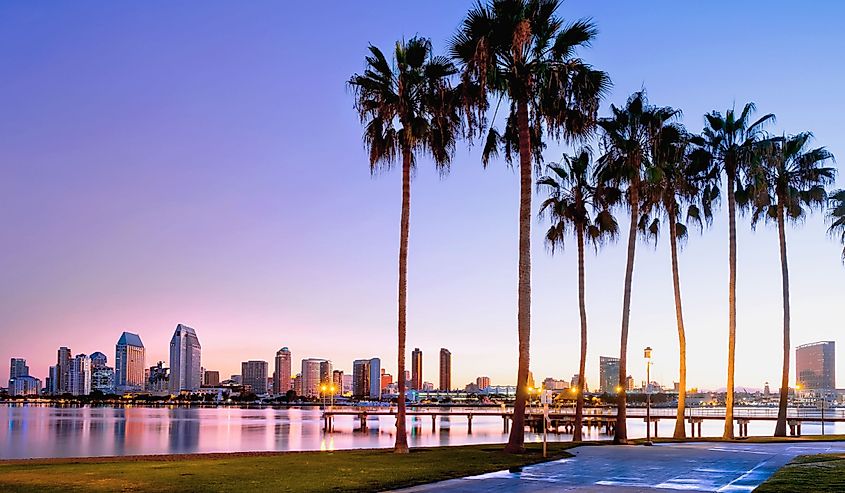

California, the Golden State, is located on the western coast of the United States and is bordered by Oregon, Nevada, and Arizona. California covers an area of 163,696 square miles, making it the third-largest state in the United States.
The borders of California were established in 1848 when Mexico ceded the area to the United States after the Mexican-American War. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo stated that "all citizens of Mexico now living in territories previously belonging to Mexico" would be recognized as U.S. citizens with full political and legal rights. This excluded Native Americans living in what is now California.
The border between California and Oregon was determined by a treaty signed by both countries in 1846, which included provisions for both sides that guaranteed free navigation along the Columbia River. The border between California and Arizona was set at its current location in 1863, although settlers had already moved into the area long before this date. Nevada's western border with California was finally finalized in 1866 when Congress passed an act creating it as a separate state.
California is home to one of the world's most extensive mountain ranges - The Sierra Nevada. Spanning 430 miles, it includes some of the highest peaks in the continental United States, including Mount Whitney – the tallest mountain in the contiguous United States(14,505 ft). The Sierra Nevada has many unique features, from rugged peaks and old-growth forests to cascading waterfalls and crystal-clear lakes.
4. Montana - 147,040 mi²
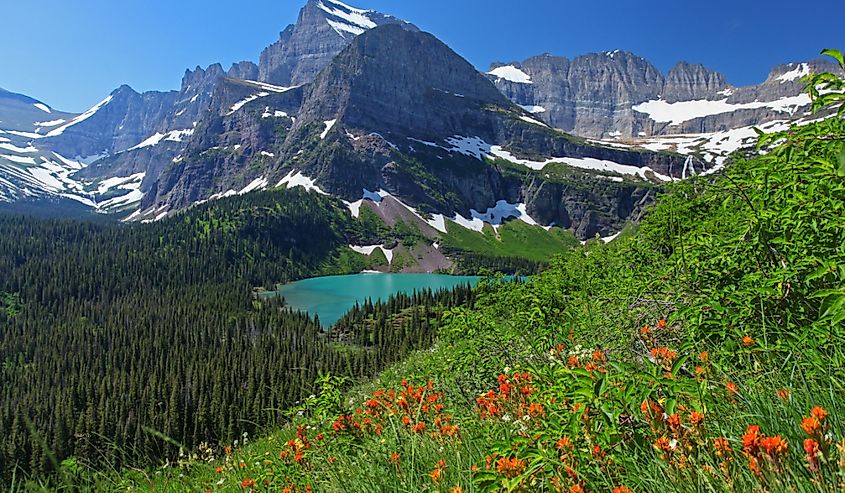

Montana is the fourth-largest state in the United States at 147,040 square miles. Montana's borders developed through historical events and treaties between Native American tribes. In 1803, the Louisiana Purchase Agreement solidified the border with Canada as it is today. The state negotiated several treaties with various Native American tribes to establish official boundaries within the state; military force was often involved. These official treaties are what define Montana's current borders.
Montana is home to many significant landforms, including two mountain ranges: the Rocky Mountains and the Continental Divide. Its expansive plains are also notable in their sheer size, covering the entire western state. However, the most significant landform within Montana is Glacier National Park, a wilderness area known for its stunning scenery and over 700 miles of trails.
5. New Mexico - 121,590 mi²
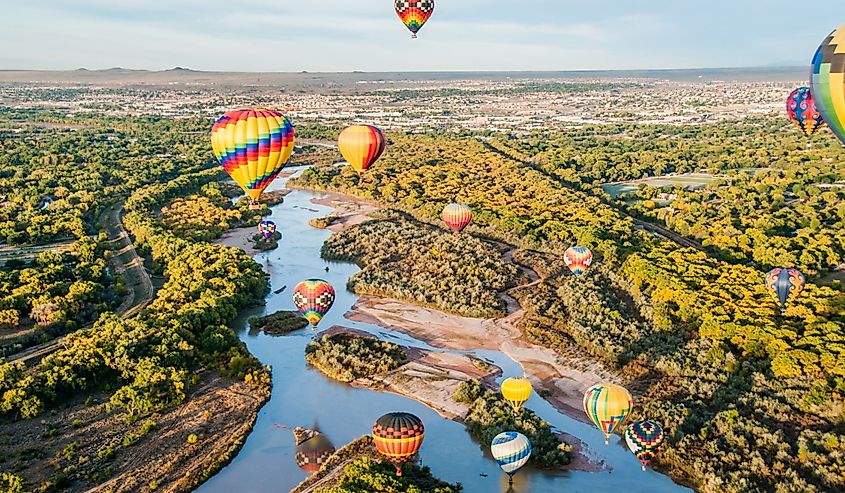

