10 Most Long-Lived Empires In History
In the history of humankind, there have been many great empires. Some rose quickly to prominence, and others took centuries to expand before collapsing. Some fell due to natural disasters, and others disappeared suddenly for unknown reasons. Regardless many vanished completely, leaving little evidence of their existence other than the rare archaeological finds or written accounts. Many factors contribute to an empire's longevity, such as its ability to adapt and expand economically and territorially, its political structure, a stable succession of rulers, and even good luck. The famous examples we know today all had something in common: they were all long-lived empires! So without further ado, here are 10 of the longest-lived empires in history.
- Byzantine Empire
- Holy Roman Empire
- Zhou Empire
- Ethiopian Empire
- Carthaginian Empire
- Khmer Empire
- Ottoman Empire
- Roman Empire
- Parthian Empire
- Han Empire
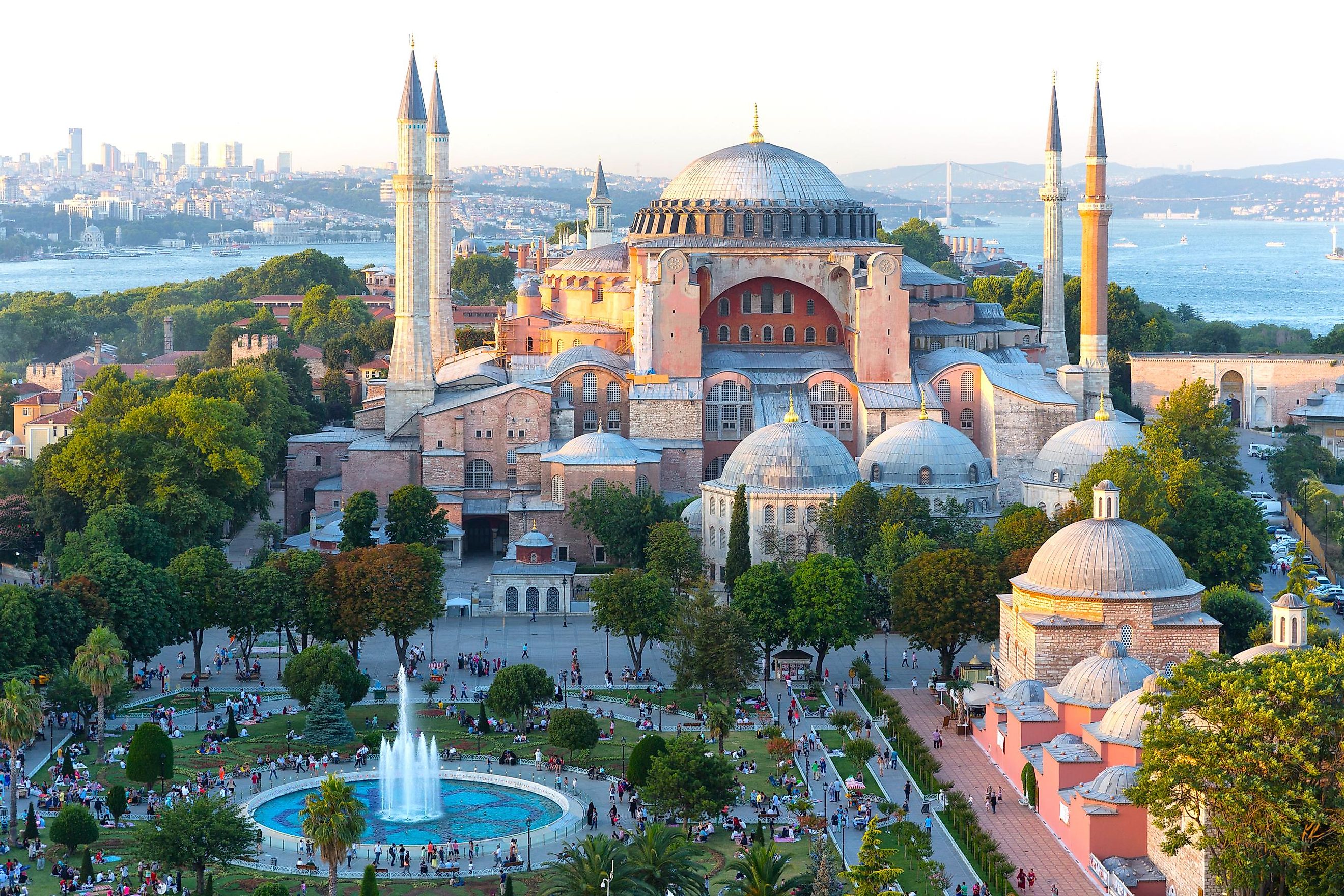
1. Byzantine Empire (330 - 1453 A.D.); ~ 1123 years
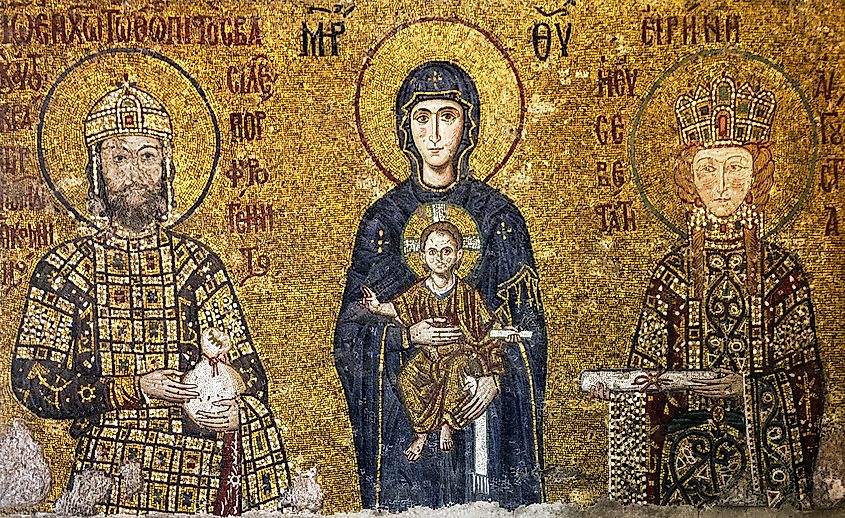

