Mekong River
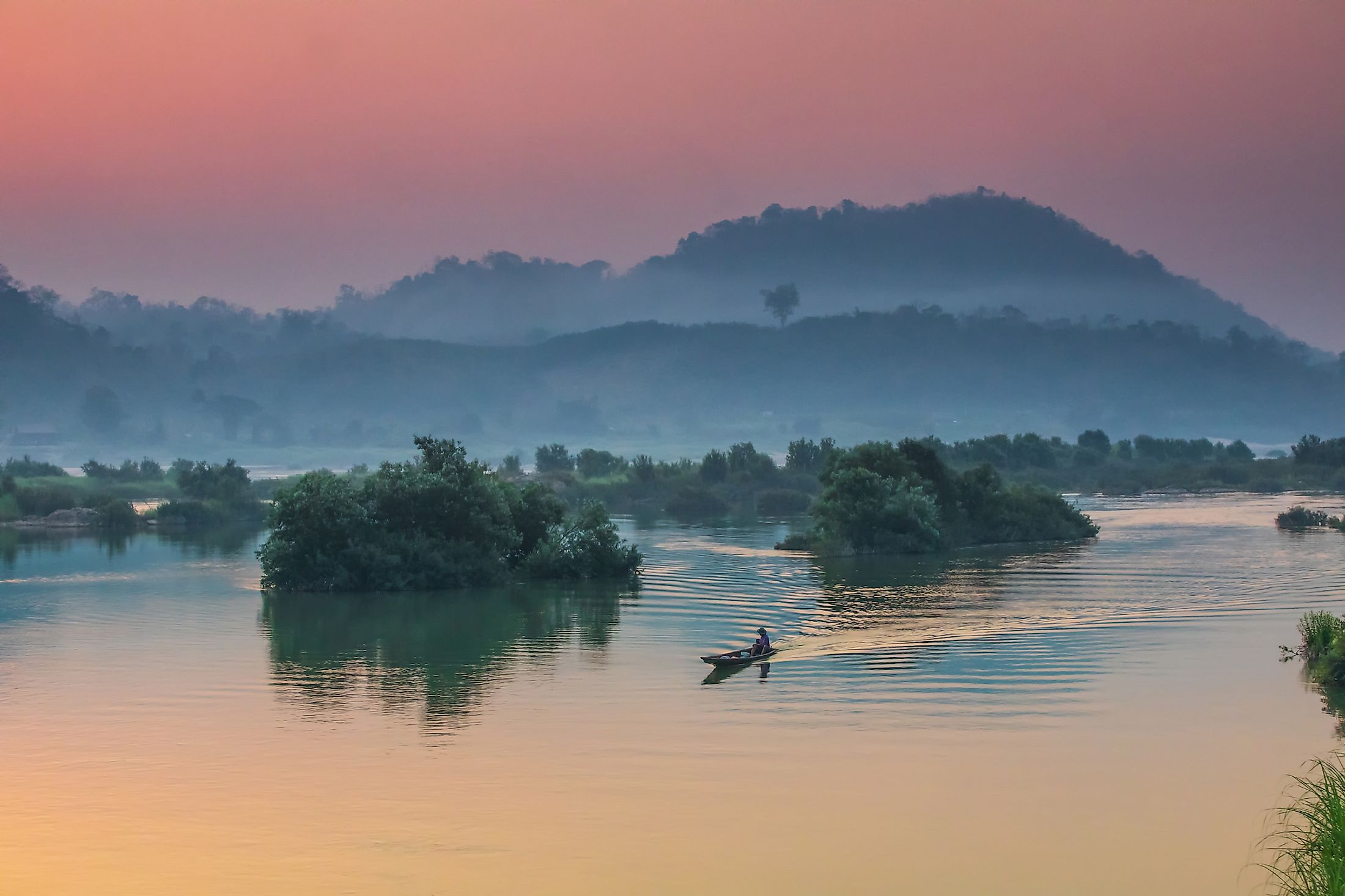
The Mekong River is the world’s 12th longest river covering close to 5,000 kilometers from its source in the Tibetan Plateau to the Mekong Delta. This transboundary river is Southeast Asia’s longest river and Asia’s 7th longest river. The river drains approximately 795,000 square kilometers and flows through six Asian countries; China, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Cambodia, where it is referred to by different names. It discharges 16,000 cubic meters of water per second or about 475 cubic kilometers annually. The Mekong Basin is home to about 65 million people, of which 80% live in the lower basin. The river is also rich in diversity, hosting about 800 fish species and over 20,000 plants.