New Mexico is the fifth-largest state in the United States, covering an area of 121,591 square miles. Colorado borders it to the north, Utah to the northwest, Arizona to the West, Texas to the East, Oklahoma to the northeast, and Mexico to the south. The land that now makes up New Mexico was historically part of what was called "the Spanish Empire," consisting of Spain's American colonies. When Mexico gained independence from Spain in 1821, it received all land from what had previously been Spanish territory within its current borders. New Mexico officially became a U.S. territory due to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which ended the Mexican–American War in 1848 and ceded much of present-day California, Nevada, and Utah to the U.S. In 1912, New Mexico was granted statehood, and its borders became official.
One of the most impressive landforms of New Mexico is Shiprock, a towering formation of eroded volcanic basalt that rises out of the desert. It's said to resemble an ancient sailing vessel, hence its name. Shiprock stands 1,583 feet tall and covers an area of 13 square miles, making it one of the largest formations in New Mexico - an impressive example of this southwestern state's sheer size and grandeur.
6. Arizona - 113,990 mi²
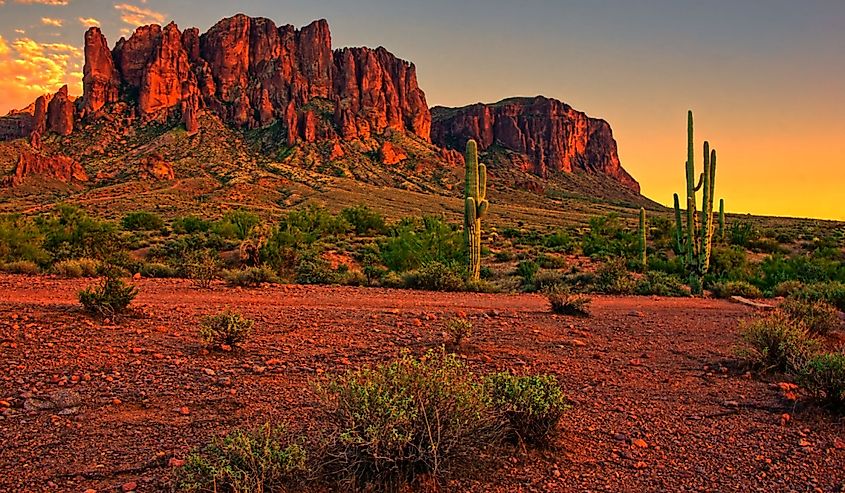

Arizona is the sixth largest state in the United States by area. It occupies an area of 113,990 square miles and is bordered by California, Nevada, Utah, New Mexico, Colorado, and Mexico.
Arizona's modern borders were first set when it was recognized as a U.S. territory in 1863. The initial territory expanded several times following the Mexican-American War due to newly acquired land from Mexico. Following statehood in 1912, Arizona's borders have formed according to geographical features like rivers and mountain ranges.
One example of its size is the Grand Canyon. The Grand Canyon is a stunning geological formation located in the northwest corner of the state, and it measures 18 miles across at its widest point and 277 miles in length. It's an incredible natural wonder that provides a fantastic view of Arizona's impressive size.
7. Nevada - 110,572 mi²
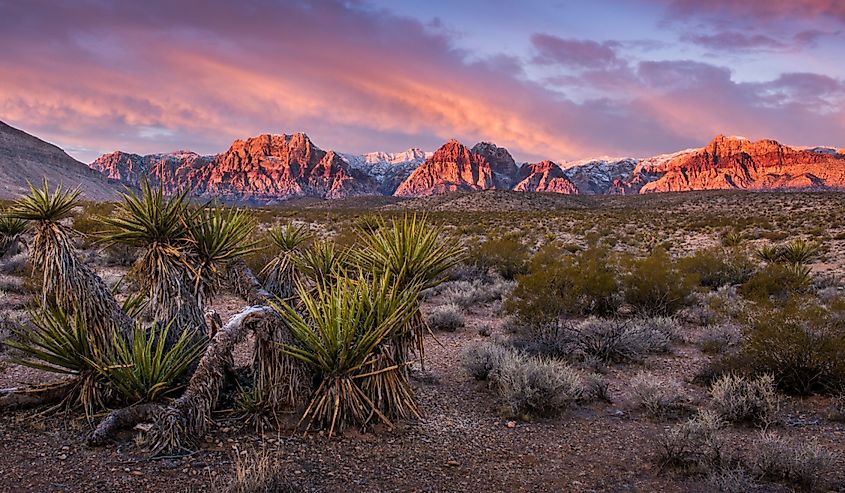

