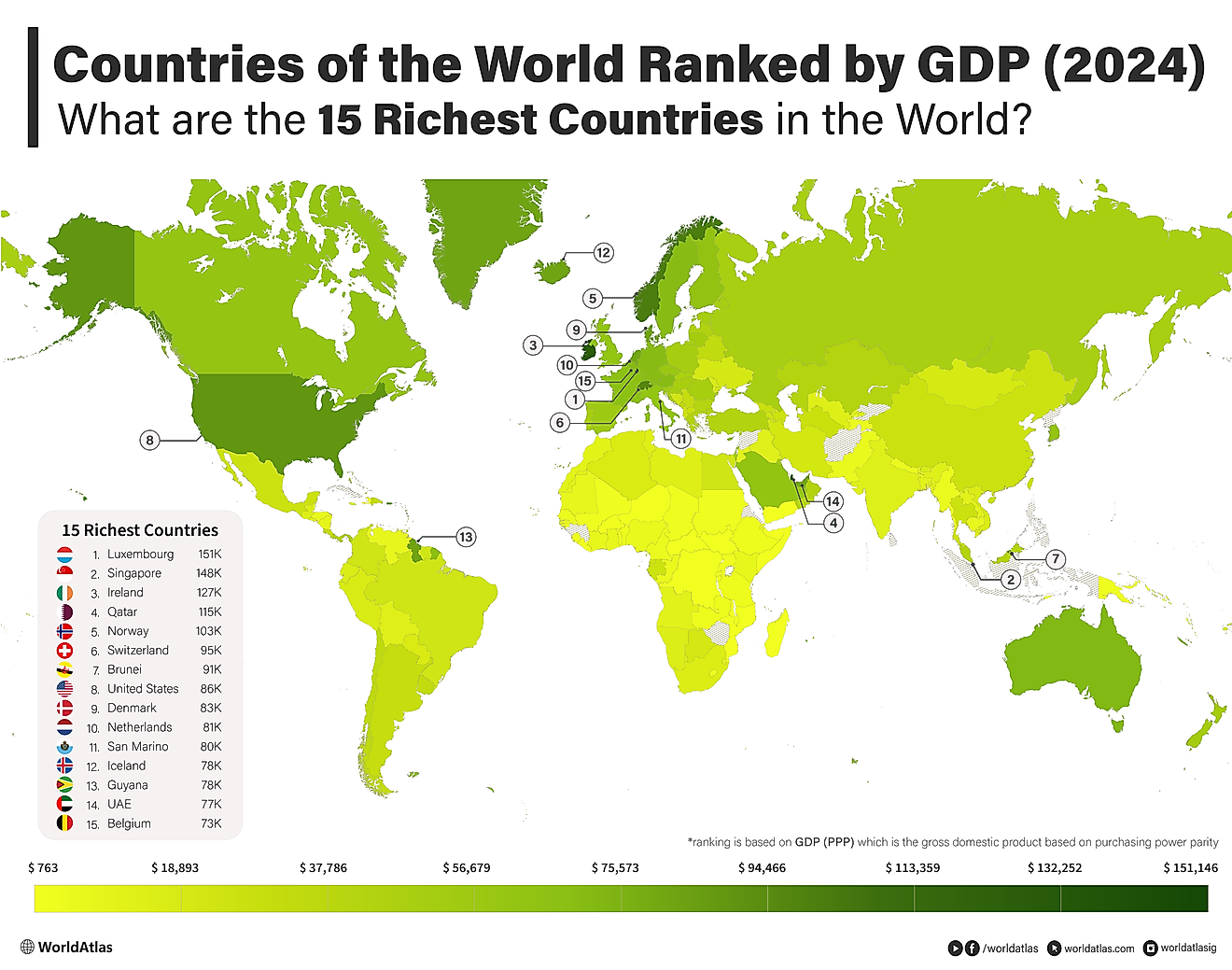
Countries with the Lowest GDP
Across the world, 2024 has been met with economic angst. According to this year's World Economic Outlook, the global inflation rate for 2024 is predicted to remain stable at 3.1%, and global inflation is predicted to drop from 6.8% to 5.8% over the course of the year. Although these figures are cause for optimism, advanced economies are projected to return to their inflation targets much sooner than emerging and developing economies. The report generally suggests that the global economy has been demonstrated to be resilient despite World Bank rate hikes. Last year's annual gross domestic product (GDP) growth for emerging and developing economies sat at 4.2%, while advanced economies saw their growth sit at 1.7%. Unfortunately, inflation was higher for emerging and developing economies, indicating that GDP growth is not universally keeping up with regional and global inflation, especially for countries with lower GDPs.
As a general principle, when a country's GDP is actively rising, its economy is growing and supportive of wide economic stability for workers and businesses. When its GDP is stable or actively decreasing, its economy is generally shrinking, and workers and businesses tend to struggle. That said, GDP is not an accurate reflection of the actual living conditions within a country; some countries with low but growing GDPs may have a high quality of living while others with a high but decreasing GDP may be seeing significant struggles for residents and citizens.
Disregarding other economic factors and markers, these countries have the lowest GDP as per the International Monetary Fund's 2024 World Economic Outlook data. Although some placements have changed since 2023's data, most of the countries on this list remain unchanged. Out of last year's 25 countries with the lowest GDP, only Cabo Verde has escaped the list, with the Central African Republic joining the list. These countries, span across Oceania, North America, Africa, Asia, and Europe, with the bulk of these nations belonging to Oceania. With their distinct histories, socio-economic fabrics, and geographic regions, each of these nations is on this list for their unique reasons and will require distinct plans to increase their GDPs in comparison to the remainder of the global economy.
1. Tuvalu - 0.07 Billion

