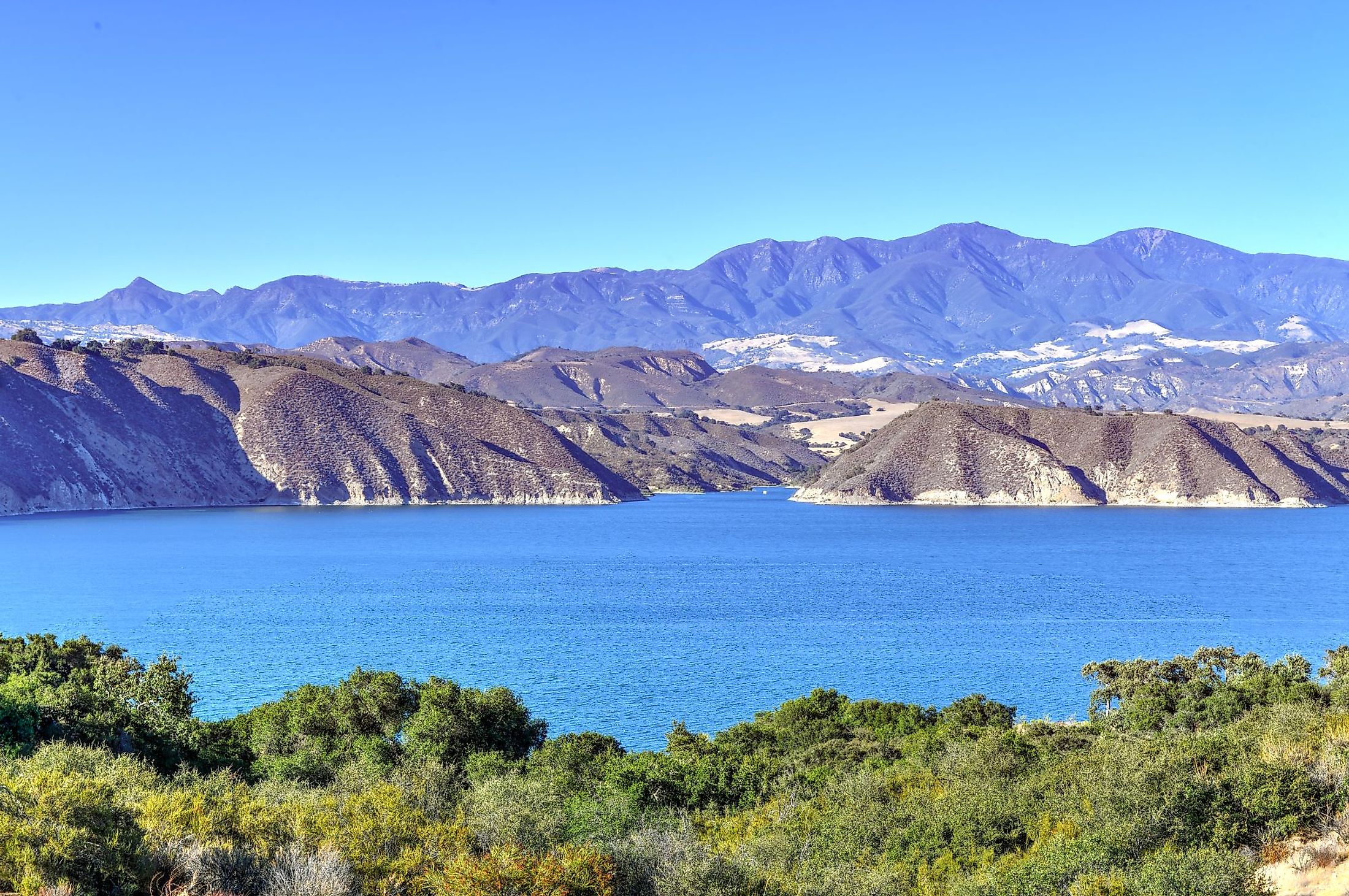
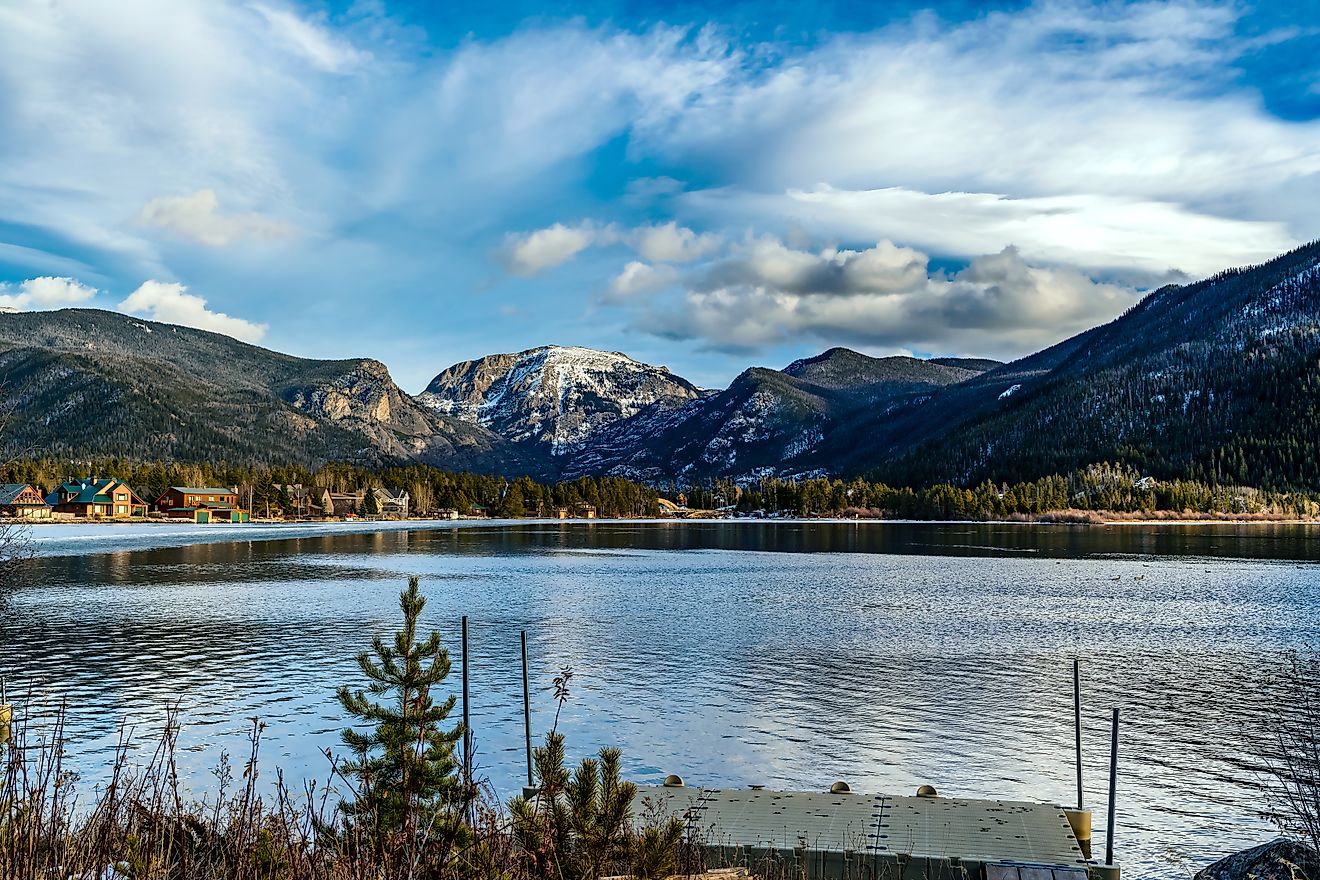
Cachuma Lake, California
Lake Cachuma is an artificial reservoir located on the Santa Ynez River in the Santa Ynez valley at the heart of Santa Barbara County in the US State of California. The lake was created due to the construction of the Bradbury Dam on the Santa Ynez River, which flows both in and out of the lake. The lake's name, "Cachuma," has been derived from the indigenous Barbareno Chumash language and was the name of a native Chumash village. Surrounded by forests, fishing and boating are popular activities on the lake, along with camping and hiking in the surrounding region. Since the reservoir provides drinking water for the region, any bodily contact with the water, including swimming, wading, or activities such as water-skiing, is strictly prohibited.