Contents:
Name
The Mekong River is referred to by different names in different countries. In Laos and Thailand, it is known as “Mae Nam Khong,” whereas Mae Nam means “Mother of Waters” while Khong means “River.” The Vietnamese refer to the river as Song Tien Giang, while Cambodians refer to it as “Mekongk. In China, the Mekong River is called “Lancang Jiang” or “Lan-Tsang Chiang. The early European traders referred to the river as Cambodia River, May-Kiang River, and Mekon River.
River Course
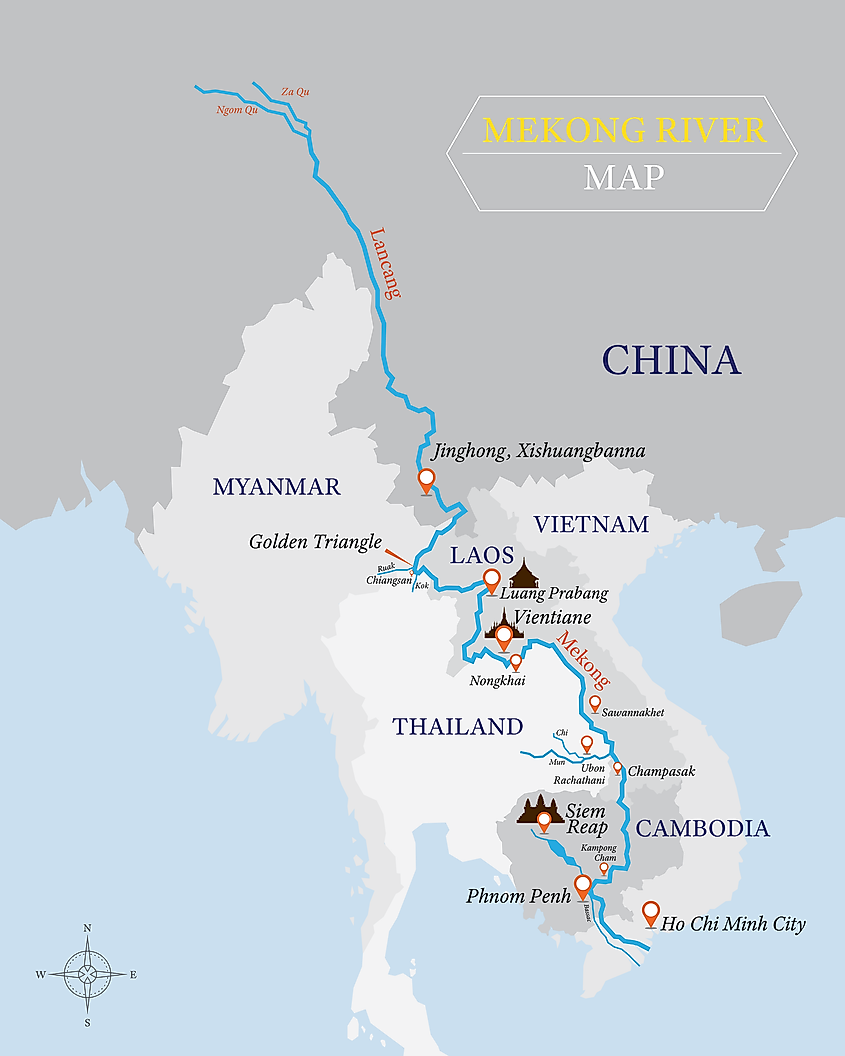
The Mekong River rises in China’s Southeastern province of Qinghai, specifically Za Qu, where it is referred Lancang. It originates from the Sanjianyuang in the Tibetan Plateau, with the area designated a national nature reserve to protect the headwaters of Yangtze, Yellow, and Mekong Rivers. From the Tibetan Plateau, the Mekong River passes through Tibet Autonomous’ eastern part to Yunnan Province’s southeastern section and the Three Parallel Rivers Area. The three Parallel Rivers Area is a UNESCO World Heritage Site with three drainage basins; the Mekong River sandwiched by Salween River on the west and Yangtze River on the east.