Nevada is the seventh-largest state in the United States, stretching across 110,577 square miles of desert, alpine mountains, and rugged plains. Located in the southwest region of the U.S., it shares borders with Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, and Arizona to the south.
Its boundaries are determined by geographical features such as rivers and mountain ridges. For example, Nevada's southernmost border follows the Colorado River from Arizona through Lake Mead into California. The western border with California is defined by mountainous terrains and several mountain ranges, such as the Sierra Nevada and the White Mountains. Additionally, Bear Lake delineates a portion of its eastern boundary with Idaho.
With over 190,000 square miles of area, the Great Basin Desert of Nevada spans the entire state and spills over into California. It stretches from the imposing Sierra Mountains in the west to the Wasatch Mountains in the east. This desert contains many unique geological features, including dunes, canyons, cave systems, and salt flats. Its climate is known for being arid, with hot temperatures during the day and bitterly cold temperatures during the night.
8. Colorado - 104,094 mi²
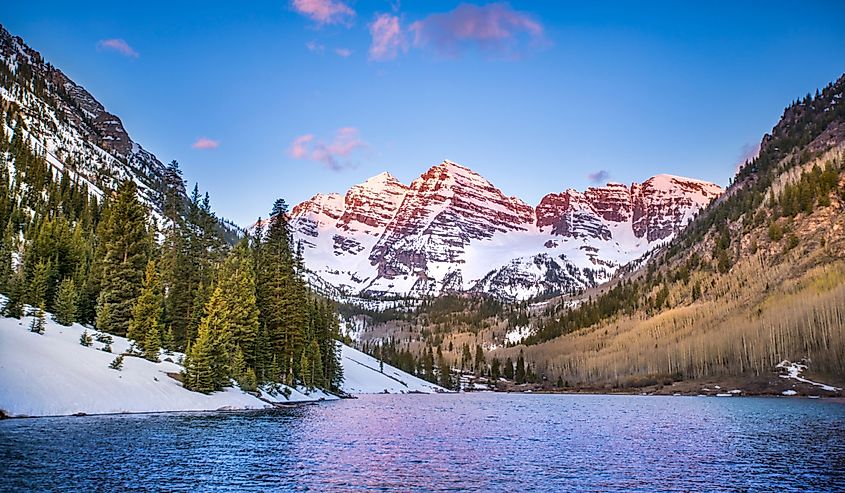

Colorado is the 8th biggest state in the US and has an area of 104,185 square miles. It borders Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas to the East, Oklahoma to the southeast, New Mexico to the south, and Utah to the West. The southwestern corner of Colorado was originally part of Mexico before 1848 when it became part of the U.S. after the Treaty Of Guadalupe Hidalgo was signed. The rest of the modern-day borders for Colorado formed because of acts passed in 1860, which established their boundaries with Wyoming, Utah, New Mexico, and Nebraska.
One of the most impressive examples of Colorado's size is the Mesa Verde National Park. This 52,000-acre park is an expansive area in the Four Corners region, filled with towering cliffs and ancient ruins of ancient Native American civilizations. The park contains some of the best-preserved archaeological sites in the world, with hundreds of cliff dwellings carved into the steep stone walls. Visitors can explore this real-life time capsule and learn about the culture and history of the people who lived here from 600CE to 1300CE.
9. Oregon - 98,379 mi²
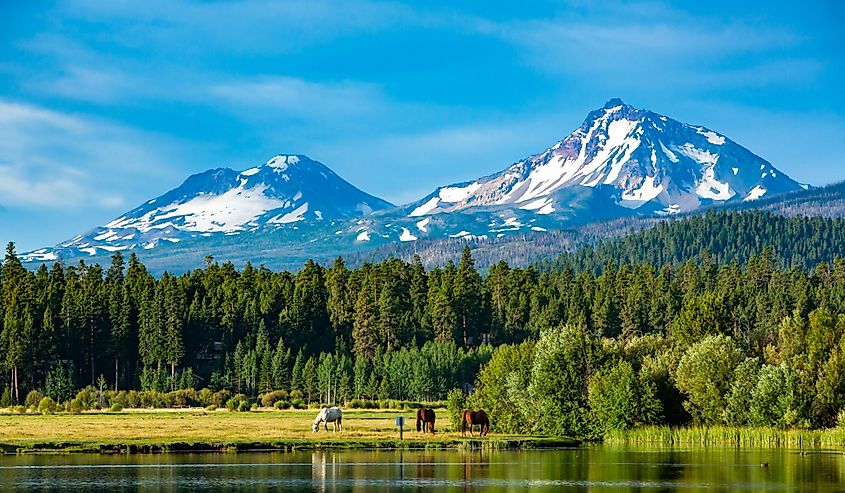