The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, traces its beginnings to the year 330 A.D. when Emperor Constantine split the Roman Empire into two parts, western and eastern. Historians refer to the eastern half as the Byzantine Empire, which remained a dominant force throughout Europe, lasting even until the middle ages. The Byzantine Empire continued until 1453, when the city of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, was finally lost to the Ottoman Turks. In total, the Byzantine Empire ruled for 1123 years.
2. Holy Roman Empire (800 - 1806 A.D.); ~ 1006 years
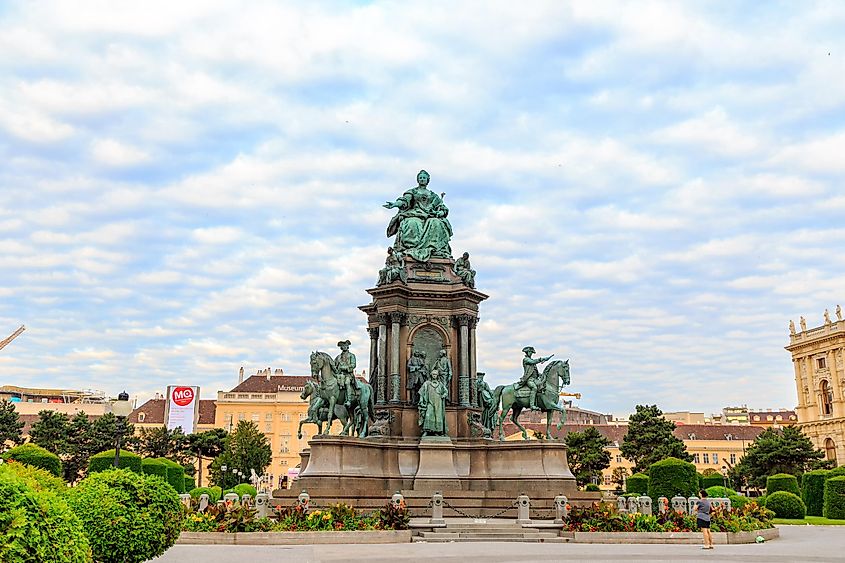

