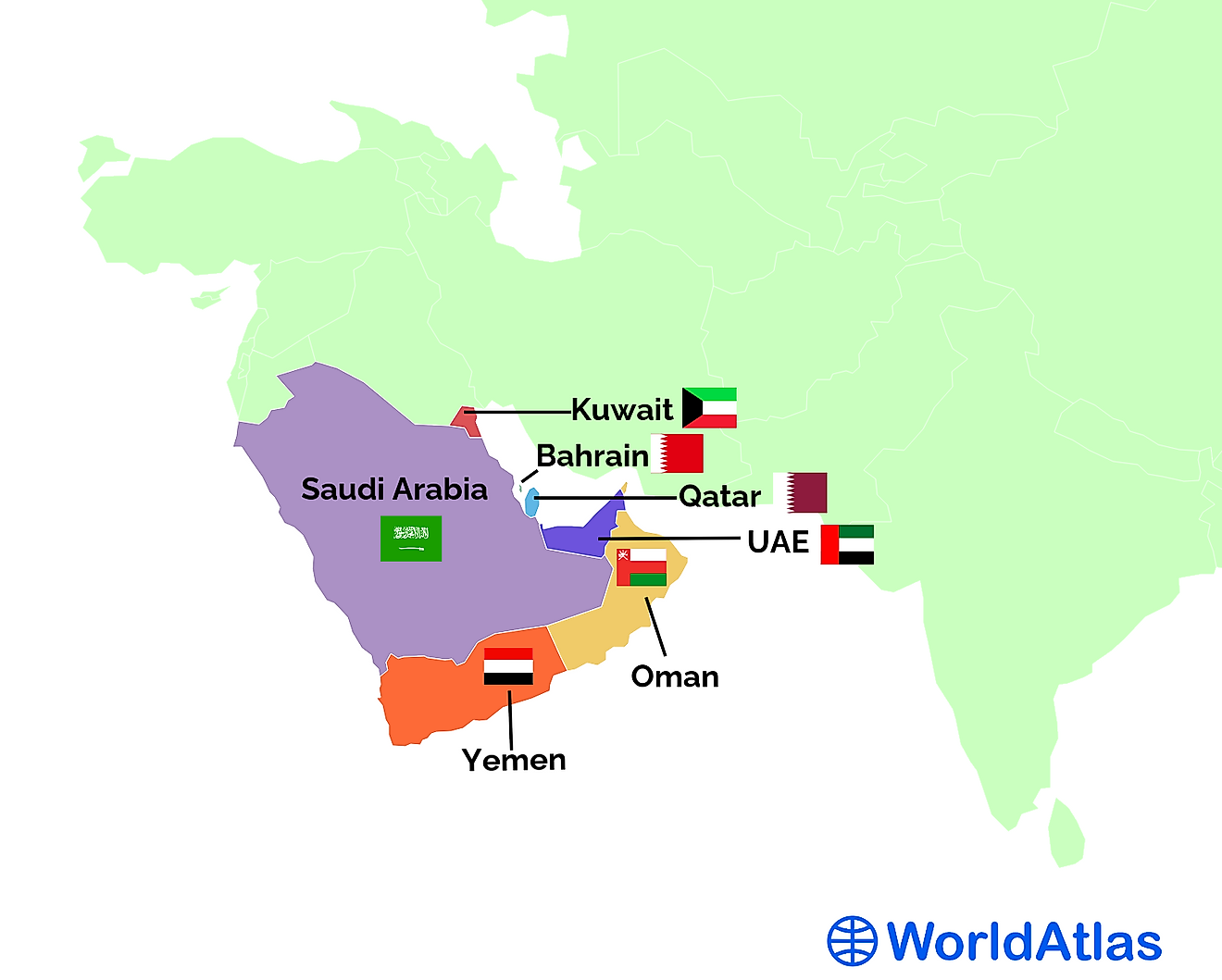
Arabian Peninsula Countries
- The Arabian Peninsula is located in Western Asia, also known as the Middle East.
- The Arabian Peninsula is the original territory of the Arab peoples.
- Islam's first and second holiest cities, Mecca and Medina, are located on the Arabian Peninsula.
- Saudi Arabia is the largest and most populous country on the Arabian Peninsula. Bahrain is the smallest and least populous.
The Arabian Peninsula is a large peninsula located in Western Asia, otherwise known as the Middle East. It is bordered to the north by Jordan and Iraq, to the west by the Red Sea, to the east by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, and to the south by the Gulf of Aden and the Arabian Sea. The Arabian Peninsula is the ancestral homeland of the Arab peoples. The peninsula consists of 7 countries, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Qatar, and Kuwait. In most of the countries on the Arabian Peninsula, oil and gas are the main drivers of the economy. In fact, almost a third of the entire world’s oil reserves are located in countries of the Arabian Peninsula. The peninsula also hosts important religious sites, as it is where Islam was founded.
Contents:
Bahrain

Bahrain is the smallest country of the Arabian Peninsula. Actually, Bahrain is not located on the peninsula, but on small islands that sit in the waters between the northwest coast of Qatar and the east coast of Saudi Arabia. Bahrain Island is the largest of the islands, and is the location of the country’s capital, Manama. Bahrain has been ruled by the al-Khalifah family since 1783. The country was a British protectorate before achieving full independence in 1971. Oil was discovered in the country in the 1930s, though in smaller quantities compared to the other countries of the Arabian Peninsula. Thus, the Bahraini government has put efforts into diversifying the economy. Bahrain’s population is about 1.7 million. While most of the country’s population adheres to Shiite Islam, the ruling family follows the Sunni branch of the religion. The Shiite majority has often complained of being marginalized by the ruling family.
Kuwait