Oregon is the ninth largest state in the United States, spanning 98,466 square miles. Washington borders it to the north, Idaho to the East, Nevada, and California to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the West. Its borders were formally established when Oregon became a state in 1859. Surveyors drew up the eastern border with Idaho following a compromise plan that involved a fair division of resources between both states. As for its western border with Washington and the northern border with Canada, they formed due to the existing early 19th-century territorial boundaries of Oregon Country.
The Columbia River Gorge is a geologic wonder located in the Pacific Northwest, running through Oregon for 80 miles, and enters into Washington. Carved by glaciers thousands of years ago, the walls of the gorge reach proportions of up to 4,000 feet high. The river winds through incredible canyons, forming waterfalls and providing beautiful views from many vantage points. A diverse landscape has developed within its boundaries, including temperate rainforest and grassland ecosystems. Native populations have thrived here for centuries, engaging in activities that are sustainable with the environment, such as fishing and camping.
10. Wyoming - 97,813 mi²
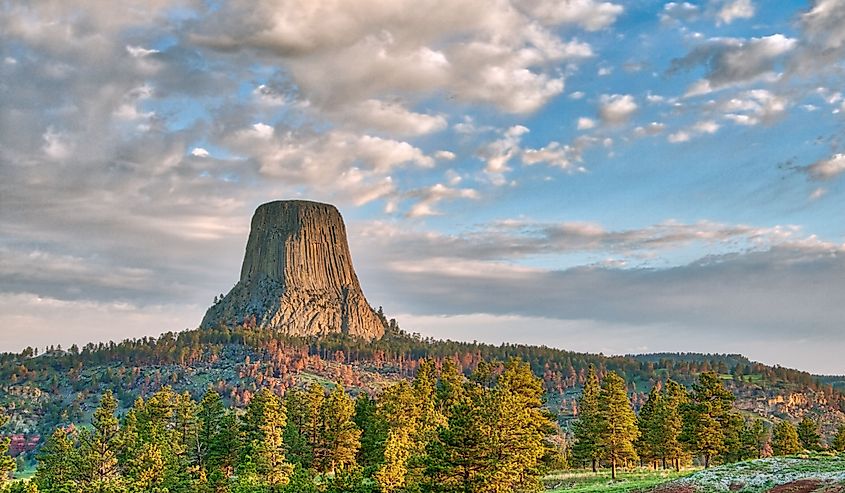

Wyoming is the 10th largest state in the United States, spanning 97,914 square miles. Moreover, Congress established its borders in 1890. Wyoming has assumed its modern form based on the region's geography and also because of political compromises between competing territories and states. One example was when Montana and Idaho were both granted land that Wyoming wanted during negotiations to become a state. These two states gave Wyoming a 'panhandle' section to rectify the situation. In 1868, Andrew Jackson signed an act that organized a territorial government based on lands from Idaho, native tribes like the Dakota, and Utah. This order was manifested by 1872, with the lines being officially declared in 1890.
One of the state's most prominent landforms is the Bighorn Mountains, located in the state's northeast corner. The Bighorn Mountains are a subrange of the Rocky Mountains and cover nearly 9,000 square miles. They formed because of uplift and tectonic activity millions of years ago, and today they stand at an average elevation of 8,000 feet above sea level. The mountains are composed primarily of sedimentary rocks such as limestone and sandstone, with some areas having metamorphic rocks like quartzite due to intense pressure and heat. Furthermore, the region around the Bighorn Mountains contains numerous rivers, hot springs, geysers, and other water features fed by melting glaciers found on their peaks.
The 10 Smallest US States by Total Area
| Rank | State | Total area (mi²) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rhode Island | 1,545 |
| 2 | Delaware | 2,489 |
| 3 | Connecticut | 5,543 |
| 4 | New Jersey | 8,723 |
| 5 | New Hampshire | 9,349 |
| 6 | Vermont | 9,616 |
| 7 | Massachusetts | 10,554 |
| 8 | Hawaii | 10,932 |
| 9 | Maryland | 12,406 |
| 10 | West Virginia | 24,230 |
Source: US Census Bureau
Ten Smallest States by Total Area
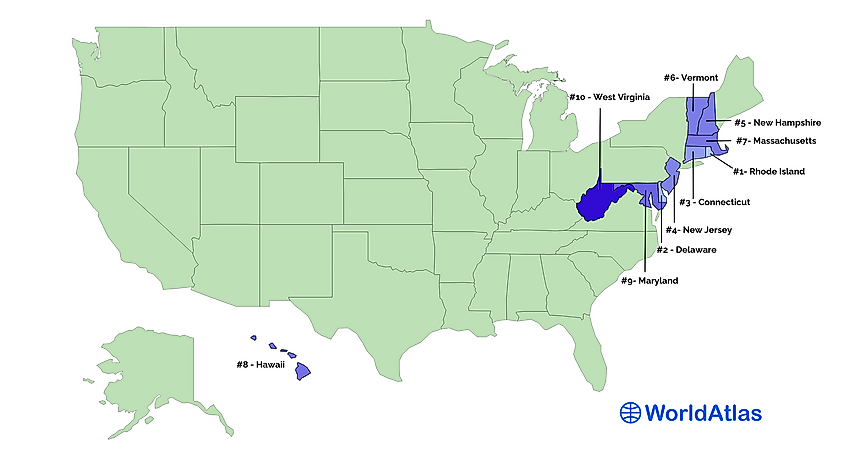
1. Rhode Island - 1,545 mi²
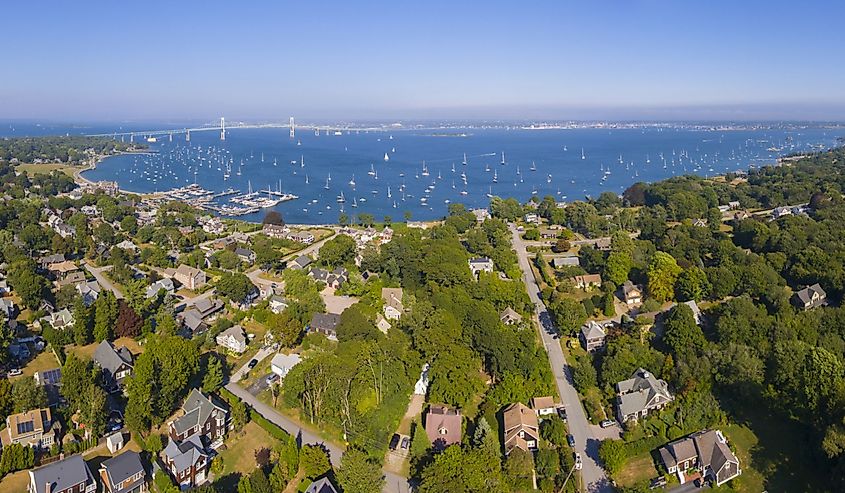