With less than half the GDP of the country with the next lowest GDP, Tuvalu currently has the lowest recorded GDP globally. Tuvalu is made up of nine small coral islands in the Pacific Ocean. Most Tuvaluans are farmers who are supported by relatives working overseas. Due to its small geographic and population sizes, as well as its poverty, Tuvalu relies heavily upon foreign aid and imports most of its food, fuel, and goods from Fiji, Australia, New Zealand, and Japan. The country is so small that there is only a single bank, and it uses Australian currency even though the government issues all amounts of its own currency. Although the country has been Westernized and is a member of the Commonwealth, only the island of Funafuti has a regular electrical supply, and the nation only has one radio station. Nevertheless, Tuvaluan culture has maintained its traditional emphasis on community consensus.
2. Nauru - 0.16 Billion

With roughly double Tuvalu's GDP but half that of the next largest nation, Nauru is another coral island nation in the Pacific Ocean. Today, most residents on the island are indigenous and speak a mixture of Nauruan and English, though very little of Nauruan is recorded. Most goods, water, and food are imported to the island, though the country does have a 200m exclusive economic zone for fishing. Since 1907, phosphate has been the nation's sole export. Once phosphate reserves began to deplete by the end of the 20th century, the country began to experience economic hardship, needing to find alternative sources of income. Today, a second wave of phosphate mining is in place, utilizing improved mining infrastructure.
5. (Tie) Palau - 0.31 Billion
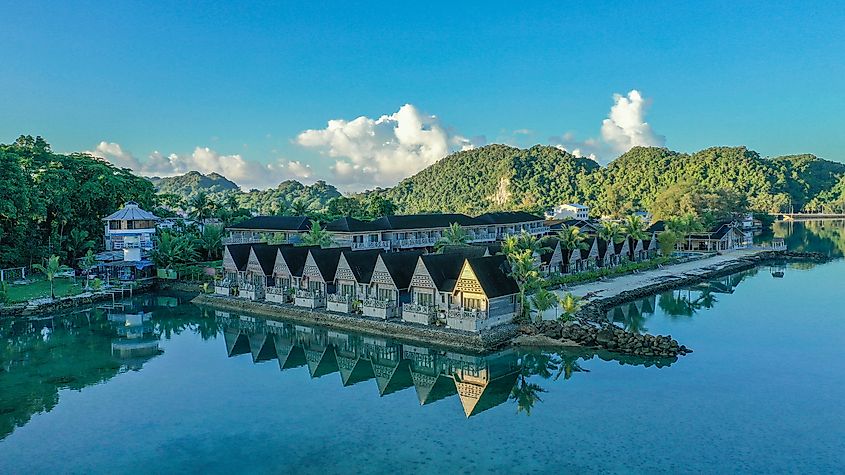