Geography Of Cachuma Lake
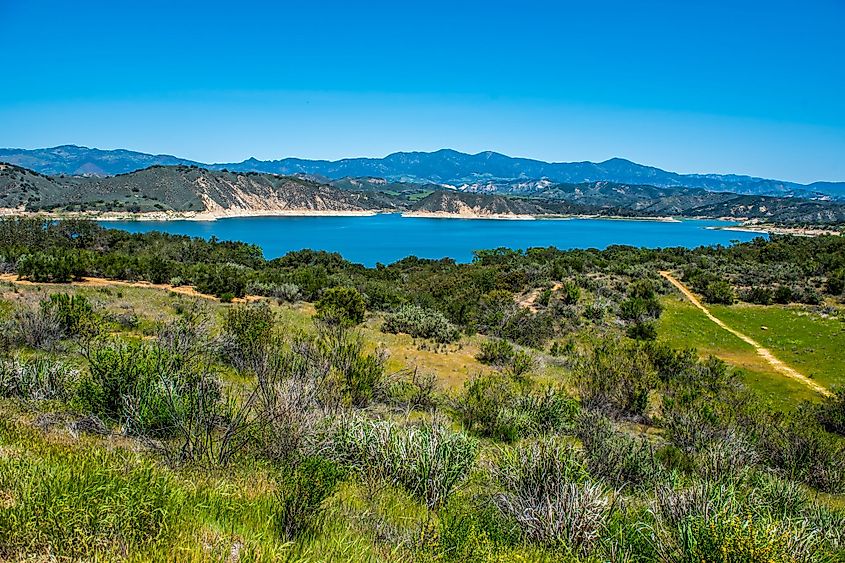

Cachuma Lake is located adjacent to the northern side of California State Route 154 and about 35 km northwest of the city of Santa Barbara. The Santa Ynez River, Santa Cruz Creek, and Cachuma Creek, along with several smaller streams, flow into the lake. Water is diverted from the lake to surrounding communities as needed via the 10 km long Tecolote Tunnel. The Los Padres National Forest borders the lake, along with the San Rafael Mountains. The closest settlement is Santa Ynez, located about 11.67 km west of the Bradbury Dam.
Geology Of Cachuma Lake
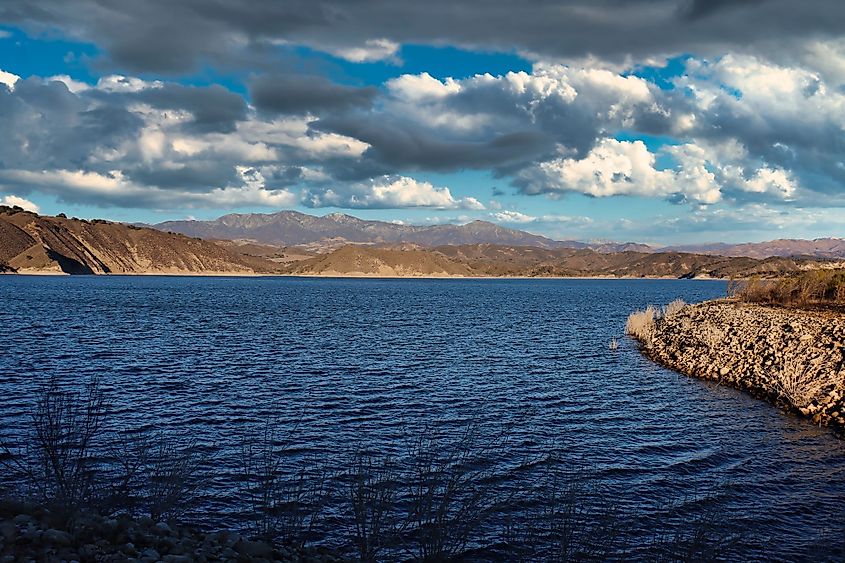

Like the San Rafael Mountains, the Santa Ynez Valley consists of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks forged by early volcanic activity. Thousands of years ago, the Santa Ynez Valley was underwater and formed a part of a prehistoric ocean. The soil in the Valley is still full of fossilized sea creatures. The shores of the lake feature inlets and coves and rugged rocky terrain. Aside from the bedrock, the lake floor consists of gravel, clay, and silt. The Cachuma Lake's surface area is about 3,100 acres, with a maximum capacity of about 253,000,000 cubic meters. However, due to sediment accumulation, the current volume is 232,000,000 cubic meters. The reservoir is placed at an elevation of 230 m above sea level, with a drainage area of 671 km.