Rhode Island, the smallest of all 50 states in the US, covers an area of just 1,214 square miles and is home to over 1 million people. Its borders were initially set out in 1636 by a group of settlers from Massachusetts and Plymouth colonies who acquired the land from the Narragansett Indians. The earliest settlement was at Providence, which has since become its capital city. Although small, Rhode Island has many beautiful landscapes and cultural landmarks, making it a popular tourist destination. It also has a booming economy based on tourism, manufacturing, technology, education, and health care services. Despite its small size, Rhode Island has achieved much throughout history and stands proud as one of the original 13 American colonies.
Rhode Island's most defining physical feature is Narragansett Bay, which covers almost 14% of the state's total area. Narragansett Bay is a large estuary and part of the larger Atlantic Ocean drainage basin. The bay's geology is composed of two distinct formations: an outer ridge that creates an embayment around inner mud flats and sandflats. The ridge is composed chiefly of granite and gneiss bedrock and was created during the Quaternary glaciation period, resulting in a series of hilly ridges that either drain into or run alongside the main bay body. The sediment deposited from this glacial activity accumulates within the bay's estuarine environment, forming mud flats and sandbars inside and outside the central Narragansett Bay area. In addition, the bay experiences both natural and human-caused erosion, leading to continual changes in its physical geography over time.
2. Delaware - 2,489 mi²
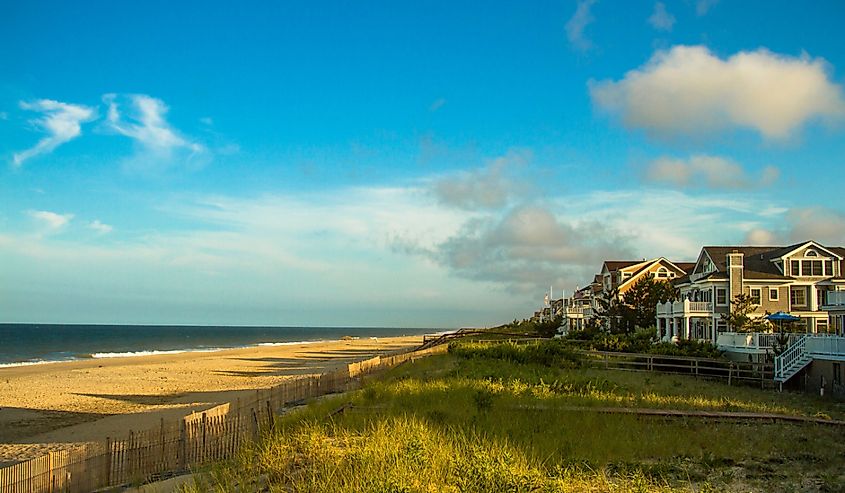

Measuring just 2,489 square miles and located on the United States East Coast, Delaware is the second smallest state after Rhode Island. Delaware was one of the original 13 colonies that declared independence from Great Britain during the American Revolution and is known as "The First State." It received its borders when the U.S. Congress passed the Treaty of Paris in 1783, officially recognizing US independence from Britain and setting boundaries between states. Today, Delaware shares borders with Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Maryland; its coast boasts some of the most beautiful beaches on America's east coast.
Acting as the border between New Jersey and Delaware, the 783.8 square mile Delaware Bay is a vital estuary supporting a variety of wildlife and habitats, including oysters, crabs, fish, eelgrass beds, and migratory waterfowl. The bay serves as a nursery for many species of fish and shellfish, allowing the population to grow. Additionally, it provides recreational activities such as fishing and boating. The bay also serves an essential role in helping protect the land from storm surge flooding and coastal erosion. It also helps to moderate regional climate by absorbing energy from the sun and heat from cities nearby.
3. Connecticut - 5,543 mi²