Tied for fifth place, Palau is another Pacific Ocean nation comprised of 340 coral and volcanic islands. A relatively young nation, Palau officially became a sovereign nation in 1994 after being a member of the UN Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands. Palau has a diverse population due to its 3,000-year history of migration from Indonesia, New Guinea, and Polynesia. There has also been an influx of immigration from Japan, Europe, and the Americas since the late 18th century. Since the end of the Second World War, the U.S. Navy has been the biggest employer in Palau. Beyond governmental employers, agriculture and fishing are the major economic activities. Today's tourism is contributing to the country's economic growth, facilitated, in part, due to the country's use of the U.S. dollar as its official currency.
5. (Tie) Kiribati - 0.31 Billion
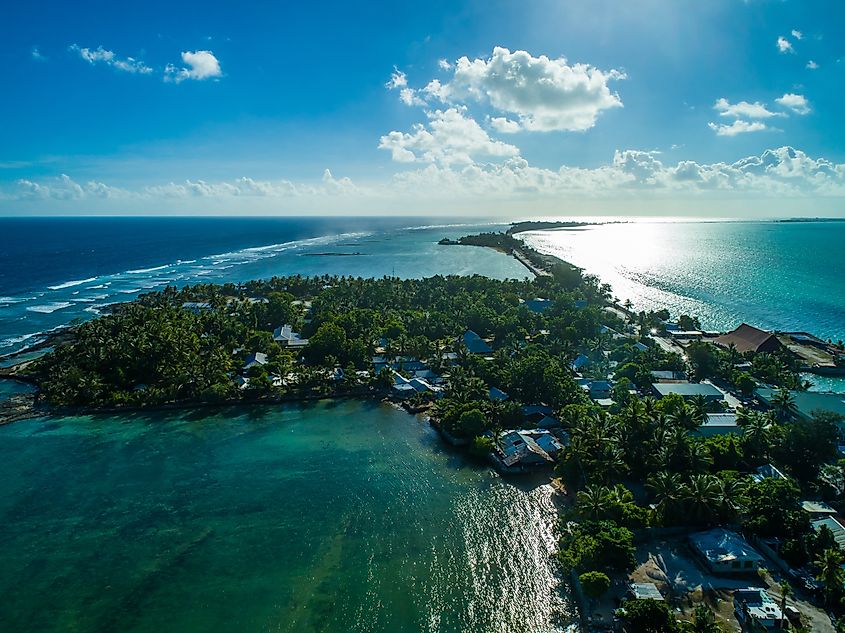

Another Oceanic island nation tied for fifth place, Kiribati, is comprised of 33 islands, 20 of which are inhabited. Although English is the official language, most people speak Gilbertese. Like Nauru, Kiribati's economy has centered around phosphate mining. Since phosphate mining has ceased, it relies heavily upon its exclusive economic zone spanning 1,350,000 square miles of ocean, cultivating fish and seaweed. The nation also has a small manufacturing sector that supports domestic consumption of goods and beverages. One-third of the nation's imports are in food, coming predominantly from Australia, Japan, Singapore, and Thailand.
5. (Tie) Marshall Islands - 0.31 Billion
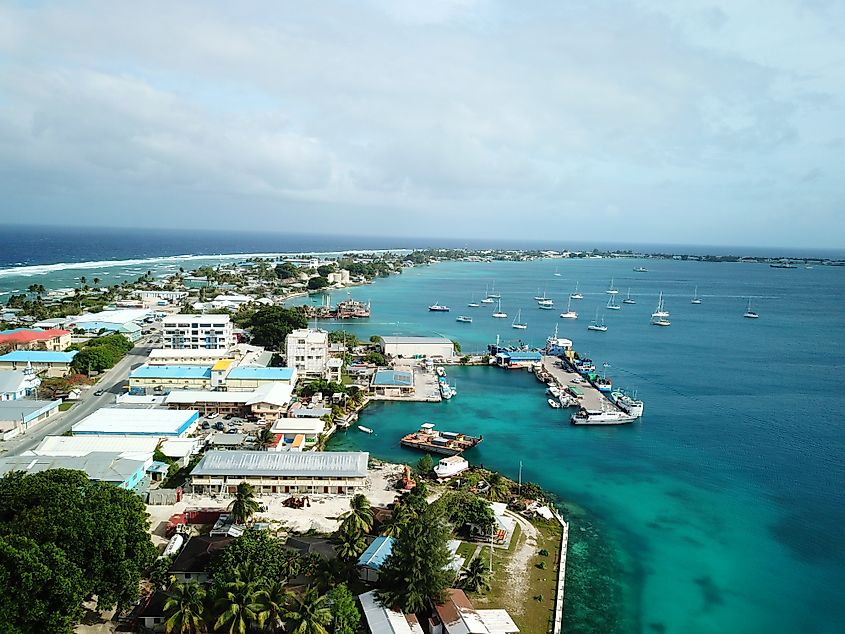

