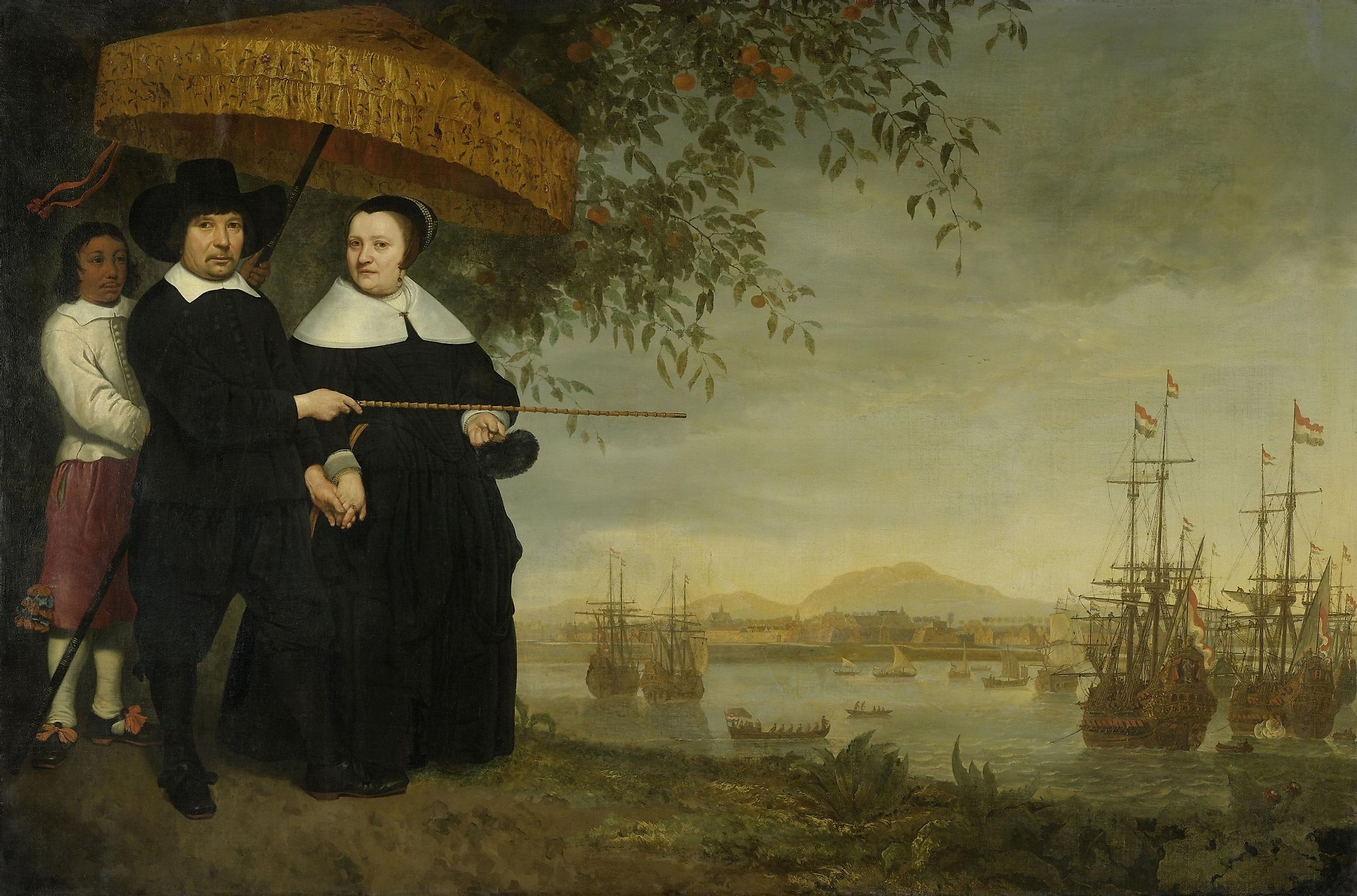
The Former Dutch Colonies
The Dutch colonial empire began in 1588 when The Netherlands united in declaring its independence from Spain, forming what was known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. The Dutch Empire eventually became one of the world's most powerful colonial powers, with outposts in 5 continents: Asia, Africa, North America, and South America. During its height, the Dutch Colonial Empire included territories scattered around the globe in countries as far-reaching as Indonesia, Suriname, South Africa, the United States, and many countries in South America. With its expansive trade network, the Dutch Empire became a major player in the global economy, becoming known for its lucrative spice trade. Additionally, many of the colonies developed under Dutch rule adopted aspects of their colonizers' culture and language. The legacy of Dutch colonialism can still be seen around the world today. In short, the Dutch colonial empire was an influential part of history, and its impact is still evident in the modern world. Indeed, it is impossible to know to what extent the Dutch Colonial Empire impacted the regions it occupied. However, one thing is clear; those regions were forever changed.