Climate Of Cachuma Lake Area
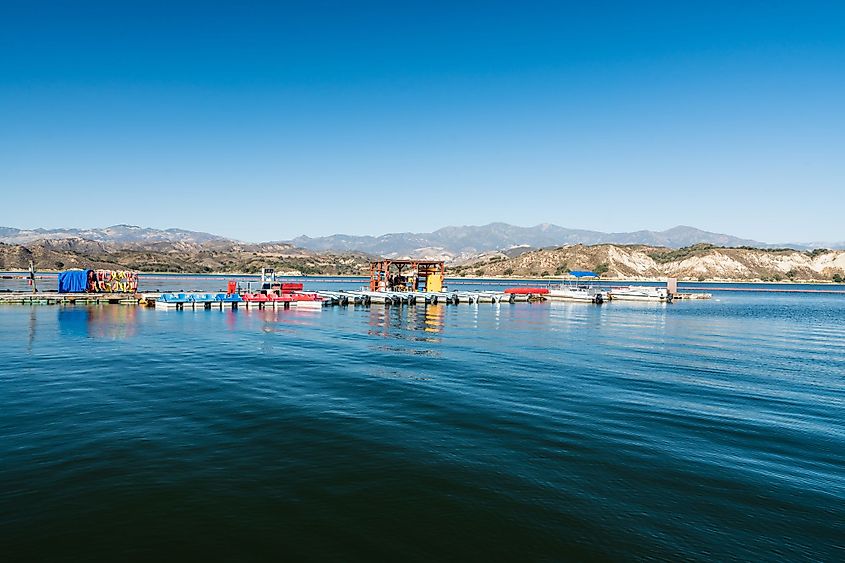

The weather of the Santa Ynez Valley is shielded from the influence of the coast by the Santa Ynez Mountains except in its northwest corner. According to the Koppen Climate Classification, the area experiences a warm-summer Mediterranean climate characterized by a short, rainy winter and a long, dry summer. During the warmest months of July and August, the average daily high is just over 32 °C. The coldest months of the year are December to February, with daily average highs of 18 °C to 19 °C. Precipitation varies from an average low of 0.254 mm in July to an average high of 121.41 mm in February. The region does not experience any snowfall.
Ecology Of Cachuma Lake
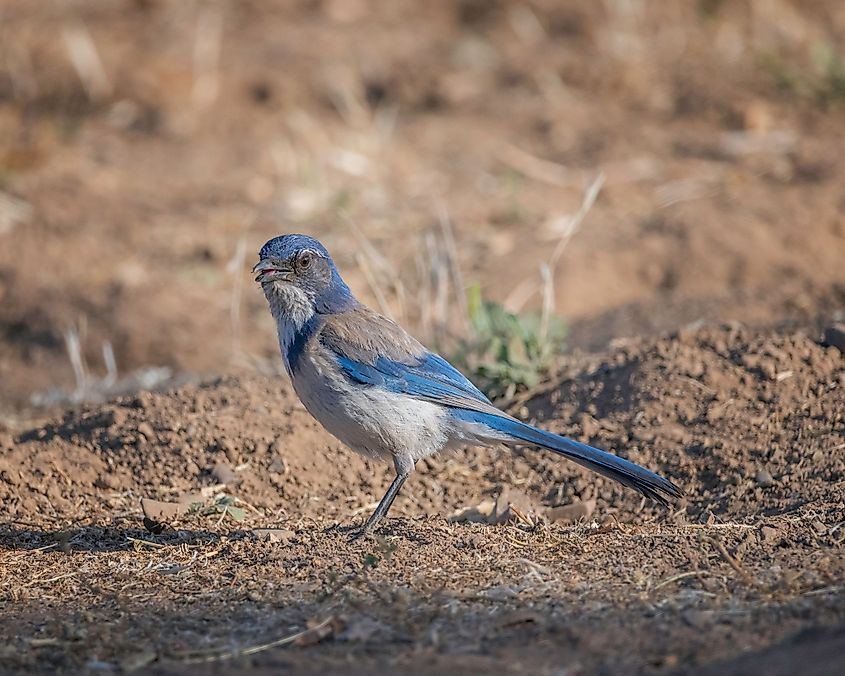

Nestled in the Santa Ynez Valley, Cachuma Lake is surrounded by oak forests. The region around the lake incorporates various environments, from the lake and its shores to the Santa Ynez River and the creeks that feed into it. The land includes oak savanna, woodlands, and chaparral or shrubland with various drought-resistant plants.