Likely the best-known island nation on this list, The Marshall Islands is made up of over 1,200 islands and islets in the Pacific Ocean. Most people on the island speak Marshallese and English. The island is heavily dependent on the U.S. for its economy, with the U.S. government leasing significant portions of land for missile testing. Farming and fishing make up the remainder of the economic activity on the islands, with coconut, pandanus, breadfruit, and taro being the major crops. Nevertheless, the country's biggest imports are processed food, followed by machinery, goods, and fuel, which come predominantly from the United States, Japan, and Australia.
6. Federated States of Micronesia - 0.48 Billion
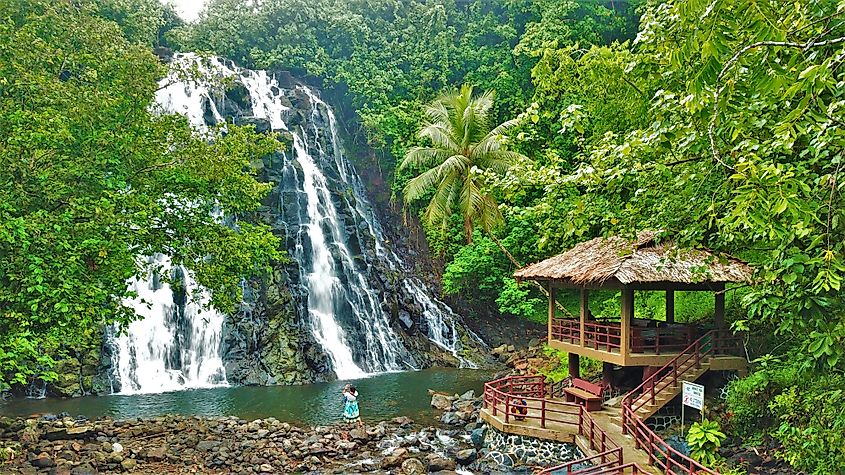

Comprised of over 600 islands, the Federated States of Micronesia is another island nation in the Pacific Ocean. The nation is culturally and linguistically diverse, with several dialects appearing within distinct languages scattered across the nation. Farming and fishing are the country's major economic activities. Like the Marshall Islands, U.S. economic activity makes up the country's major revenue source. Within the nation, most income is generated through its service sector, including government services. The country imports most of its goods, food, and fuel from countries such as the United States, Guam, Singapore, Taiwan, and Thailand.
7. Tonga - 0.58 Billion

Tonga, the seventh Pacific Ocean island nation on this list, is comprised of 170 islands. Agriculture makes up the bulk of Tonga's economy, raising large squash, coconut, banana, and vanilla bean crops. Although the Tongan monarchy owns most of the land, all males over 16 are entitled to a plot of land for personal cultivation. Tonga's products are mostly consumed domestically, though it does import most of its goods from New Zealand, Singapore, the United States, Fiji, and Australia. The nation primarily exports goods to New Zealand, Japan, Australia, and the United States.
8. Dominica - 0.71 Billion