From the Yunnan Province, the Mekong River forms the international boundary between Myanmar and China, flowing for about 10 kilometers on that border before reaching the tripoint of Myanmar, China, and Laos. From here, it flows southwestwards and forms the Myanmar-Laos border for approximately 100 kilometers until it gets to a second tripoint known as the Golden Triangle (Laos, Myanmar, and Thailand), which is also its confluence with the Ruak River.

From the tripoint, the river flows southeastwards and form the border between Thailand and Laos then turns east into Laos, flowing for about 400 kilometers before forming the border with Thailand again, where it flows for about 850 kilometers. The river then turns souths and flows through Laos for the second time, passing through Pakse before flowing south and crossing into Cambodia. In Cambodia, the Mekong River is joined by Tonle Sap lake and the river system at Phnom Penh. When Mekong’s level is low, water Tonle Sap becomes its tributary, while when the river floods, it becomes Tonle Sap’s tributary.
Once the Mekong is joined by the Sap River, the Bassac River (Mekong’s first distributary) branches towards the west bank. Mekong (or eastern branch) and Bassac enter Vietnam shortly after, where they are respectively referred to as Tien and Hua Rivers. In Vietnam, Mekong (eastern branch)’s main distributaries are Ba Lai, My Tho, Co Chien, and Ham Luong Rivers.
Geography
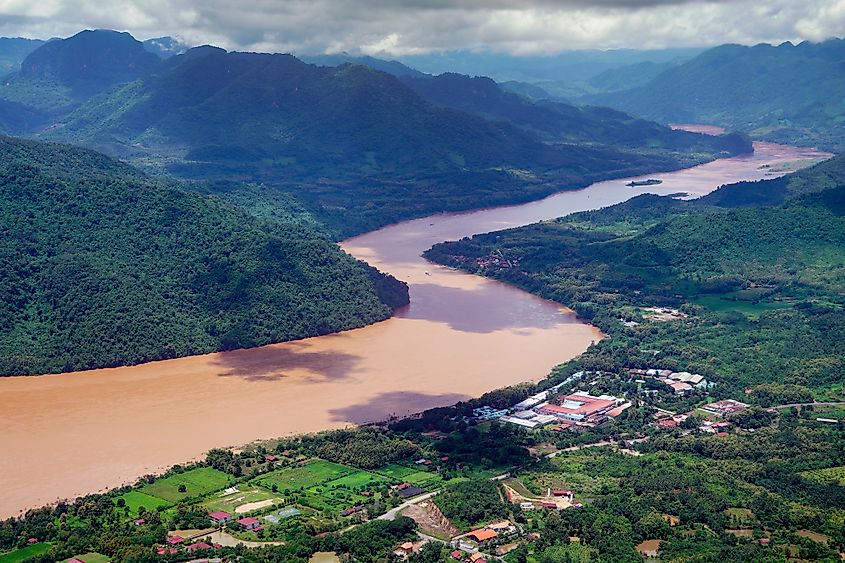

The Mekong River is Southeast Asia’s longest river, covering approximately 4,900 kilometers from its source in China’s Tibetan Plateau to its mouth in Vietnam’s Mekong Delta. It drains six countries with its drainage basin spanning 795,000 square kilometers. The Mekong River basin has diverse drainage patterns, topography, and geomorphology, with the river basin divided into upper and lower basins.