The Holy Roman Empire is traditionally believed to have been established by Charlemagne in 800 A.D. It ruled over much of western and central Europe from the 9th to the 19th century until its dissolution in 1806, during the Napoleonic wars. However, the Holy Roman Empire wasn't unified in the same way that many of the other empires were. It was more of a collection of sovereign nations existing together in a loosely defined alliance. The glue that held the empire together was the Catholic Church which had the authority to name the emperor. In total, the Holy Roman Empire lasted 1006 years.
3. Zhou Empire (1046 - 256 BC); ~ 790 years
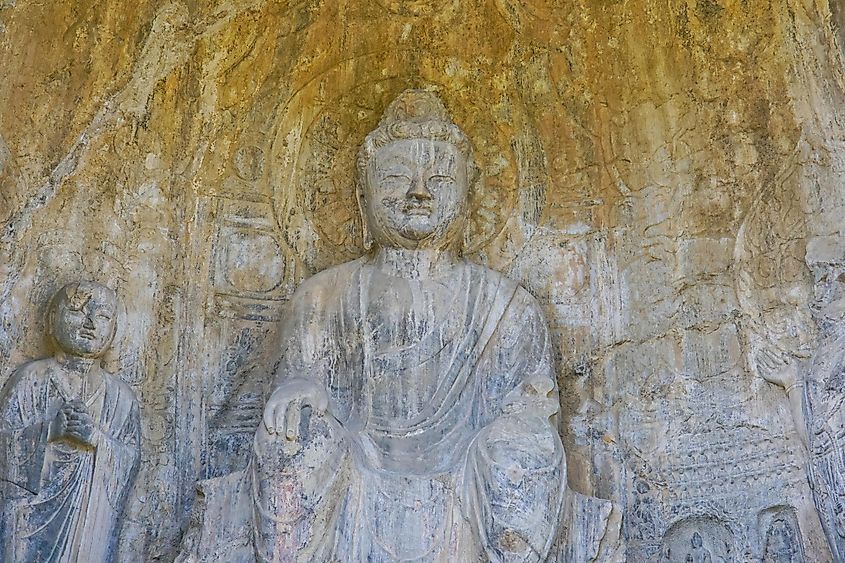

The Zhou Empire was among the most significant of the early Chinese dynasties and was also the longest-lasting in China's history. It can be separated into two periods, Western Zhou (1046-771 BC) and Eastern Zhou (771-256 BC). However, a little over 800 years later, the Zhou Empire began to lose control, and the many states that made up the empire began going to war. At this point, the end was imminent. Finally, the Qin Dynasty rose to power, bringing the Zhou Empire to a dramatic end. In total, the Zhou Empire lasted 790 years.
4. Ethiopian Empire (1270 - 1974 A.D.); ~ 704 years
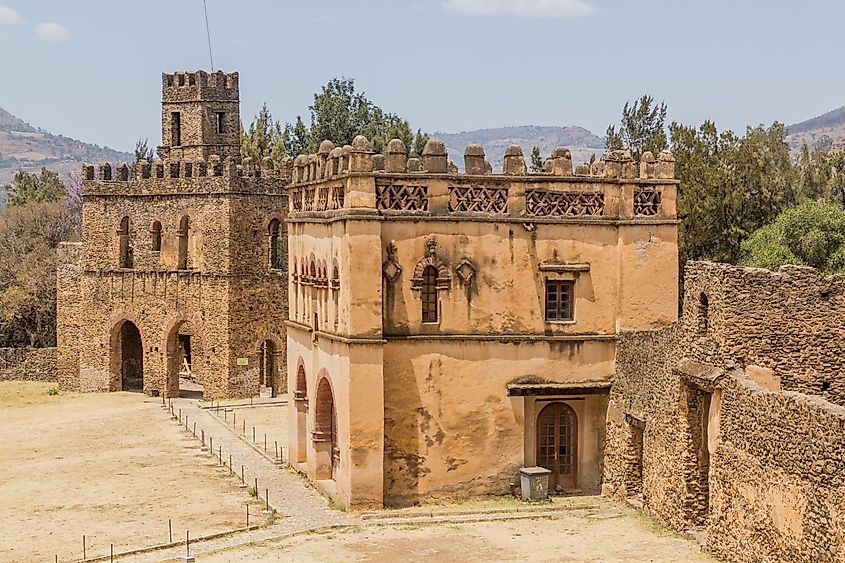

