What Is A Constituent Nation?
A constituent nation is an area or region within a country that is usually given considerable autonomy pertaining to local laws and policies or is ruled indirectly by another larger country. While not enjoying full independence, a constituent nation is often able to have considerable amounts of influence within the borders that they control and sometimes even have their own governments and capital cities.
All Constituent Nations & Their Respective Countries
| Country | Constituent Nations |
|---|---|
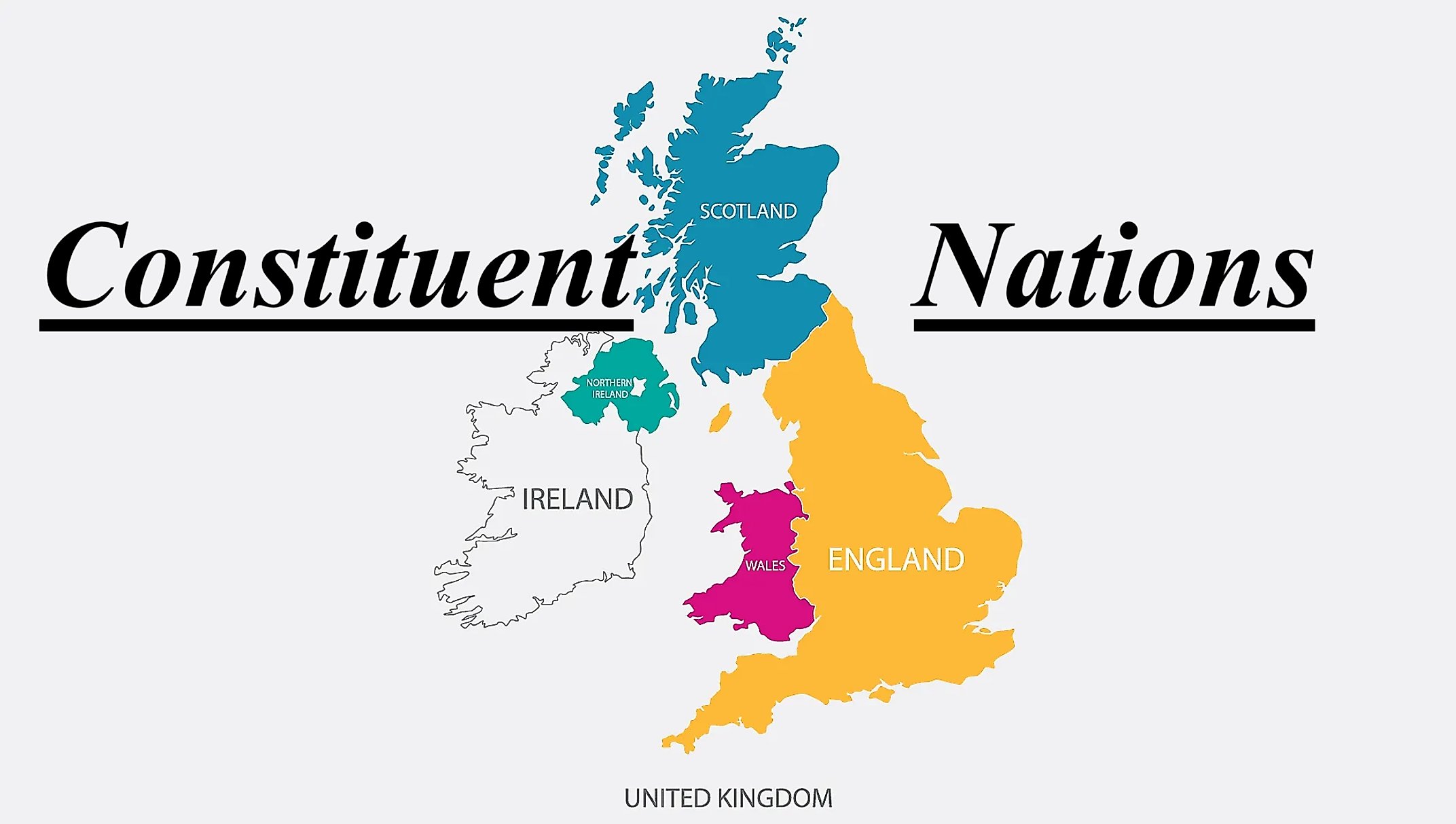
| United Kingdom | England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland |
| Kingdom of Denmark | Denmark, The Faroe Islands, Greenland |
| China | Hong Kong, Macau |
| Uzbekistan | Karakalpakstan |
| Moldova | Gagauzia, Transnistria |
| Tanzania | Zanzibar |
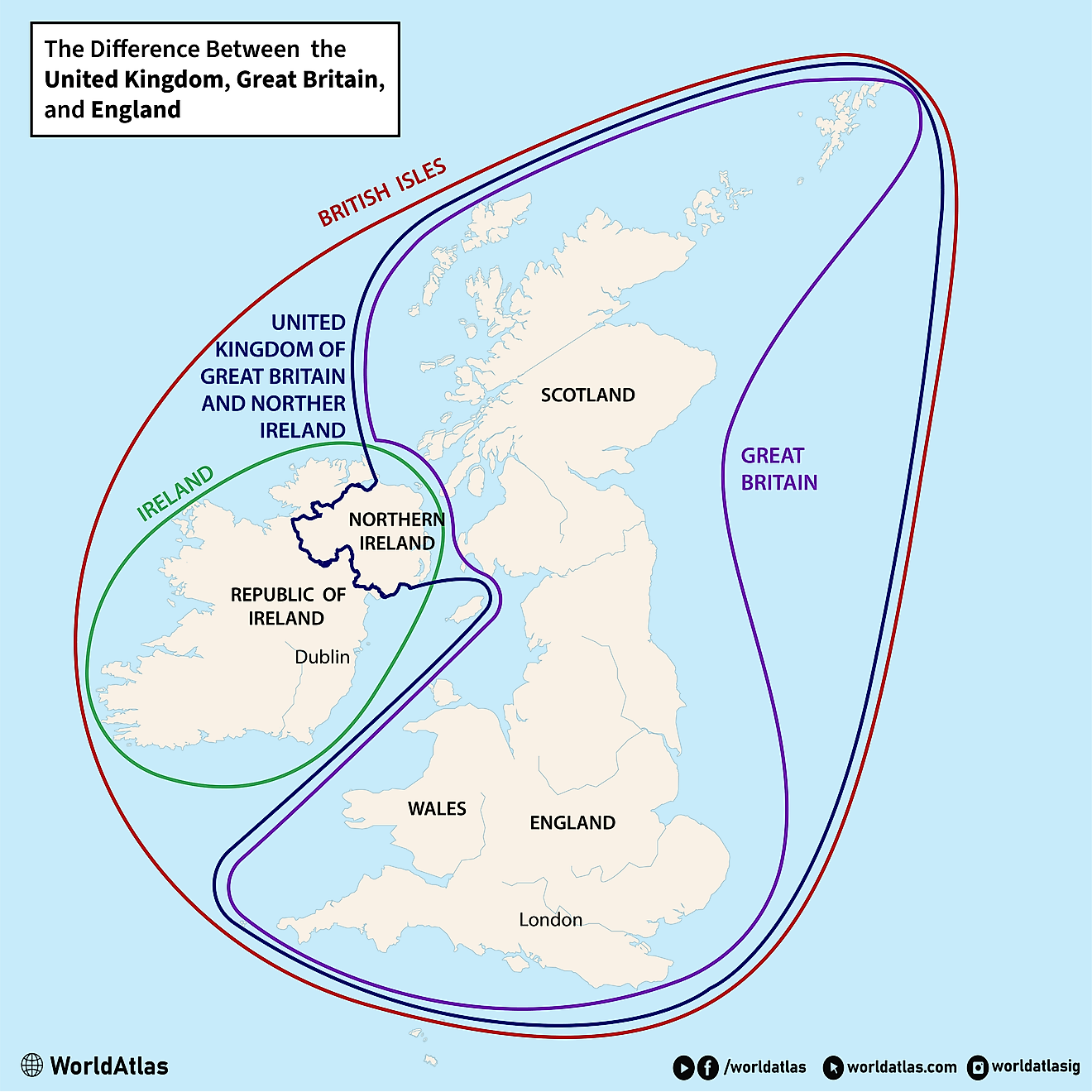
The United Kingdom

The United Kingdom is one of the more well-known countries that is home to many constituent nations. Officially formed in the early 1700s, the United Kingdom originally consisted of Wales, England, and Scotland, finally incorporating Ireland (now Northern Ireland) in 1803.
England

Even though the United Kingdom is supposedly a union of the four nations, in reality, England holds the majority of the political power. London is of course the capital of the United Kingdom and is home to the national parliament.
The larger population and economy of England have always made it the leading partner of the United Kingdom ever since its inception more than 300 years ago. This has created a certain amount of discontent and turmoil amongst the other members both historically and in present times.
Scotland

Scotland is the largest of the union's members outside of England. Scotland enjoys a significant amount of autonomy within the United Kingdom and even has its legislature that convenes in Edinburgh.
On top of a localized government, Scotland also sent its representatives to London to participate on a national level as well. In 2015, Scotland nearly left the United Kingdom and became independent after a referendum narrowly failed.
Wales

Wales has been in union with England since 1277 AD, much longer than any other member. Wales, similar to Scotland, has its regional government that meets in the capital city of Cardiff.
The Welsh government has largely been concerned with preserving and promoting the Welsh language and culture in schools. The Welsh language, one of the oldest in Europe, has been on the decline for centuries. In recent years there have been considerable efforts made by the Welsh government to keep their native language alive.
Northern Ireland

Famously, Ireland used to be a part of the United Kingdom until it revolted in the early 20th century. All that remains now is Northern Ireland. Much like Scotland and Wales, Northern Ireland has its regional government that gathers in Belfast.
Talks of joining the Republic of Ireland always bubble up the surface every few years or so but there has been no considerable headway made on that front for decades. As it stands it appears that Northern Ireland is going to remain a part of the United Kingdom for the foreseeable future.
Kingdom of Denmark

It often shocks people to know that Denmark still controls a large amount of territory outside its own borders. While it might have never had the vast colonial empire that other European powers once enjoyed, it still clings on to a handful of overseas constituent nations.
Denmark

Denmark, the obvious head of the Kingdom of Denmark, is the largest and most powerful member of this political union. Its capital city, Copenhagen, is the center of political power across the union.
The economy and population of Denmark dwarf the other constituent nations as well with the Danish population making up nearly 99% of the kingdom's entire populace.
The Faroe Islands

The Faroe Islands are a remote chain of islands that can be found in the far reaches of the North Sea between Great Britain and Iceland. The capital city of Tórshavn is home to the vast majority of the 52,000 people who call the islands home.
Danish, English, and the native language Faroese are all spoken here. The Faroese language descends from Old Norse and shares many similarities with Icelandic.
Greenland

The largest island in the world, Greenland, is the third member of the Kingdom of Denmark. Its capital, Nuuk, is home to its regional seat of government. One of the most remote places in the world, Greenland is sparsely populated.
Of the people who do call Greenland home, the vast majority are not Danes but rather belong to the indigenous Inuit population. Greenland is given considerable autonomy and is particularly mindful of preserving their culture and unique way of life.
China

Much controversy has surrounded the constituent nations of China in the last few decades. Both Macau and Hong Kong were handed over by the Portuguese and British in the 1990s but were done so in a way that ensured large amounts of autonomy for both regions. The interests of the Chinese government in Bejing occasionally challenge this autonomy.
Hong Kong

The most famous constituent nation within China is Hong Kong. Hong Kong was a British territory for more than 150 years; the United Kingdom returned it to China in 1997. It was then considered a "Special Administrative Region" (SAR) under China's jurisdiction.
Hong Kong, both post and pre-independence, was an economic powerhouse. Its bustling economy and thriving culture have made it one of the great success stories of Asia, along with Taiwan and Singapore. Only time will tell what the growing influence of China will have on this small semi-autonomous region.
Macau

Often overlooked, the city of Macau is often described as the "Las Vegas of Asia" due to the near-endless casinos and extraordinary nightlife that it has to offer. Similar to Hong Kong, Macau was handed over to the Chinese government in 1999 under the condition it would remain autonomous for another 50 years, and it also received the SAR stamp of status.
Today, millions of tourists from Mainland China and the rest of Asia flock to Macau each year. International travel remains the bedrock of the local economy and it will likely remain that way for a long time.
Uzbekistan

The central country of Uzbekistan is also home to a constituent nation. Uzbekistan is home to many ethnic groups some of which have expressed their will to live with an increased level of autonomy and self-rule.
Karakalpakstan
The Republic of Karakalpakstan is located in the northwest of Uzbekistan. Home to the Karakalpak people, this autonomous zone even predates independence from Soviet rule. Although the republic was first established in the 1930s the Karakalpaks have lived in this area for hundreds of years sharing many similarities in culture and language with the Kazaks and Noghais.
Moldova

The small Eastern European country of Moldova came into existence during the breakup of the Soviet Union in the late 1980s and early 1990s. However, when Moldova became a nation, it brought two constituent nations for the ride.
Gagauzia
Gagauzia, getting its name from the Gagauz are thought to have descended from the Bulgars or Turkmen sometime during the Dark Ages in Europe. Regardless, they are seen as a distinct ethnic group in Moldova that is largely separate from the wider society.
In the early 1990s, there were serious calls for independence but total separation was avoided after the Gaguaz people were given their own semi-autonomous zone.
Transnistria
Transnistria was another breakaway region from Moldovia. However, unlike Gagauzia, Transnistria essentially operates as its own country with its own military, government, and constitution that is separate from Moldova.
Transnistria's independence is not recognized by the United Nations and relationships between Moldova have cooled off in recent years.
Tanzania

The small East African country of Tanzania also oversees its own constituent nation. In 1964 the British colony of Tanganyika and the island protectorate of Zanzibar merged to form the modern United Republic of Tanzania. Tanzania's capital city is Dodoma.
Zanzibar

Zanzibar is a small collection of islands that can be found off the coast of East Africa. These island chains were the center of trade in the region for centuries. The islands changed hands multiple times before they ended up in British control.
Today Zanzibar enjoys a certain level of autonomy that other regions in Tanzania do not have. The local government meets in the capital, Zanzibar City. Zanzibar differs from the rest of Tanzania for its Arab and Muslim influence.
Final Thoughts
The manifestation of constituent nations might vary across the world but they all share similar characteristics. Many constituent nations are the result of various ethnic, religious, or cultural groups that exist within the same borders wanting to safeguard and protect their way of life.
Rather than becoming independent countries, these constituents work within a delicate yet beneficial relationship with their often larger and more powerful parent nations.