The Dutch Colonization Of North America

The Dutch began colonizing North America in 1609. This early colonization began with the founding of New Amsterdam, more commonly known in our modern-day as Manhattan, New York, by the Dutch West India Company in 1625. The Dutch also established several other settlements in what is now upstate and downstate New York, as well as in Delaware, Pennsylvania, and other areas along the East Coast. These settlements were often very profitable for the Dutch, thanks to the trading of furs and other commodities. However, these early Dutch settlements were eventually ceded to the British and became part of the United States of America. While the Dutch no longer control North America, their early influence can still be seen today.
The Dutch Colonization Of South America
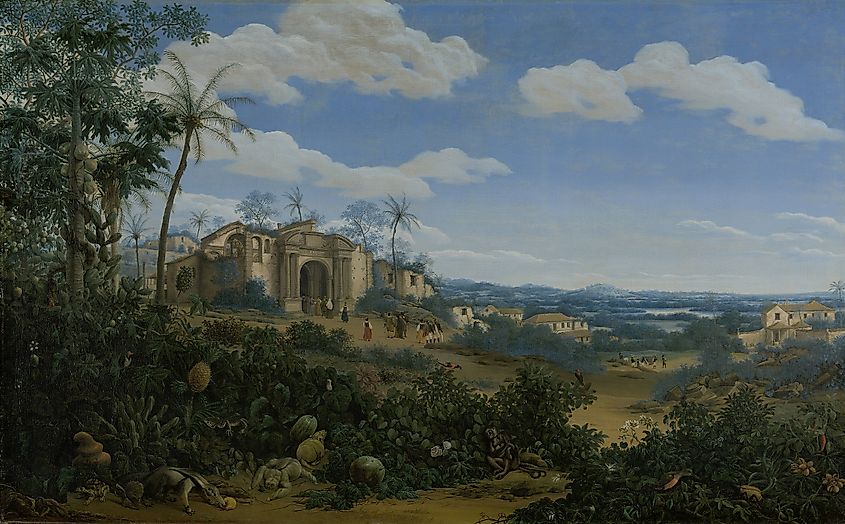

The Dutch turned their attention to South America in the mid-17th century when Dutch merchants began trading with the Dutch West India Company. Dutch ships started transporting goods to and from Dutch colonies throughout the region. Dutch settlements were established in what are now Suriname, Guyana, Venezuela, and Dutch Guiana (now part of French Guiana). Dutch colonists brought enslaved Africans to work on plantations, and Dutch traders established trading posts throughout the region. Dutch rule in South America continued until the late 20th century; while the Dutch lost many colonies in South America, they did not relinquish control of Suriname until 1975. To this day, Dutch colonial influence can still be seen in many parts of South America. A small but distinct minority speaks Dutch in Suriname, and Dutch names can still be seen in Suriname, Guyana, and Dutch Guiana. Additionally, Dutch-style architecture is common throughout the region, particularly in cities such as Paramaribo and Willemstad.
The Dutch Colonization Of Africa
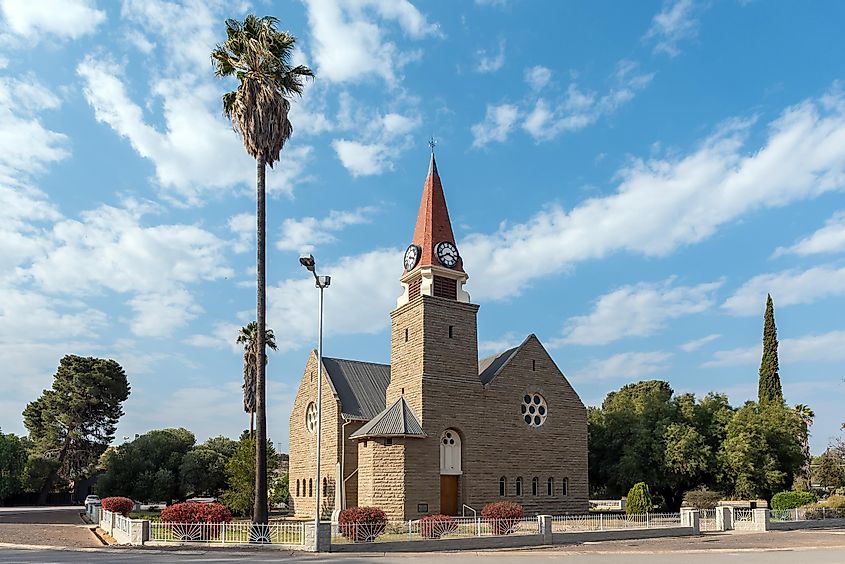

The Dutch first began colonizing Africa in the 17th century when Dutch ships began trading with African coastal tribes. Dutch traders eventually established settlements in current-day Angola, as well as a few other locations throughout the continent. Dutch rule over Africa ended by the 18th century when the Netherlands lost its colonies to other European powers. Dutch influence can still be seen in the region today, particularly in Dutch-style architecture. Dutch names and Dutch loanwords are still used in the local dialect. The Dutch had colonies in several African countries, such as the Ivory Coast, Dutch West Africa, which is now part of modern-day Senegal, and Dutch East Africa, known today as Tanzania. The Dutch have left an indelible mark on the world, and Dutch colonialism has had a lasting impact in Africa. As with all empires, the Dutch Colonial Empire brought much harm to the people of Africa. Their land and resources were used to further the goals of the Dutch Colonial Empire, which often excluded the prosperity of the native population in the colonies.