The Ethiopian Empire, also referred to as the Abyssinia Empire by historians, was located in what is now Ethiopia. This long-lasting empire existed from approximately 1270 until 1974, when the monarchy was overthrown in a coup d’état. This powerful African empire ruled for centuries, controlling a large territorial state that gave access to the rich trading routes in the Middle East and India. The Eritrean war for independence was the cause of related events that led to the end of the empire in 1974. In total, the Ethiopian Empire lasted 704 years.
5. Carthaginian Empire (814-146 BC); ~ 668 years
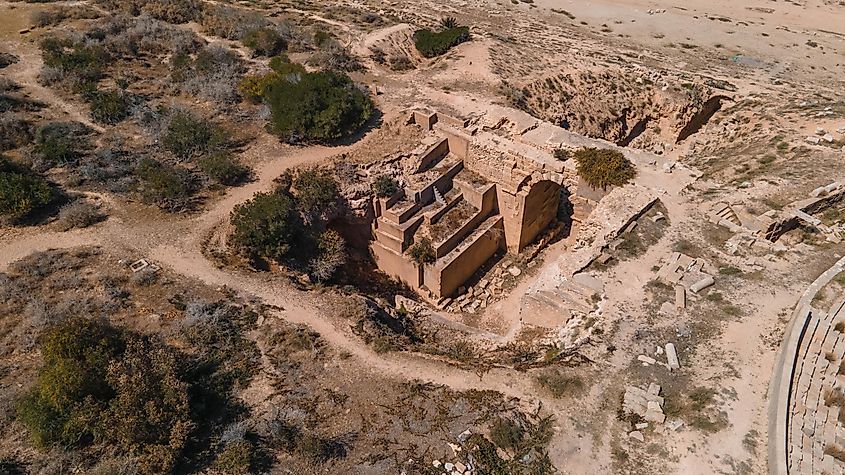

The Carthaginian Empire was based out of the city of Carthage, a settlement in modern-day Tunisia. At its height, in the fourth century B.C., Carthage was one of the largest metropolises in the world, and the center of the Carthaginian Empire, a major power in the ancient world that dominated the western Mediterranean. After a long conflict with the emerging Roman Republic, known as the Punic Wars (264-146), Rome finally ended the Carthaginian Empire. In total, the Carthaginian Empire lasted 668 years.
6. Khmer Empire (802 - 1431 A.D.); ~ 629 years
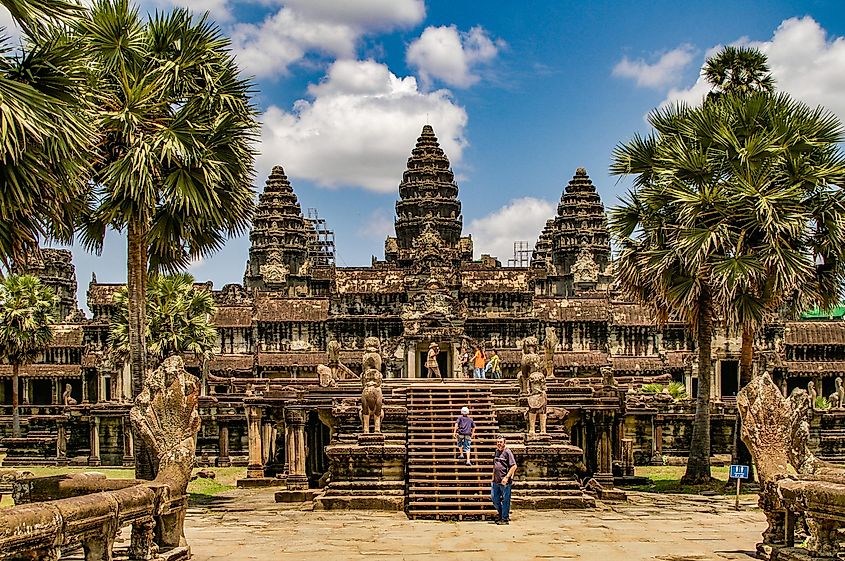

