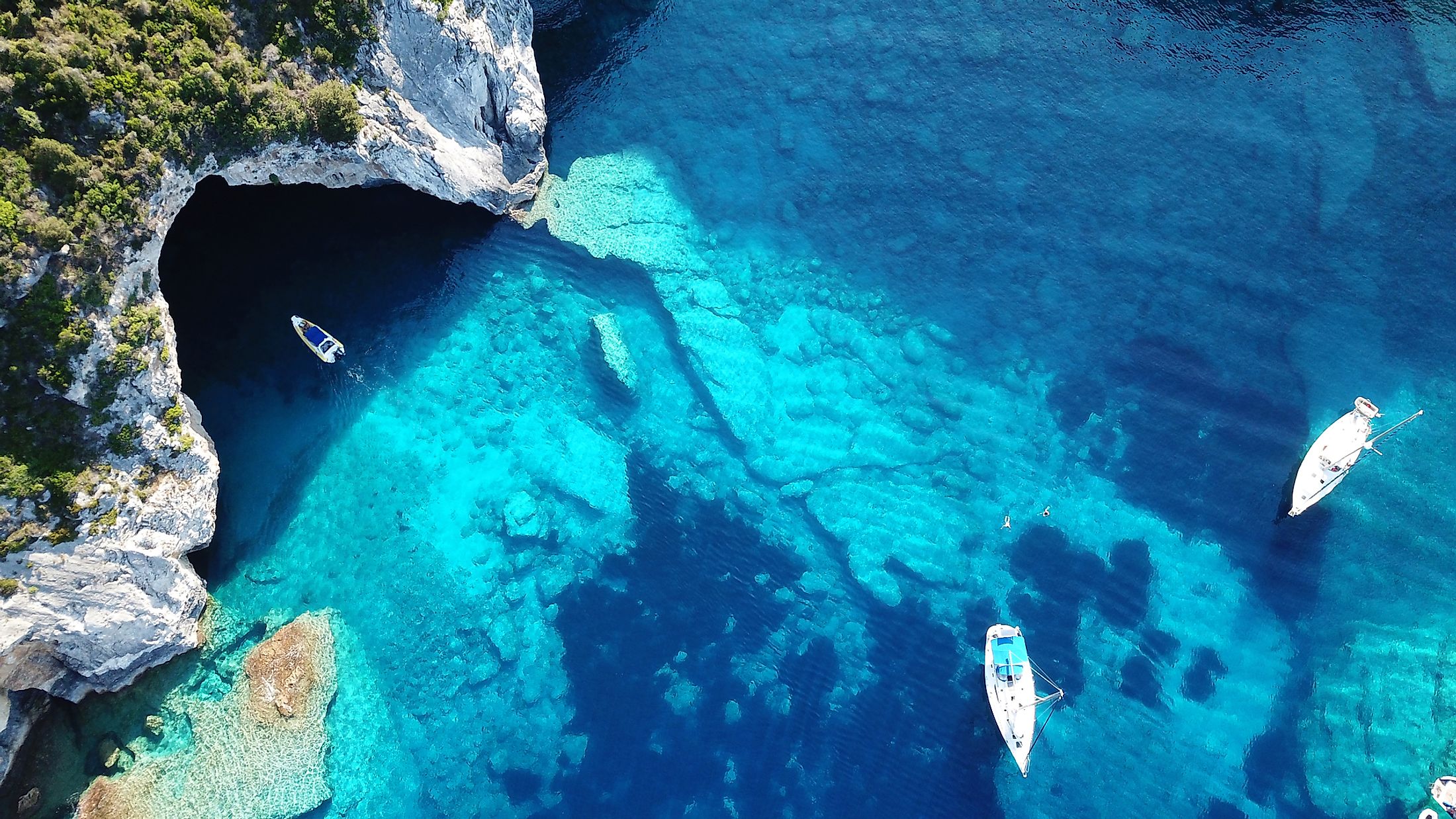
Caribbean Sea
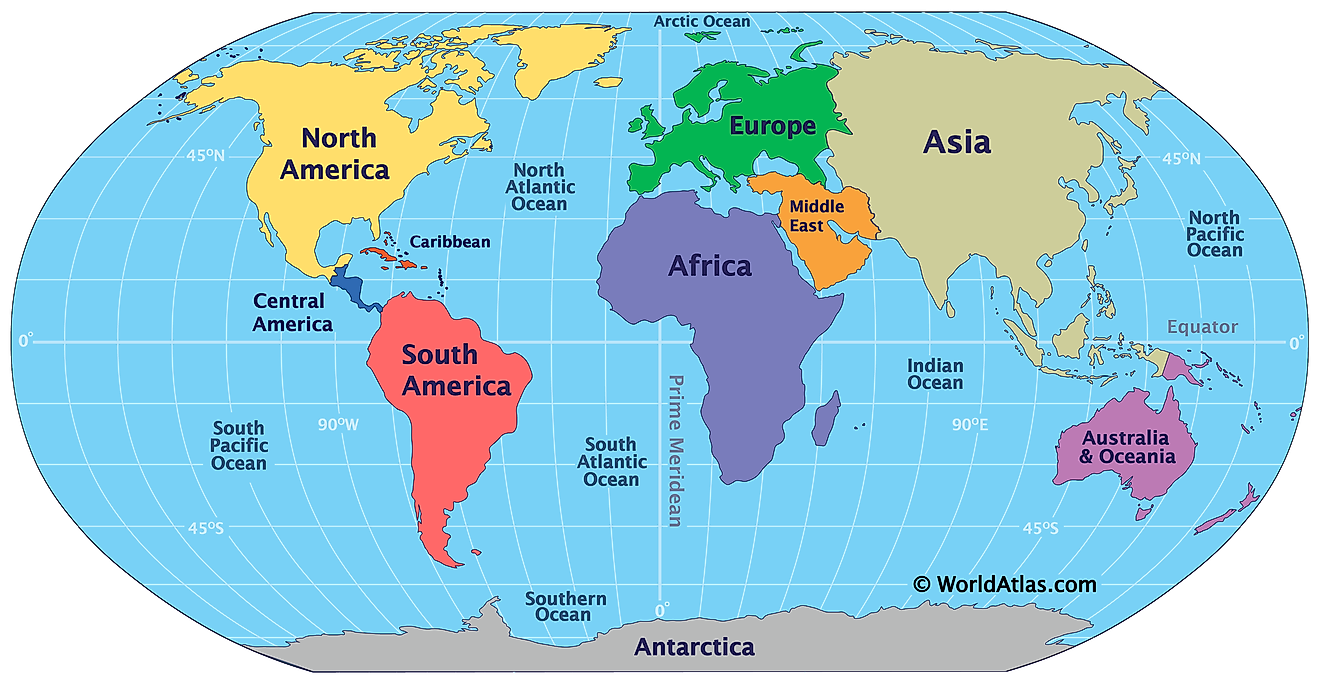
Marginal seas are large, shallow bodies of water that are positioned along the margins of the continents. With a total area of 106,460,000 sq. km, the Atlantic Ocean contains several notable marginal seas. The Caribbean Sea is the Atlantic Ocean’s 2nd largest marginal sea that is geographically positioned between the continents of North and South America in the Western Hemisphere.