Located in the Caribbean Sea, Dominica is a Commonwealth island nation known for its heavy forests. Although English is the official language, French and Carib are also commonly spoken throughout Dominica. The poorest Caribbean nation, Dominica, is heavily reliant on its agriculture, which has been repeatedly destroyed by hurricanes. Tourism is a growing sector and has been successful in increasing economic activity. At the end of the 20th century, bananas accounted for roughly half of Dominica's exports, but natural disasters significantly reduced the country's ability to grow this crop.
9. São Tomé and Príncipe - 0.75 Billion

An African island nation, São Tomé and Príncipe is comprised of two major islands and several islets. The population is mainly composed of Forros and Angolares, with Portuguese being the main language spoken. This country has faced severe economic hardship due, in large part, to colonial stagnation. The World Bank and International Monetary Fund have been offering tutelage to the nation since the 1980s with little success. Agriculture is the main economic function on the islands, although high unemployment rates and labor shortages persist.
10. Samoa - 1.02 Billion

Known as the "Cradle of Polynesia," Samoa is a well-known Pacific micronation that gained its independence from New Zealand in 1962. Nine-tenths of the population are of Polynesian heritage and of Samoan ethnicity, with Samoan being the country's official language. Somalia has historically been a collectivist society, with its cash-based economy only being born following European contact. Since the 1950s, tourism and manufacturing have become the major functions of the canopy. The country also relies upon grants from the United States, the Commonwealth, and the United Nations.
12. (Tie) Saint Vincent and The Grenadines - 1.13 Billion
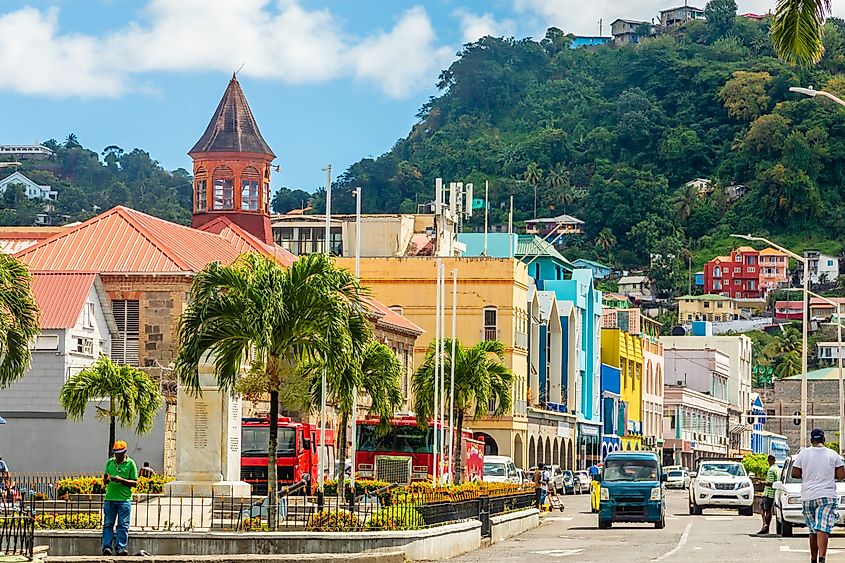

Tied for twelfth place on this list, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is another island nation located within the Caribbean Sea. Most inhabitants are of African descent, and English is the main language spoken throughout the country; like many of the other nations on this list, Saint Vincent and The Grenadines' economy is predominantly based upon agriculture and is one of the globe's main producers of arrowroot. Bananas are currently the largest export, followed by potatoes, plantains, yams, coconuts, and taro, in no particular order. Fishing is also of major economic importance, with the country exporting large volumes of lobster, conch, tuna, and swordfish. Tourism is also a major economic activity, and the Grenadines are well known internationally for their coral reefs and beaches.
12. (Tie) Saint Kitts and Nevis - 1.13 Billion
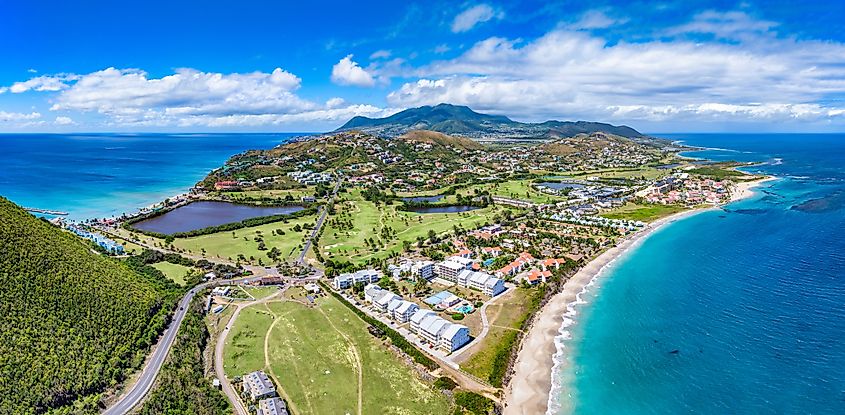

