How Many Countries Are There In Oceania?
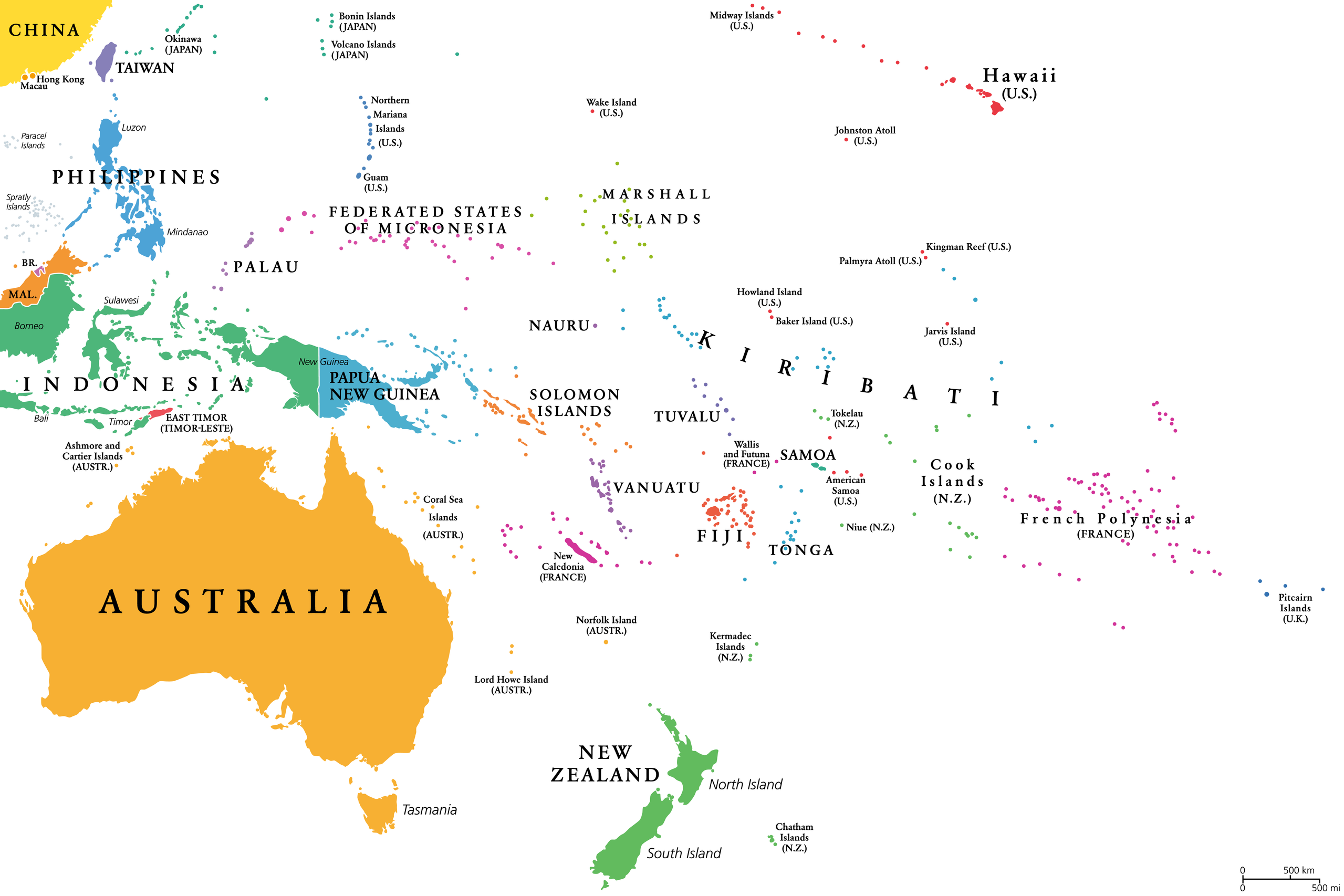
Although Oceania is the smallest continent, it is home to a surprising palette of creatures, traditions, and greenery. This region encompasses 14 countries, home to over 46 million people and more than 10,000 islands. The countries that constitute Oceania include Australia, Fiji, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Nauru, New Zealand, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, the Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu.
All 14 Countries Of Oceania
| Countries | Population 2024 | Land Area |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | 27,307,000 | 7,741,222 km² |
| Fiji | 900,300 | 18,274 km² |
| Kiribati | 126,700 | 811 km² |
| Marshall Islands | 39,700 | 181 km² |
| Micronesia | 105,400 | 702 km² |
| Nauru | 12,100 | 21 km² |
| New Zealand | 5,378,000 | 268,838 km² |
| Palau | 17,600 | 459 km² |
| Papua New Guinea | 13,620,000 | 462,840 km² |
| Samoa | 210,800 | 2,831 km² |
| Solomon Islands | 815,500 | 28,896 km² |
| Tonga | 99,900 | 747 km² |
| Tuvalu | 10,600 | 26 km² |
| Vanuatu | 332,600 | 12,189 km² |
Australia
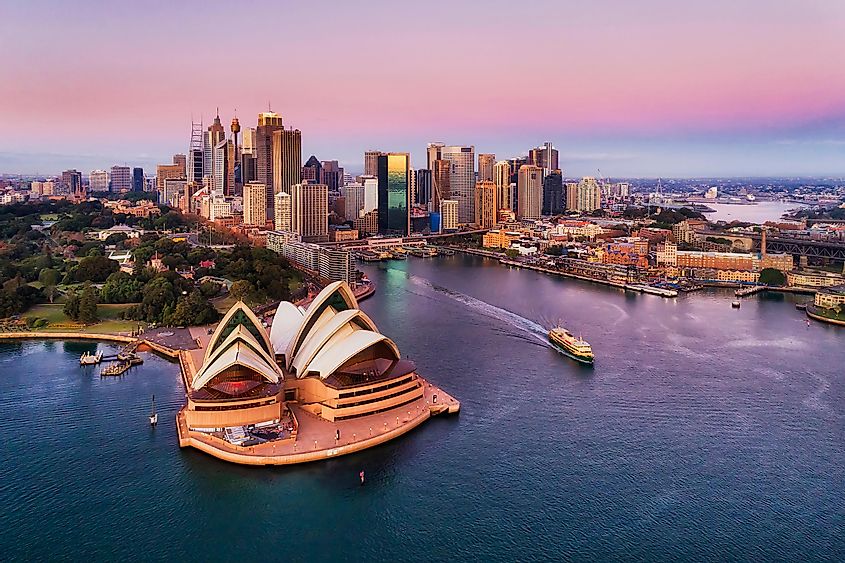