Contents:
Location
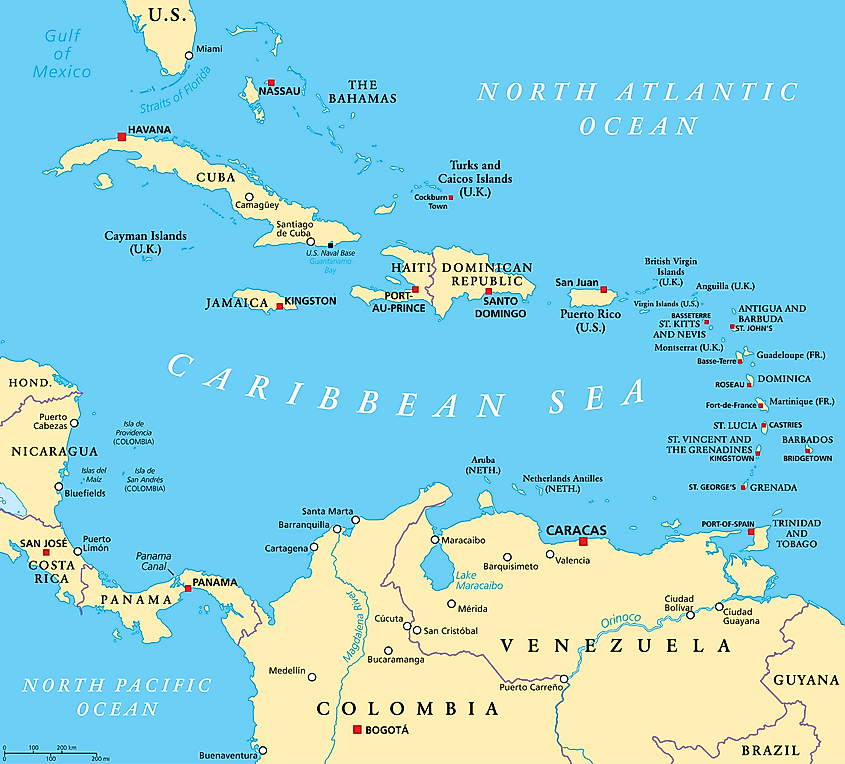
Covering an area of about 2,754,000 sq. km, the Caribbean Sea is bordered by the countries of Colombia, Panama, and Venezuela in the south; by Belize, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula in the west; by the Greater Antilles islands in the north; and by the Lesser Antilles islands in the east. The Caribbean Sea is connected with the Gulf of Mexico in the north via the Yucatan Channel.
The name “Caribbean” has been derived from “Caribs”, a Native American group of indigenous people that lived in the region during the late 15th century. Christopher Columbus was the first European to enter the Caribbean Sea and land on the Island of Bahamas in 1492. Following the region’s discovery by Columbus, the Caribbean islands began to be colonized by several countries including Spain, Dutch Republic, France, England, Denmark, etc.
Geography

The Caribbean Sea mostly occupies the Caribbean Plate and features many island arcs which separate it from the ocean. It is estimated that the geological age of the Caribbean Sea is between 160 and 180 million years, and was formed during the Mesozoic Era when a horizontal fracture led to the split of the supercontinent of Pangea. Situated on the floor of the western Caribbean Sea between the Jamaica and Cayman Islands is the Cayman Trench (Bartlett Deep), which reaches a depth of 7,686m below the sea level and is the deepest point of the Caribbean Sea. The highly indented Caribbean coastline features many bays and gulfs including the Gulf of Venezuela, Gulf of Honduras, Gulf of Darién, Gulf of Paria, etc. The Sea is also home to numerous coral reefs, including the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef, which is the 2nd largest barrier reef in the world that runs for about 1,000km along the coasts of the countries of Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, and Mexico.
Some of the major rivers that drain into the Caribbean Sea include Magdalene, San Juan, Chagres, Coco, etc. Lake Enriquillo, located in the Dominican Republic is the largest lake in the entire Caribbean region.
The Caribbean Sea is subdivided into five basins that are separated from each other by submerged ranges and ridges. These submarine basins are the Colombian Basin, Cayman Basin, Grenada Basin, Venezuela Basin, and Yucatan Basin. The Yucatan Basin is partially separated from the Cayman Basin by the Cayman Ridge, which rises above to form the Cayman Islands. The Cayman Basin is in turn separated from the Colombian Basin by the Nicaraguan Rise. The Colombian Basin is separated from the Venezuelan Basin by the Beata Ridge, while the Grenada Basin is separated from the Venezuelan Basin via the Aves Ridge. The Caribbean Sea floor also features two deep oceanic trenches namely the Puerto Rico Trench and the Cayman Trench, which makes the entire Caribbean Sea region highly seismically active. The deep basins and trenches in the Caribbean Sea bed are covered by deep red clay sediments, whereas the ridges and the continental slopes are covered by calcareous silts.
Climate
The Caribbean Sea experiences a tropical climate that is highly influenced by elevations, trade winds, and tropical ocean currents. The major ocean current greatly influences the area’s climate is the North Equatorial Current, which enters the Caribbean Sea region from the tropical Atlantic Ocean. The rainfall varies with the elevation and water current and ranging from less than 12 inches a year on the Bonaire Island to about 350 inches a year in the areas around Dominica. The eastern trade winds blow across the region leading to the creation of semi-arid and rainforest climates in the area. It is observed that the lowland areas between Belize and Costa Rica experience a tropical rainforest climate, while the Yucatan Peninsula, Cuba, and Venezuela experience dry tropical savanna climates. The islands of Curaçao and Aruba experience arid climates.