The Dutch Colonization of Asia
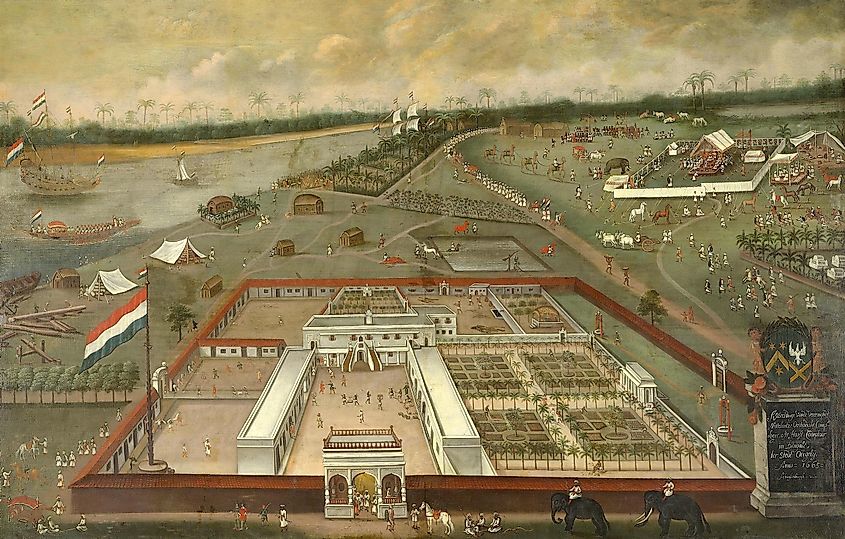
It was not until the 17th century that Dutch colonization extended to Asia. Dutch merchants began trading with Asian countries, and the Dutch East India Company was established in 1602. Dutch traders quickly set up ports in India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, and the Malacca Straits. Dutch colonies were also established in Taiwan and the East Indies (now known as Indonesia). Under Dutch rule, Dutch colonialists brought Dutch culture and language to the region, as well as Dutch architecture and Dutch-style infrastructure. Dutch cultural influences can still be seen in the region today, from Dutch names to Dutch loanwords in various languages.
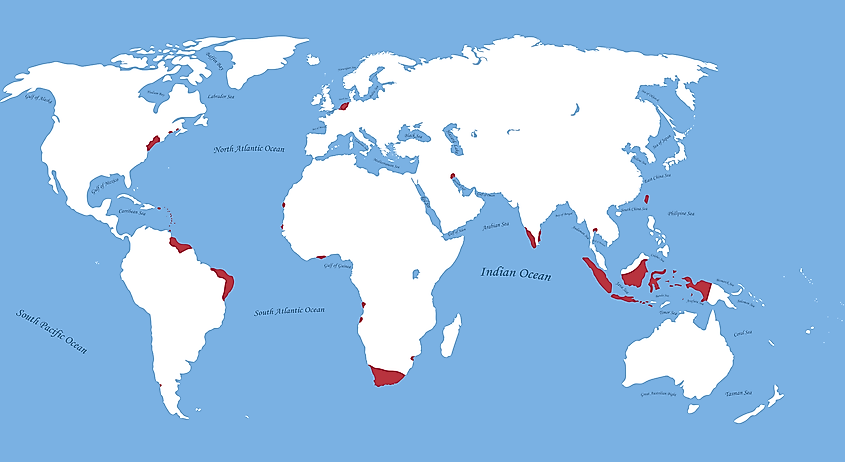
In conclusion, Dutch colonialism was a far-reaching force that shaped modern-day culture, language, and infrastructure around the world. The Dutch colonial empire was an important part of history, and the influence the Dutch Colonial Empire wielded in its colonies around the world was huge.