Australia, the biggest country in Oceania, is located south of Indonesia and Papua New Guinea between the Pacific and Indian Oceans. The capital is Canberra, while the most populous city is Sydney. Australia is also the most populous country in the continent, with 27.31 million residents.
Australia ranks among the most urbanized nations globally, with nearly 90% of its population residing in cities, predominantly near the coast. In stark contrast, the iconic Australian outback spans over 70% of the country and is characterized by its remote and sparsely populated expanse, encompassing extreme arid, tropical, and temperate climates.
Fiji

Fiji is an archipelago country in the South Pacific Ocean. It is about 2,100 kilometers north of Aukland, New Zealand. Fiji’s capital and most populous city is Suva, and the country has a population of approximately 900,300 people.
Roughly 300 islands and 540 islets compose the country of Fiji, although only 100 of the islands are actually inhabited. Fiji’s economy is one of the most developed among the Pacific Island countries. The island’s resources include gold, copper, timber, fish, offshore oil, and hydropower. Tourism also represents roughly 40% of GDP.
Kiribati

Kiribati is a country composed of multiple islands situated in the central Pacific. Its nearest neighbors are Tuvalu and Tokelau to the south and Nauru to the west. Tarawa is both the capital and most populous city, located on the Gilbert Islands.
Thirty-three islands form Kiribati, although only 20 of them are inhabited. In the 1960s, the British and United States used the island’s land for nuclear weapon testing. Today, fish farms, a large coconut plantation, and satellite telemetry stations occupy the land, supporting the economy. Kiribati, however, has the lowest GDP per capita in Oceania, making it the most impoverished country.
Marshall Islands