Another Caribbean island nation, Saint Kitts and Nevis is a two-island nation known for its historic sugarcane industry that ended in 2005. Today, most of the island nation's economy centres around tourism. The Eastern Caribbean dollar is the official currency and the United States, United Kingston, and Trinidad and Tobago are the nation's chief trading partners. Saint Kitts and Nevis is still a member of the Commonwealth but has had independence since 1983.
13. Vanuatu - 1.29 Billion
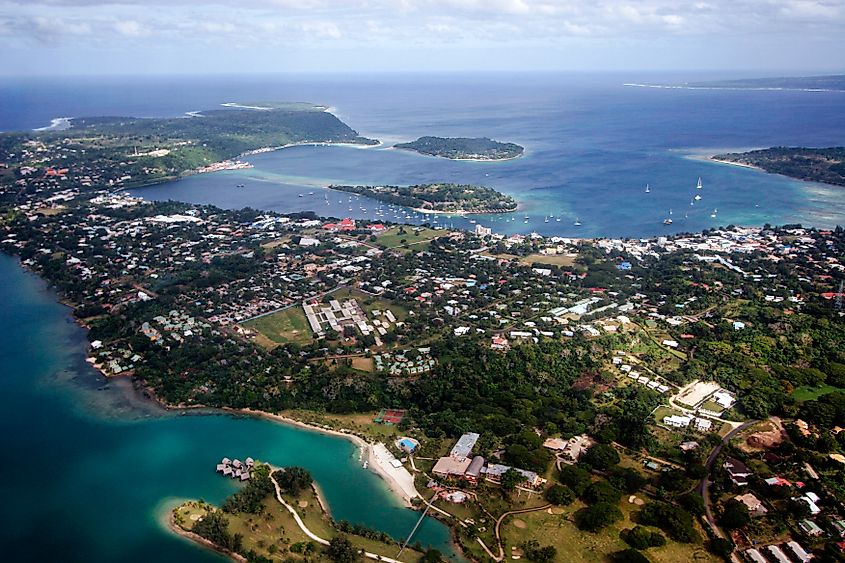

500 miles from Fiji, Vanuatu is another Pacific Ocean island nation, made up of 13 major islands among many small ones aligned in a 'Y' shape. A diverse nation, over 100 languages and dialects are spoken, though Bislama is the national language, followed by English and French; Kava, beef, copra, timber, and cocoa are the nation's major exports today, trading mostly with Australia, New Caledonia, Japan, and New Zeland. Vanuatu imports machinery, food, animals, and mineral fuels from Australia, Singapore, New Zealand, and Fiji. Due to the nation's vulnerability to weather and climate change, the nation is currently working toward strengthening its agricultural sectors to stabilize its economy.
14. Grenada - 1.41 Billion
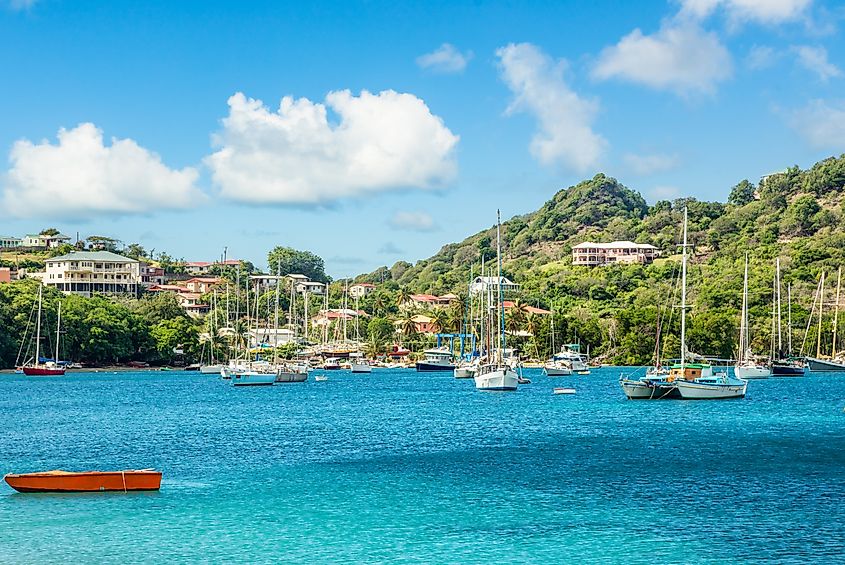