Connecticut is the third smallest state in the United States regarding the land area, with just 5,543 square miles. It has an average width of 90 miles and a length of 50 miles. The Connecticut Colony was founded by Thomas Hooker in 1636 and was one of the original 13 colonies that formed the United States. Initially, its borders extended from the Saybrook Colony at the mouth of the Connecticut River to present-day Rhode Island. Further expansion came when eastern parts of New York and parts of Massachusetts joined during colonial times. The border between Connecticut and Rhode Island was finalized in 1703 after much dispute over the interpretation of charter rights and survey measurements; it remains virtually unchanged today.
Pachaug State Forest is the largest state forest in Connecticut, covering more than 26,000 acres of wooded landscapes. Located on the border of Rhode Island and Connecticut, the forest's ancient woodland preserves a rich land use history that dates back to colonial times. The diverse ecology includes hardwood forests, wetlands, grasslands, shrublands, and many different species of birds, mammals, and reptiles. Visitors frequently explore trails leading through the gentle hills and valleys and enjoy recreational activities such as camping, hunting, and fishing. Boating is also available in many areas within the forest. There are several hiking loops around ponds with scenic overlooks as well as longer trails providing access to remote backcountry sites.
4. New Jersey - 8,723 mi²

New Jersey is the fourth-smallest state in the United States at 8,722 square miles. It is bordered to the north by New York, east by the Atlantic Ocean, south by Delaware, and west by Pennsylvania. Its borders have been shaped since its first settlements in 1664 when the Dutch and English crowns divided land on the east coast. The original boundaries were determined using geography, including rivers, lakes, oceans, and mountains. Through centuries of disagreements between states over land ownership and shifting political boundaries, modern-day borders around New Jersey were resolved in 1787.
The notable Wharton State Forest is a protected area of woodlands in the Pine Barrens region of southern New Jersey. Comprising over 122,000 acres, it is the largest state forest in New Jersey. Most of the land consists of pine forests, freshwater lakes, and streams, Atlantic white cedar swamps, and cranberry bogs. Wildlife inhabiting the forest includes white-tailed deer, foxes, mink, muskie, and wild turkey. Despite New Jersey's small size, Wharton State Forest and the adjacent reserves prove that the community wishes to protect the state from overdevelopment.
5. New Hampshire - 9,349 mi²

New Hampshire is the fifth-smallest state in the U.S., covering an area of 9,349 square miles. Forests and mountain ranges cover nearly two-thirds of New Hampshire's land. More than half of its land area is part of the White Mountain National Forest.
New Hampshire's borders date to 1741 when King George II granted its charter: surveyors determined the boundaries stated in the charter, which stretched from Black Point in Cape Ann to the Connecticut River's northern border. It defined an area that stretched along multiple rivers, such as Merrimack and Pemigewasset Rivers, as well as Lakes Winnipesaukee and Sunapee. This charter remains unchanged today and still stands as New Hampshire's current state borders, although a few changes have occurred since then, such as adjustments to Massachusetts' border.
White Mountain National Forest, found in the Eastern region of New Hampshire, is a national forest established in 1918 and comprising over 800,000 acres of land. This diverse landscape features forests, valleys, hills, and streams, providing habitats for many species of flora and fauna. In addition to its natural beauty, the White Mountain National Forest is rich with hiking trails and campgrounds that offer a unique outdoor experience. Visitors can also enjoy fishing in the fast-flowing streams or skiing at nearby ski resorts. The White Mountain National Forest is an important asset to the people of New Hampshire due to its recreational opportunities and role in preserving biodiversity and natural resources.
6. Vermont - 9,616 mi²