Kuwait is a small country that lies at the western end of the Persian Gulf. In the late 18th and early 19th century, Kuwait was part of the Ottoman Empire. It was brought under British protection in 1897, and achieved independence in 1961. In 1990, Kuwait was invaded and occupied by Iraq, but was subsequently liberated by a U.S.-led international military coalition. As with most countries on the Arabian Peninsula, oil is the mainstay of the Kuwaiti economy. The population of Kuwait is approximately 4.3 million, 70% of whom are expatriates. Although Kuwait is economically advanced, it is still a conservative country by Western standards. In fact, up until 2006, women were not allowed to vote in parliamentary elections.
Oman

Oman is located on the southeast corner of the Arabian Peninsula. The current ruling dynasty of Oman, the Al-Saids, took power in 1749. In the 1950s, oil was discovered in the country. In 1970, Oman’s sultan was overthrown by his son, who set about instituting economic reforms and modernizing the country, which had previously seen little economic development. Oman continues to be ruled by an absolute monarchy, headed by a sultan. The oil industry makes up the overwhelming majority of Oman’s economic activity, though the government has been making efforts to diversify the economy. Oman’s population is approximately 5.2 million, most of whom are adherents of a form of Islam known as Ibadism.
Qatar

Qatar is comprised of a small peninsula that juts out into the Persian Gulf from the east coast of the Arabian Peninsula. Qatar was originally under the control of Bahraini sheikhs, but in 1867, the Qatari people revolted against them. In an attempt to pacify the Qataris, the British installed the head of a powerful Qatari family, Muhammad ibn Thani al-Thani as the country’s ruler. The al-Thanis have ruled the country ever since. Oil was discovered in Qatar in the 1940s, and has since been the main driver of the country’s economy. In 1971, the country became an independent state. Today, Qatar has a population of approximately 2.9 million people, of which nearly 90% are expatriates. The country is the home of the widely-popular news channel, Al Jazeera, which is based in the capital, Doha.
Saudi Arabia

Saudi Arabia is the largest and most populous country on the Arabian Peninsula. More than 35.2 million people live in the country, which has a land area of 2,149,690 sq. km. The country was founded by Ibn Saud, the first of the Saudi rulers, for whom the country is called. In 1901, Ibn Saud seized control of Riyadh, which is the Saudi capital today. Five years later, the Saudis controlled the entire region of Najd, which is the large interior region of the Arabian Peninsula. In 1925, the Saudis conquered Hejaz, a region comprising most of the Arabian Peninsula’s west coast. The two regions of Najd and Hejaz were merged in 1932 to form the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. One year later, the Saudis took control of the southwestern region of Asir.
Today, Saudi Arabia is governed as an absolute monarchy, and is largely regarded as the most conservative country on the Arabian Peninsula and the Middle East as a whole. In the last few years, however, the government has introduced certain reforms to liberalize and modernize the conservative kingdom. Greater rights and freedoms for women have recently been introduced, as have measures to allow for the creation of a modern entertainment industry. Saudi Arabia also seeks to diversify its economy, which is still heavily dependent on oil. Indeed, Saudi Arabia has the world’s second largest oil reserves. The country is also known for its important religious sites, specifically the two cities of Mecca and Medina, Islam’s first and second holiest cities respectively. Mecca is home to the Kaaba, Islam’s holiest shrine. Every year, millions of Muslims from around the world come to Mecca to take part in the Islamic Hajj, or pilgrimage.
United Arab Emirates (UAE)

The United Arab Emirates is a federation of seven emirates (countries ruled by an emir) located in the eastern end of the Persian Gulf. The territory that now constitutes the UAE was known as the Trucial Coast when it was a protectorate of the British Empire. Oil was discovered in the area in the 1930s, though exports did not begin until the 1960s. In 1971, the seven emirates of the Trucial Coast united to become the independent state of the United Arab Emirates. As is the case with most of the countries on the Arabian Peninsula, the UAE is heavily dependent on oil exports. Now, however, the UAE is also a mecca for real estate and tourism. Nearly 10 million people live in the UAE, but only 10% of them are UAE nationals, called Emiratis.
Yemen

A country of about 30.4 million people, Yemen is located on the southwest coast of the Arabian Peninsula. It is both the poorest and most unstable country on the peninsula. Yemen was originally composed of two parts, North Yemen and South Yemen. The north was part of the Ottoman Empire, but gained independence in 1918. The south was controlled by the British Empire. In 1962, the ruler of North Yemen was killed in a military coup, and a civil war ensued, which lasted until 1970. In 1967, South Yemen achieved independence and became a communist state shortly thereafter. Armed clashes between North and South Yemen occurred during the 1970s. In 1986, a power struggle began in South Yemen, which would eventually lead to its union with the north in 1990. War broke out again in 1994 as rebels in the south tried to recreate a separate South Yemen. Since the dawn of the 21st century, war has persisted in Yemen. The country has become a bastion for terrorist groups, like Al-Qaeda and the Islamic State. In addition, Yemen’s government has been battling Shiite Islamist militants known as Houthis since 2004, which has recently led to one of the worst humanitarian disasters in the world.
Arabian Peninsula Countries
| Rank | Country | Total Area in km2 | Population | GDP per capita (current US$) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bahrain | 760 | 1,641,170 | 23,504.0 |
| 2 | Kuwait | 17,818 | 4,207,080 | 32,000.4 |
| 3 | Oman | 309,500 | 4,974,990 | 15,343.1 |
| 4 | Qatar | 11,586 | 2,832,070 | 62,088.1 |
| 5 | Saudi Arabia | 2,149,690 | 34,268,530 | 23,139.8 |
| 6 | United Arab Emirates | 83,600 | 9,770,530 | 43,103.3 |
| 7 | Yemen | 527,968 | 29,161,920 | 774.3 |