The Khmer empire hailed from what is now Cambodia and was the largest continuous empire in Southeast Asia. While the Khmer Empire was in its formation, it relied heavily on Java as a trade partner. The Khmer Empire also formed alliances with the Srivijaya Empire, which was located on the empire's southern border. The Khmer Empire had its capital in the city of Angkor until the Thai armies conquered it. After losing the capital to Thai invaders, the Khmer Empire relocated its capital to the city of Phnom Penh, which eventually became an important trade center due to its location on the Mekong River. In total, the Khmer Empire lasted for 600 years until overspending and conflict within the ruling family led to its collapse. In total, the Khmer Empire lasted 629 years.
7. Ottoman Empire (1299 - 1922 A.D); ~ 623 years
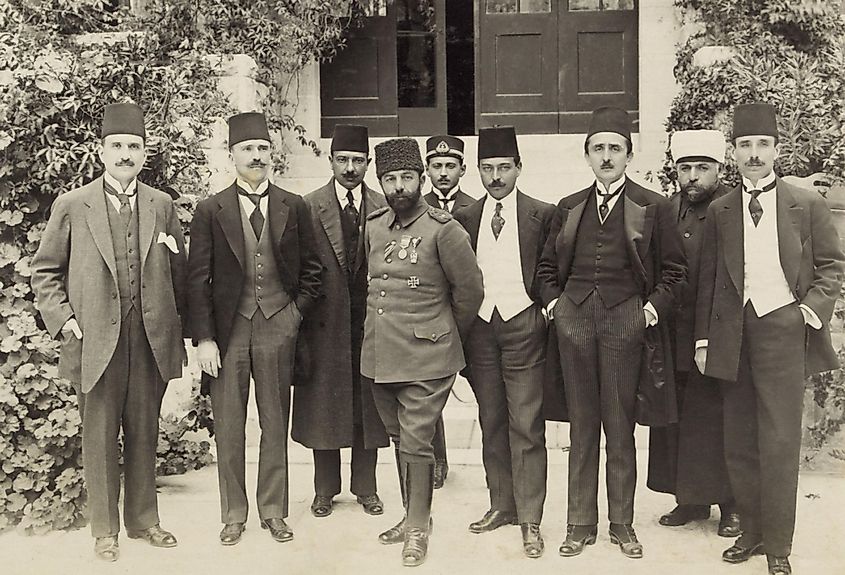

The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the fall of Constantinople in 1453. Under the leadership of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire was at the highest peak of its power and prosperity. The Ottomans, one of the greatest empires in history, ruled for more than 600 years before its destruction on the battlefields of World War I. In total, the Ottman Empire lasted 623 years.
8. Roman Empire (27 B.C. - 476 A.D.); ~ 503 years

The Roman Empire started in 27 B.C and dominated as a world power until 476 A.D. The Roman Empire was unmatched in its military. Indeed, civil war and not foreign armies finally caused the implosion of the Roman Empire. This vast empire that spanned as far as Europe to the Middle East was undone from within. As the empire expanded, it was simply unable to support the weight of its success. By the early first century A.D, this hugely successful empire spanned three continents, including Asia Minor, northern Africa, and most of Europe. By 400 A.D., the cracks in this struggling empire began to be noticed, and in 476 A.D, the unthinkable happened. Rome fell, ending the Roman Empire. In total, the Roman Empire lasted 503 years.
9. Parthian Empire (247 B.C. - 224 A.D.) - 471 years

The Parthian Empire, also referred to as the Arsacid Empire by historians, lasted from 247 BC to 224 AD creating a large empire that stretched from the Mediterranean in the west to India and China in the east. The Parthian Empire was known for its unique and extremely successful fighting style. Indeed, the vast areas they conquered allowed them to assimilate the cultures and advancements of different nations. Its immense territory led to an inevitable civil war. And finally, in 224 A.D., the Persis revolted against the Parthian Empire and killed their leader, ending the Parthian Empire. In total, the Parthian Empire lasted 471 years.
10. Han Empire (206 B.C. - 220 A.D.) - 426 years

The Han Empire came to power in 206 BC, abruptly ending the chaos that followed the collapse of the Qin dynasty. The Han Empire was the second imperial dynasty of China and ruled for more than 400 years, with the only exception being a brief period between 9 and 23 A.D. when a powerful leader named Wang Mang seized the throne. After Mang's short insurrection was quelled, the Han Dynasty continued without any further interruption. The Han Empire is responsible for many achievements and inventions. The Han Empire is credited with inventing paper, water clocks, and sundials, to name a few. However, despite its contributions, the empire eventually fell in 220 A.D because of economic collapse fueled by weak leadership. In total, the Han Empire lasted for 426 years.
All these long-lived empires left behind a legacy that impacts not only the present-day society and culture of their area of rule but also of places far away. Their achievements and their losses continue to teach valuable lessons to people worldwide. Most importantly, the fact that these once-powerful empires all had their fall reminds us that nothing lasts forever if not handled with wisdom.