There are many opportunities for bird watching in the Cachuma Lake Recreation Area. In total, more than 275 species of bird are found in the Recreational Area. Bald eagles are seasonal visitors to the coves and other out-of-way areas. Cliff swallows nest on the sandstone cliffs of the mountains. The recreational area is home to western grebes, red-winged blackbirds, hawks, and osprey, along with waxwings, quail, junco, bluebirds, and many other songbirds. Cachuma Lake is considered one of the best places for recreational fishing in Southern California. The lake's topography consists of rocks and drop-offs, with large shallow areas supporting a healthy plant bed ecosystem. It creates a rich environment for large fish populations, including rainbow trout, bluegill, sunfish, catfish, small and largemouth bass, and many more.
Brief History Of Cachuma Lake
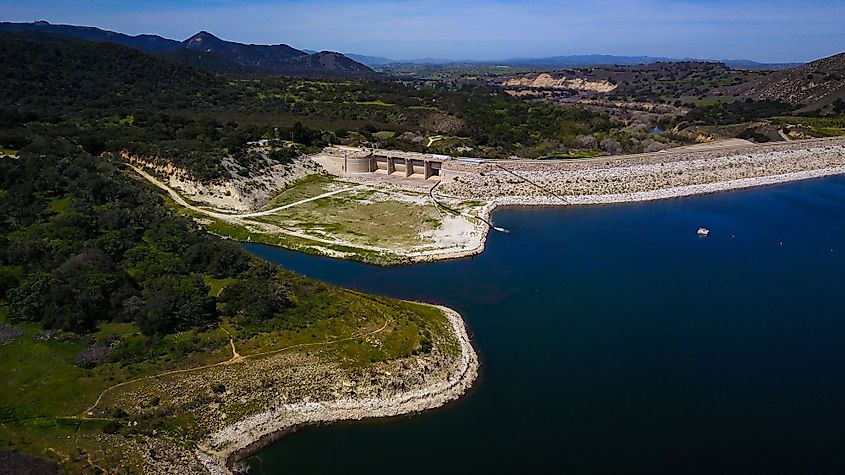

The Chumash people lived in the area and along the California coast, dating back approximately 15,000 years ago. They were drawn to the region by the mild climate and abundant resources, including fresh water, forests, hunting on land, and fishing in the sea. Known locally as the Tecolote, Lompoc, Sisquoc, and Suey tribes, it is estimated there were approximately 15,000 living in the area when the Spanish settlers arrived. These settlers founded Mission Santa Inés in September 1804 as one of the 21 Missions in California. The Township of Santa Ynez was founded in 1882 along a stagecoach route. When the railroads came to the area, however, they passed the Santa Ynez Valley, opting for a route closer to the coast. It slowed the level of growth and ensured largely rural development of the Valley.
The State of California established the Water Agency in 1945, which entered into a contract with the USBR for the development of the Cachuma Project and other area water projects. Construction of the Cachuma Project, now known as the Bradbury Dam, began in 1950 and was completed in 1953. It took a three-year period for the lake to fill to its present capacity. Also, in 1953, the County signed a long-term lease with the Federal Bureau of Reclamation to manage the approximately 3,640 hectares that make up the Cachuma Lake Recreation Area.