Grenada is another Caribbean island nation known both for its agriculture and tourism. Grenada received financial support from the United Kingdom and relies heavily upon this support. Cocoa, bananas, nutmeg, and mace are Grenada's main exports. Like most of the countries on this list, tourism is a major part of Grenada's economy, with the government investing in airports and harbors. Grenada primarily trades with the United States, but it also trades with Germany, Malaysia, The Netherlands, and Egypt.
15. Comoros - 1.42 Billion
The country with the 15th lowest GDP is composed of three islands located in the Indian Sea. Comoros' residents are diverse, with many having immigrated historically from Arab and Persian nations as well as from Madagascar. Comorian, Bantu, Arabic, and French are widely spoken across the islands. Comoros' economy is based on agriculture and fishing. France, Saudi Arabia, Japan, and Kuwait have all offered major financial aid to the country since 1975. Today, the country faces high unemployment rates, overpopulation, and poor harvests, all contributing to the nation's economic hardship. That said, Comoros' GDP is growing faster than its population, offering some optimism for the country's economic future.
With the world's economy projected to continue to rise in 2024, there is hope that the nations with the lowest GDP will have economic success and growth throughout the year. However, the global economy's stability is at risk due to growing environmental and political issues. Climate change threatens each of the nations on this list, as tropical and island nations are more at risk of the adverse effects of natural disasters and rising sea levels. Escalating tensions in the Middle East, South China Sea, and Eastern Europe threaten pre-existing trade partnerships and routes. Escalating combat also reduces advanced economies' cash reserves, threatening the steady supply of financial support many of these nations rely on each year. Although the International Monetary Fund projects that the global economy will continue to grow into 2025, this is uncertain, and it will take months to see how nations' financial positions settle at the end of the current year.
The 25 Countries With The Lowest GDP
| Rank | Country | GDP in Billions of US Dollars (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Tuvalu |
0.07 |
| 2 |
Nauru |
0.16 |
| 5 (tie) |
Palau |
0.31 |
| 5 (tie) |
Kiribati |
0.31 |
| 5 (tie) |
Marshall Islands |
0.31 |
| 6 |
Federated States of Micronesia |
0.48 |
| 7 |
Tonga |
0.58 |
| 8 |
Dominica |
0.71 |
| 9 |
São Tomé and Príncipe |
0.75 |
| 10 |
Samoa |
1.02 |
| 12 (tie) |
Saint Vincent and The Grenadines |
1.13 |
| 12 (tie) |
Saint Kitts and Nevis |
1.13 |
| 13 |
Vanuatu |
1.29 |
| 14 |
Grenada |
1.41 |
| 15 |
Comoros |
1.42 |
| 16 | 1.71 | |
| 17 | 1.99 | |
| 18 | 2.03 | |
| 19 | 2.13 | |
| 20 | 2.15 | |
| 21 | 2.2 | |
| 22 | 2.4 | |
| 23 | 2.58 | |
| 24 | 2.69 | |
| 25 | Central African Republic | 2.81 |