The Marshall Islands, in the Central Pacific Ocean, contains some of the easternmost islands in Micronesia. The country has a small population of just 39,700 people. Its capital and most populous city is Majuro.
The Marshall Islands include over 1,200 islands and islets, although only 24 are actually inhabited due to the rest offering poor living conditions, rain scarcity, or nuclear contamination from U.S. nuclear bomb tests in the 1940s and 1950s. Today, the service sector largely drives the economy through industries such as retail, restaurants, insurance, and banking.
Micronesia

Micronesia is an island country in the western Pacific Ocean. The country of Palau lies to the west and the Marshall Islands to the east. The capital of Micronesia is Palikir, located on the island of Pohnpei, while the most populous city is Weno, located on Chuuk Island.
607 islands compose the country of Micronesia, but only 65 are inhabited. Micronesia as a whole is very diverse culturally and linguistically. People speak Yapese on Yap Island, for example, while the residents of Chuuk speak Chuukese. Although the languages across the islands are distantly similar, they are generally not mutually intelligible.
Nauru

The island country of Nauru is located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, about 40 kilometers south of the Equator. The island of Banaba, part of Kiribati, is its closest neighbor at approximately 300 kilometers to the east. Nauru does not officially have a capital city, but its government offices are in the Yaren district.
Most residents in Nauru are indigenous Nauruans, and their official language is Nauruan. The country has a tropical climate and no rivers or streams, so residents must depend on water obtained from roof catchments and drinking water imported from ships.
New Zealand

The island country of New Zealand is situated in the South Pacific Ocean and is in the southwesternmost portion of Polynesia. It is over 1,600 kilometers southeast of Australia. The two main islands are the North Island and South Island. The country’s capital is Wellington, while Auckland is the most populous city. New Zealand has a total population of 5.38 million.
The service industry is the most important contributor to New Zealand’s economy, accounting for approximately two-thirds of GDP. It also has a significant wine sector, with Sauvignon Blanc, Pinot Noir, Pinot Gris, and Chardonnay representing four important varieties.
Palau

Palau is an archipelago country located in the western Pacific Ocean, with New Guinea neighboring 650 kilometers to the south and the Philippines 890 kilometers to the west. The capital of Palau is Melekeok, on Babelthuap island, while Koror is the most populous city and island.
Approximately 340 volcanic and coral islands compose Palau, but only nine are inhabited. One of Palau’s most prominent geographic features is Jellyfish Lake, a 400-meter-long by 30-meter-deep lake filled with approximately 5 million golden jellyfish, a subspecies unique to the lake.
Papua New Guinea
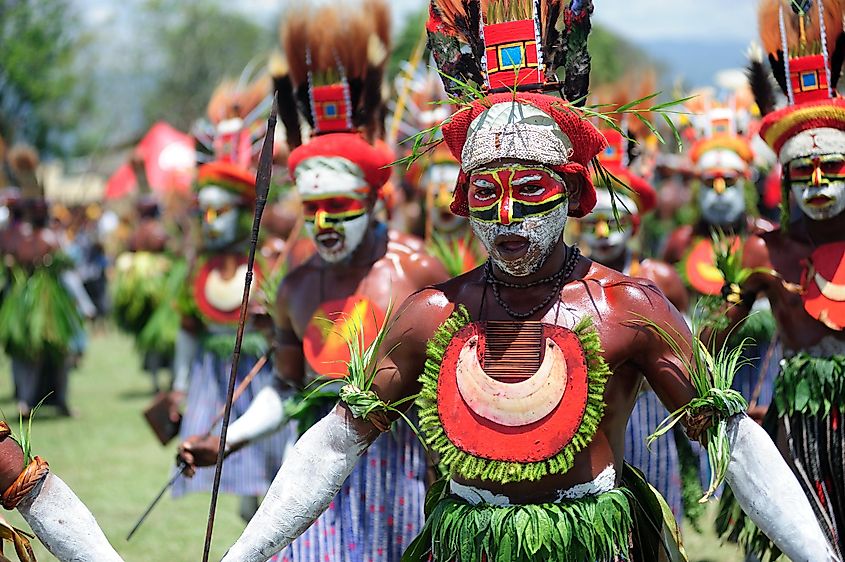