Vermont is the 6th smallest state in the United States, covering an area of only 9,622 square miles. It shares borders with New York to the west, Massachusetts to the south and east, Canada to the north, and New Hampshire to the east. Vermont received its present-day borders in 1777 when it declared independence from Britain during the American Revolutionary War. It joined the Union as part of a series of states that made up the original 13 colonies, along with Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New Jersey.
Nestled in the northeastern corner of Vermont, Lake Champlain is an expansive body of water comprised of 435 square miles of freshwater. One of the oldest and longest lakes in North America, it is home to a diverse ecosystem that includes over 80 species of fish and 125 species of birds. Its crystal-clear waters enable visitors to enjoy swimming, fishing, kayaking, and sailing. In addition to its natural beauty, the lake is steeped in history, having played a significant role during the French and Indian War and the American Revolution. Bordered by villages and magnificent mountains, the lake is a testament to the scale of even the smallest states in the U.S.
7. Massachusetts - 10,554 mi²
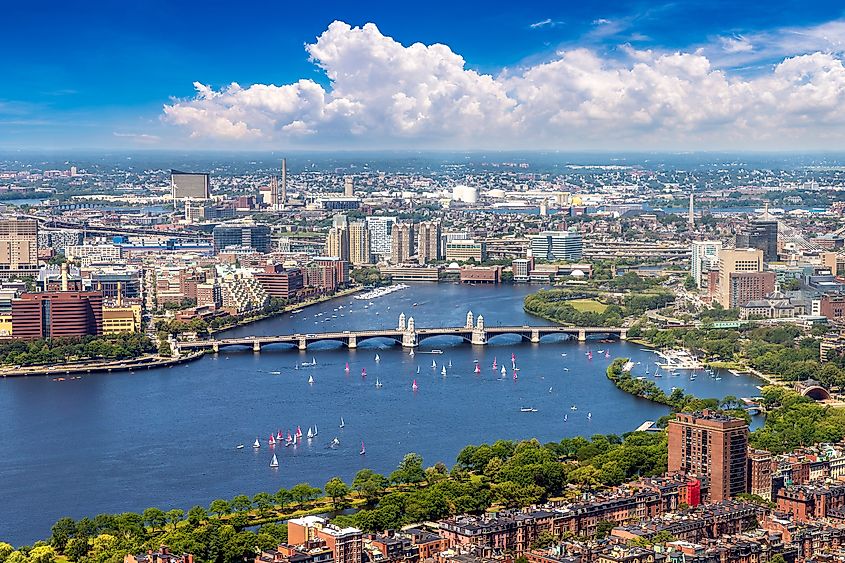

Massachusetts is the seventh smallest state in the United States, with an area of 10,565 square miles. It is bordered by Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south, New Hampshire and Vermont to the north, New York to the west, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. The borders were established in 1643 when Plymouth Colony joined forces with Massachusetts Bay Colony and other colonies that eventually became part of what is currently Rhode Island and parts of Connecticut. This development resulted in a border more or less in line with today's borders. However, in 1820 the entire state of Maine separated from Massachusetts; if that had not happened, Massachusetts would be 35,285 square miles larger.
Despite that split, the state retains remarkable landforms like Cape Cod, a peninsula on its southeastern coast. The Atlantic Ocean surrounds the cape to the east and Buzzards Bay to the west. The area is known for its beaches, lighthouses, cranberry bogs, and vibrant maritime history. Cape Cod's culture has been shaped over many centuries of fishing, whaling, and shipbuilding industries, as well as its popularity as a summer resort destination. Its moderate summer climate, ideal for recreational activities such as swimming, sailing, and beach-going, draw visitors from around the world.
8. Hawaii - 10,932 mi²
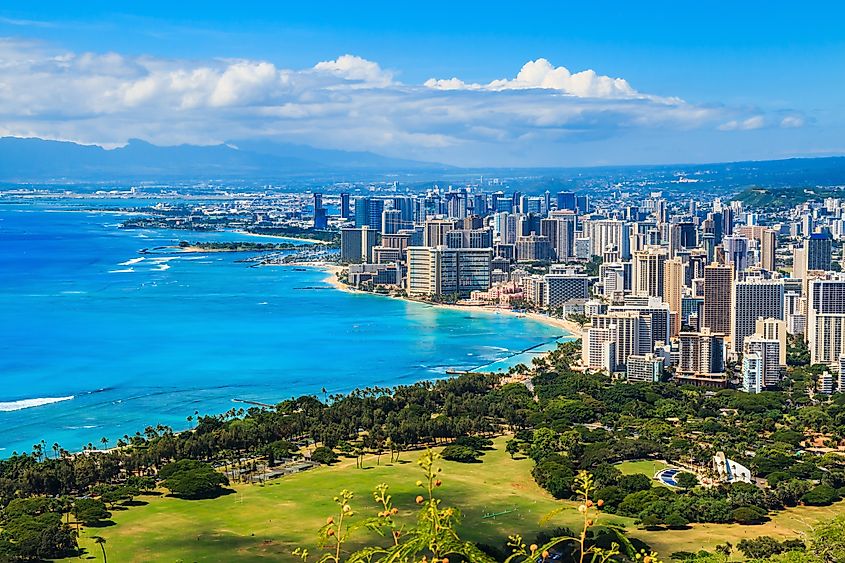