The nations that surround the Caribbean Sea are also prone to tropical cyclones and the Caribbean hurricane season lasts from June to November, with most of the hurricanes occurring between August and September.
Islands

There are more than 7,000 islands including 12 countries and 22 island territories in the Caribbean Sea. The islands are further divided into three distinct island groups: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Bahamas Archipelago. Located in the northern part of the Caribbean Sea is the Greater Antilles Island group. The islands which make up the Greater Antilles include Hispaniola Island (shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic), Jamaica, Cuba, Cayman Island, and Puerto Rico. Located between the islands of the Greater Antilles and the continent of South America on the Caribbean Sea’s eastern part is the Lesser Antilles. The Lesser Antilles are further divided into three major island groups: the Leeward Islands comprising of Anguilla, British Virgin Islands, Guadeloupe, US Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, Saint Martins, Saint Kitts, and Nevis, Saint Barthelemy, and Montserrat. The Windward Islands comprising of Trinidad and Tobago, Dominica, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Barbados, Martinique, and Saint Vincent and Grenadines. The Leeward Antilles comprising of the three Dutch Islands of Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao. The Bahamas (Lucayan) Archipelago includes the island of the Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Marine Life
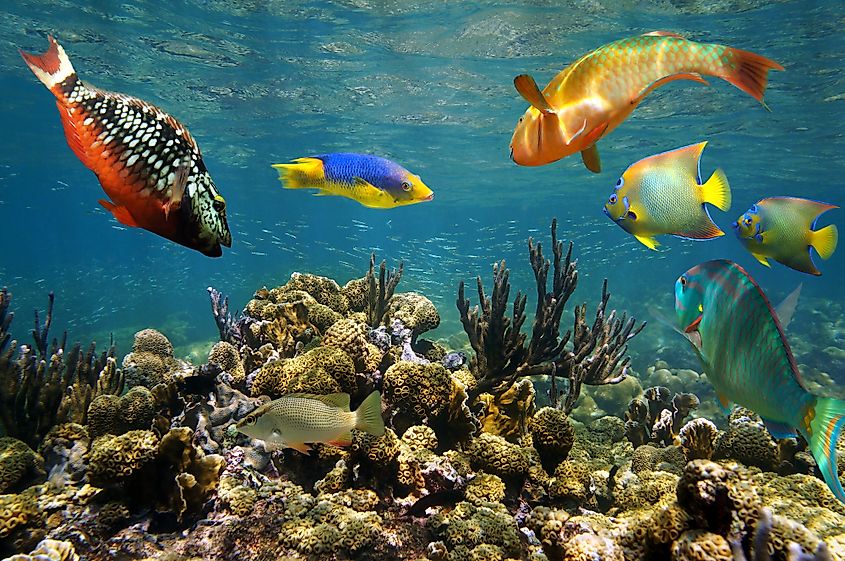

The Caribbean region has rich biodiversity containing many endemic species. The region is mostly dominated by tropical vegetation and comprises more than 13,000 plant species of which 6,500 plant species are endemic to the region. Some of these notable endemic floral species include guaiac wood, Bayahibe rose, and ceiba. Other floral species that are found in the Caribbean region include mahogany, caimito, coconut palms, and mangroves. In the shallow waters mainly turtle grass, manatee grass, and shoal grasses are found.
Approximately 1,000 fishes have been recorded in the Caribbean Sea including flying fish, angelfish, manta ray, Caribbean reef shark, silky shark, bull shark, tiger shark, butterflyfish, Atlantic Goliath grouper, moray eels, lobsters, sardines, parrotfish, etc. More than 90 mammalian species are found in the Caribbean including dolphins, humpback whales, sperm whales, manatees, Solenodons, hutias, etc. About 500 reptiles are found in the Caribbean including the blue iguana, rhinoceros iguana, Mona ground iguana, green turtle, loggerhead turtle, Atlantic ridley turtle, leatherback turtle, etc. More than 170 species of amphibians are found in the Caribbean including poison dart frogs, tree frogs, etc. About 600 avian species such as the American yellow warbler, Fernandina’s flicker, palmchat, black-fronted piping guan, etc have also been recorded here.