Papua New Guinea, an island nation in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, occupies the eastern half of New Guinea, with Indonesia covering the western half. The country also comprises several offshore islands. Papua New Guinea’s capital and most populous city is Port Moresby. The country’s total population is 13.62 million. Remarkably, the island is home to roughly 600 different tribes that speak a collection of over 800 languages.
Papua New Guinea is renowned for its incredible levels of biodiversity, including figs, orchids, false beech (Nothafagus), cassowaries, kangaroos, cuscus (a phalanger), and birds-of-paradise, butterflies, and more. The government has implemented conservation measures to protect and maintain the country’s biodiversity.
Samoa

Samoa is the westernmost island country in Polynesia, located in the southcentral Pacific Ocean. New Zealand lies about 2,900 kilometers to the southwest. Apia is the capital and most populous city in the country. Samoa has a total population of approximately 210,800 people.
Samoa boasts a tropical, humid climate with abundant waterfalls and lush vegetation, including cloud forests and inland rainforests. The coast is now largely covered by coconut groves and taro plantations. The island is home to at least 16 species of indigenous birds, such as the tooth-billed pigeon, and also hosts the native flying fox, which is currently endangered.
Solomon Islands

The Solomon Islands are located in the southwestern Pacific, consisting of coral atolls and two chains of volcanic islands. Papua New Guinea, to the west, and Vanuatu, to the southeast, are the country’s nearest neighbors. Honiara is both the capital and the most populous city.
Over 80% of Solomon Islands residents live in rural areas, relying on pig raising, fishing, and subsistence gardening. However, the country is rapidly urbanizing, with an urbanization rate approaching 4%. Palm oil and copra are two of the country’s significant cash crops as well.
Tonga

The island country of Tonga is located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. Fiji neighbors it to the west and Samoa to the north. Tonga’s capital and most populous city is Nukuʿalofa. The total population of the country is approximately 99,900.
While approximately 170 islands compose Tonga, only 36 are actually inhabited. The majority of the island’s population is of Polynesian descent, largely sharing ancestry and culture with Samoans and other Polynesian groups. Squash, bananas, coconuts, and vanilla beans are some of the principal cash crops.
Tuvalu

Tuvalu is located in the west-central Pacific, with Kiribati neighboring to the north and Fiji to the south. Vaiaku is the de facto capital, where the majority of government offices are found. Funafuti, however, is the most populous town. Tuvalu is the fourth smallest country in the world, with a land area of just 26 square kilometers. Nine tiny coral islands compose the country.
Tuvalu’s islands are very flat, most being just four to five meters above sea level. Rain catchments and wells are the only freshwater sources, as there are no rivers in the country. The Tuvaluan people are Polynesian, with their language, Tuvaluan, closely resembling Samoan.
Vanuatu

Vanuatu consists of a chain of islands situated in the southwestern Pacific. It is about 1,770 kilometers east of Australia and 800 kilometers west of Fiji. The country’s capital and largest city is Port Vila. Vanuatu has a total population of approximately 332,600 people.
80% of Vanuatu’s population works in the agricultural sector, ranging from subsistence farming to smallholder farming of cash crops. Copra, timber, beef, and cocoa are some of the most important cash crops in the country, and there is a fishing industry as well, although fish is not typically exported.
Conclusion
Oceania offers a remarkable variety of geological, cultural, and ecological diversity. The 14 countries in this region each boast unique characteristics, from Australia's urban centers and vast outback to Papua New Guinea's rich biodiversity. Understanding Oceania involves appreciating its varied ecosystems, economic activities, and cultural practices. This continent not only enriches our global heritage but also serves as a vital area for studying environmental conservation, sustainable development, and cultural preservation.