At 10,932 square miles, Hawaii is the eighth-smallest U.S. state. The islands that make up this tropical paradise stretch more than 1,500 miles across the Pacific Ocean. Hawaii's borders have always been defined by geography, with its boundaries set by the U.S. Congress in 1898 when it became a U.S. territory. The borders were later confirmed by Congress in 1959 when Hawaii became a state. Hawaii has grown significantly since then; for example, two islands that make up the archipelago—Midway Atoll and Palmyra Atoll—were annexed and are now part of the state.The landform that stands out the most is Mauna Loa, an active shield volcano located in the Hawaiian Islands. With a height of more than 13,600 feet above sea level, it is the largest mountain in the world measured from its base on the sea floor. It covers approximately 1.900 square miles and half of Hawaii (Big) Island's landmass. Mauna Loa has been erupting for about 700,000 years and is one of Earth's most active volcanoes. Its last eruptions occurred in 2022 and 1984 and caused widespread disruption to Hawaii Island's agriculture, transportation, and infrastructure.
9. Maryland - 12,406 mi²
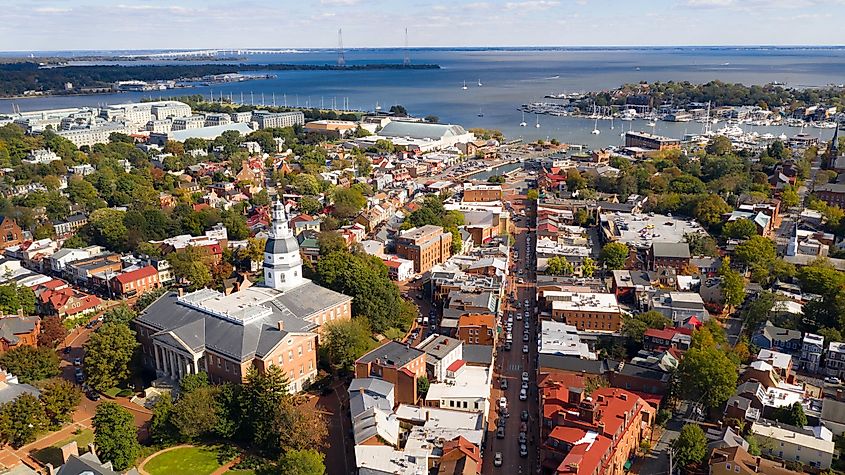

The state of Maryland is the ninth-smallest in the United States, spanning 12,407 square miles. Its borders were a compromise between its original colonies, Maryland and Virginia. Maryland was granted its southern boundary at the Potomac River, while Virginia was named ruler of the land currently known as West Virginia. King Charles I set out this border in a 1632 charter. In addition to this main boundary line, Maryland's coastal borders were also drawn up by the royal proclamation in 1763. As a result, the Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries form part of Maryland's Atlantic borders, now recognized as the most substantial in length among all U.S. states.
At the heart of this small state is the Chesapeake Bay, an integral part of Maryland's distinct geography and ecology. Fed by the Susquehanna River and other tributaries, the bay's unique composition provides a habitat for myriad aquatic species. It serves as a center of commercial activity due to its natural abundance. In addition, its shallow waters are nourished by nutrients entrapped by the bay's numerous wetlands, contributing to its popularity among water enthusiasts. Chesapeake Bay is both an important cultural icon and core ecosystem for Maryland because of its diverse wildlife, expansive shoreline, and various recreational opportunities.
10. West Virginia - 24,230 mi²
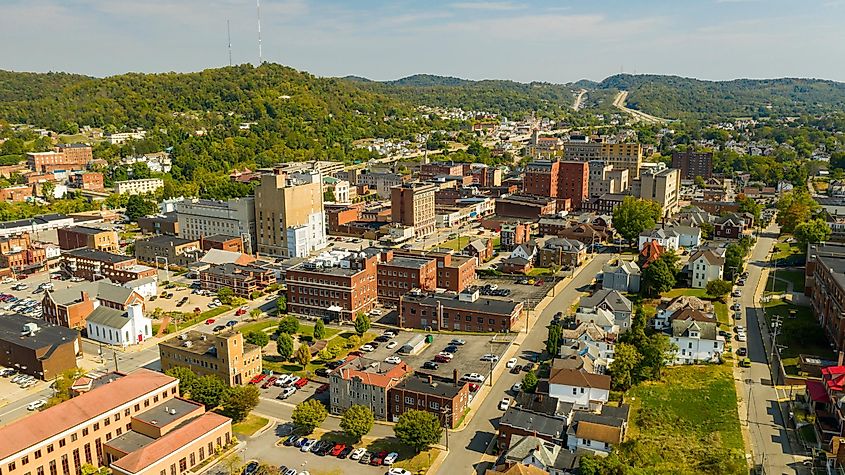

West Virginia is the 40th largest state in the United States, covering an area of 24,230 square miles. It spreads over several counties and borders six other states: Kentucky, Ohio, Maryland, Pennsylvania, and Virginia. During the American Civil War, Union and Confederate disagreements carved West Virginia out of the western part of Virginia. After the War ended in 1865, a new state constitution was drafted and accepted by Congress. The borders were finalized in 1866 when Congress passed a bill making West Virginia its own state.
The 200-mile Allegheny Mountain stretch in West Virginia is a pristine example of Appalachian Range geology, renowned for its robust and often rugged landscape. Characterized by steep inclines, deep gorges, and coniferous forests, the region is a natural marvel. The highest peak in the range is Spruce Knob, which stands 4863 feet above sea level. Many of the streams within the Allegheny Mountains are home to some of the most diverse fish populations in the Appalachian region. In addition to its rich aquatic life, the range hosts a wide array of mammals, including bears, deer, foxes, and raccoons, and majestic birds of prey such as hawks and eagles. Its abundance of flora stretches far beyond trees, with numerous ferns, shrubs, and wildflowers contributing to West Virginia's entire ecosystem.