The source of Mekong, including its principal headwaters, the Za Qu River, originates from Tanggula Mountain’s northern slope. Several tributaries feed the Mekong throughout its course. The tributaries are classified into two groups; the right-bank tributaries draining the lower relief region and the left-bank tributaries draining high rainfall areas. The left-bank tributaries include Nam Ou, Tha, and Nam Khan, while the right-bank tributaries are Ruak, Kok, Tonle Sap, and Mun.
Drainage Basin
The Mekong River Basin is divided into two parts; upper and lower river basins. The upper basin comprises the Tibet area in China where the river is commonly referred to as Lancang River. It stretches about 2,200 kilometers, with the elevation dropping from 5,224 meters to 4,500 before joining the lower basin. The upper basin accounts for 24% of the basin’s total area (190,800 square kilometers) and contributes between 15 and 20% of the waters flowing into the Mekong River.
The Upper Mekong Basin comprises the Tibetan Plateau, Three Rivers Area, and Lancang Basin. The Tibetan Plateau stretches over 2.5 million square kilometers, of which 316 square kilometers form the Mekong River’s headwaters. The densely glaciated plateau, located 5,160 meters above sea level, is the source of the Mekong River. The Three Rivers Area is a mountainous region in China where the Mekong runs parallel to two other rivers; Yangtze and Salween. The Lancang Basin is a plateau and highland area in China located to the Three Rivers Area’s south, about 3,000 meters above sea level.
Lower Basin
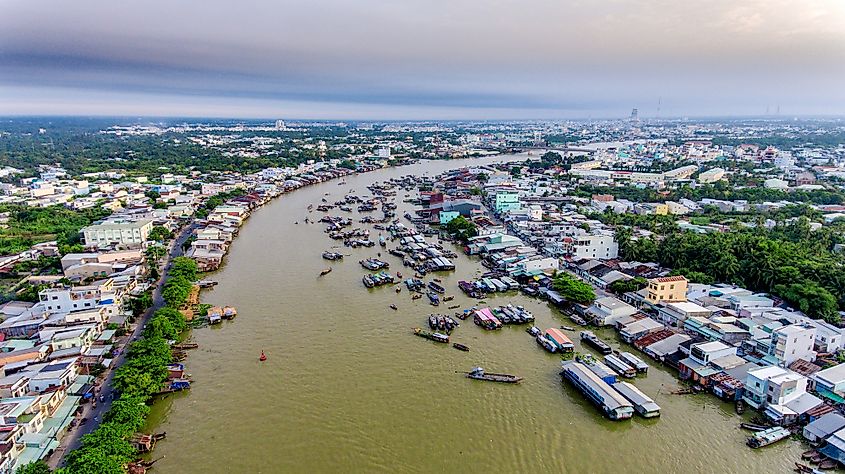

The Lower Mekong Basin stretches from Yunnan to the South China Sea, covering 571,000 square kilometers. It covers almost entire Cambodia and Laos, northeastern Thailand, and Vietnam’s southern tip. The basin is divided into four regions; the Northern Highlands, Khorat Plateau, Tonle Sap Basin, and the Great Lakes. The Northern Highlands cover northern Thailand, northeastern Myanmar, and northern Laos and have tributaries such as Nam Ou, Nam Ta, and Nam Khan. The Khorat Plateau is a vast plateau in northeastern Thailand where Mun and Songkhram Rivers join the Mekong River on the right bank. Tonle Sap basin is an alluvial plain located east of Khorat. At the southern end, the river breaks into different channels, with the central and western sections forming the Great Lake.
Natural Resources

The Mekong River Basin is characterized by vast climatic and geographic zones, resulting in abundant and diverse natural resources. Part of the basin falls within the Indo-Burma biodiversity hotspot, with the entire basin containing 16 ecoregions. Its biodiversity is only second to the Amazon River Basin and contains about 20,000 plant species, 1,200 birds, 430 mammals, 800 amphibians and reptiles, and 850 fish species. The Mekong is the river with the most large fish species, including giant freshwater stingrays, giant pangasius, Mekong giant catfish, and giant barb. Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve protects the river’s headwaters in Zadoi County, with the reserve also protecting headwaters of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers.