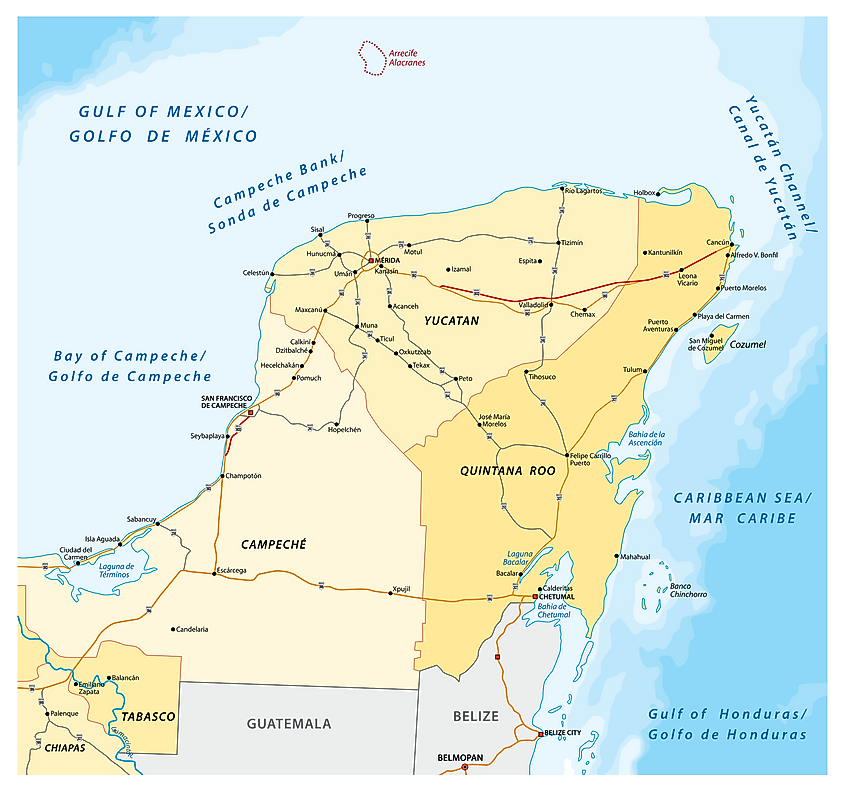
Yucatan Peninsula
Mexico is one of the few countries whose parts of their territories extend into more than one peninsula. Two of the Mexican states, Baja California and Baja California Sur are on the Baja California Peninsula, while Yucatan, Quintana Roo, and Campeche are located on the Yucatan Peninsula. Yucatan Peninsula is a peninsula in Central America, separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. Besides the three Mexican states, the peninsula also includes parts of Guatemala and Belize.
Contents:
Where Is The Yucatan Peninsula?
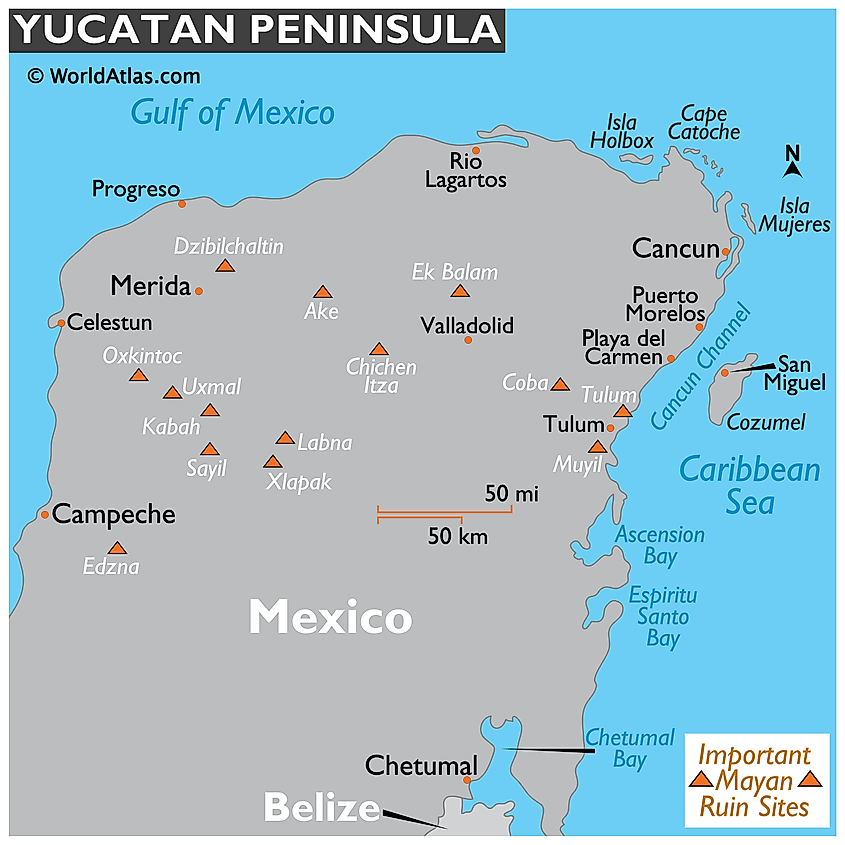
The Yucatan Peninsula is Mexico’s southeastern projection, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It separates the Gulf of Mexico to the north and west from the Caribbean Sea to the east. The peninsula forms part of Guatemala’s northern half, while Belize is located almost entirely on the Peninsula’s south. It is separated from Cuba to the northeast by the Yucatan Channel, while the Cayman Islands are further east. The US states of Texas and Louisiana are on the peninsula’s north, across the Gulf of Mexico.
Origin Of The Name
The origin of the name “Yucatan” is a highly debated subject. According to Diego Lopez de Cogolludo, the word may have come about in two ways. First, when Francisco Hernandez de Cordoba landed on the peninsula in 1517, he inquired from a local about a certain settlement’s name, for which the local responded “I don’t know” in the Yucatec Mayan language. However, the response may have sounded like “Yucatan” to Hernandez. The second theory suggests that “Yucatan” may have been derived from the name of a crop known as “yuca.”
Geography

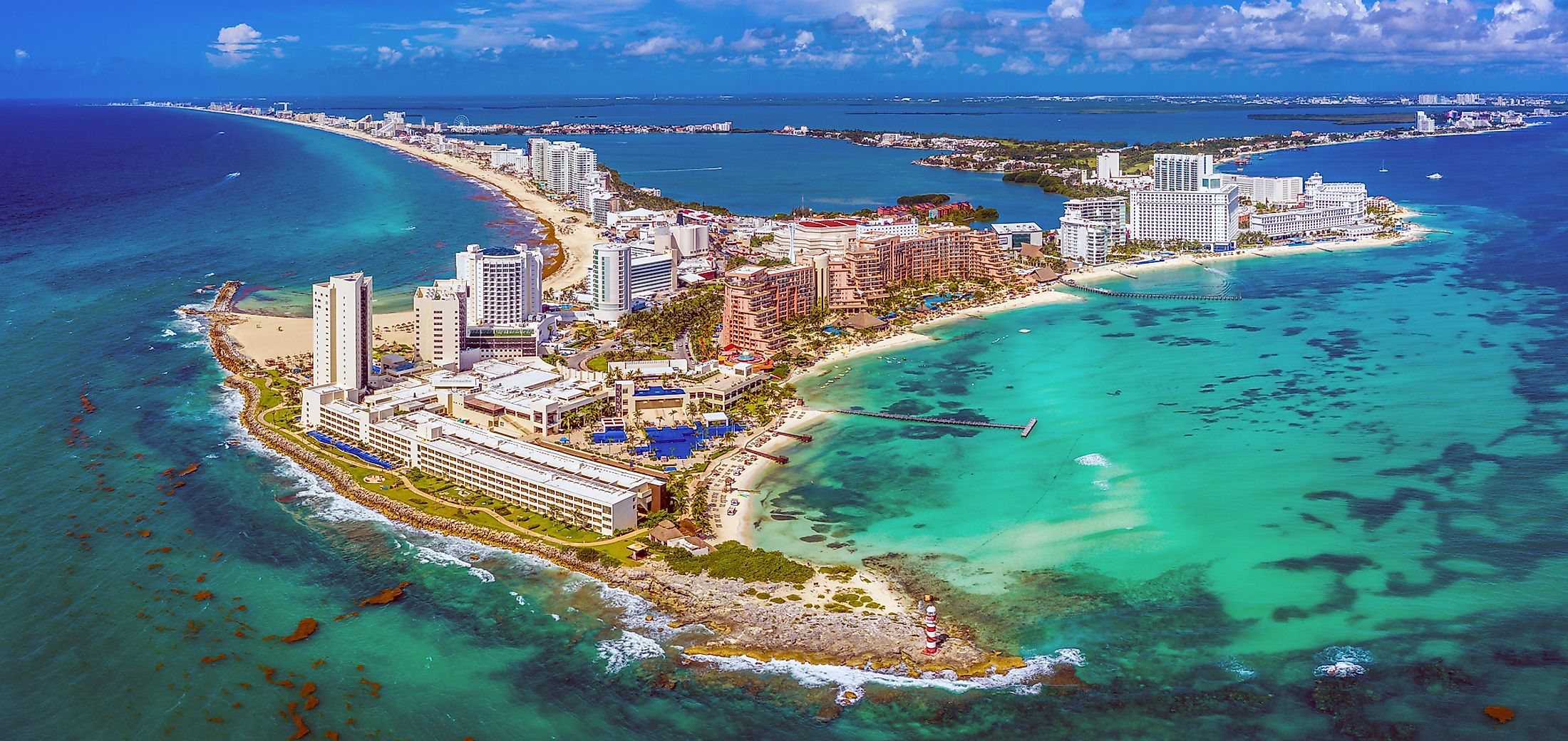
Yucatan Peninsula covers approximately 181,000 square kilometers, with a mean breadth of 320 kilometers and a coastline of 1,100 kilometers. The northern coast is low, sandy, and semi-barren, while the eastern coast is bordered by smaller islands and characterized by bluffs. Some of the islands bordering the eastern coast are Isla Mujeres and Cozumel. There are excellent beaches along the peninsula’s coast, including Cancun, a major resort area and popular destination.
The Yucatan Peninsula is part of the larger Yucatan Platform, a partially submerged landmass, and is the platform’s only portion above the water. Yucatan is composed of soluble and carbonate rocks, mainly limestone rocks. The rocks are covered by a thin soil layer, formed from the weathered rocks. Due to the peninsula’s karst nature, there are no rivers on its northern half. Lakes and swamps mainly have marshy and unpotable water.
Brief History

The Yucatan Peninsula was an important region for the Mayan Civilization. The Mayan culture spread from the south of the peninsula into Honduras, Guatemala, and the Chiapas highlands. In 1517, Hernandez de Cordoba became the first Spanish to reach the Peninsula. The following year, Juan de Grijalva explored most of Yucatan’s coast before setting sail further west. By 1550, the Spanish had managed to conquer the peninsula. Their conquest was partly aided by smallpox disease, which killed 75-90% of the native population. The Spanish occupied Mexico, including the Yucatan Peninsula, until 1821 upon independence.
Population

The Yucatan Peninsula comprises three Mexican states, almost the entire Belize, and Peten Department (Guatemala). The three Mexican states (Yucatan, Quintana Roo, and Campeche) have a combined population of 5.1 million people. Guatemala’s Peten Department is home to 567,000, while 419,000 Belizeans live on the peninsula. Meride, Yucatan State, is the most populated area. The majority of the peninsula dwellers are Mestizos and Maya.











