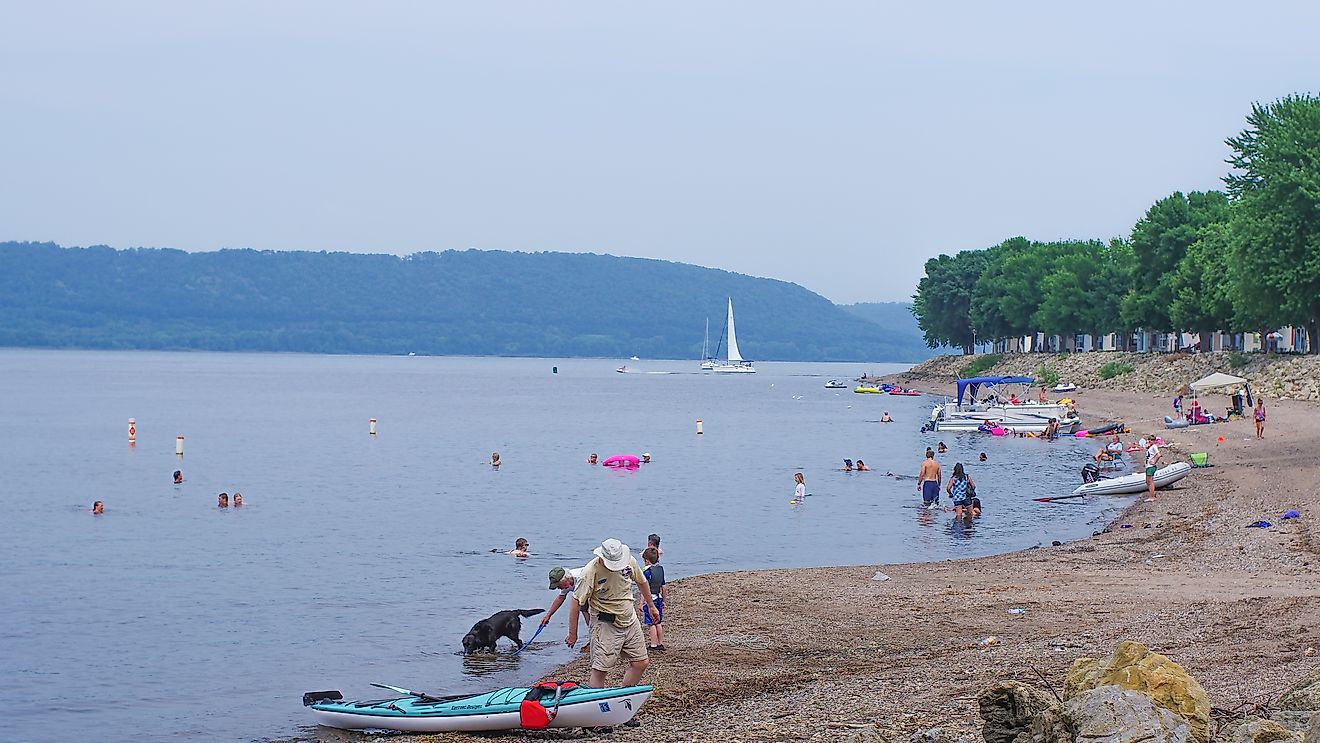Lake Tahoe
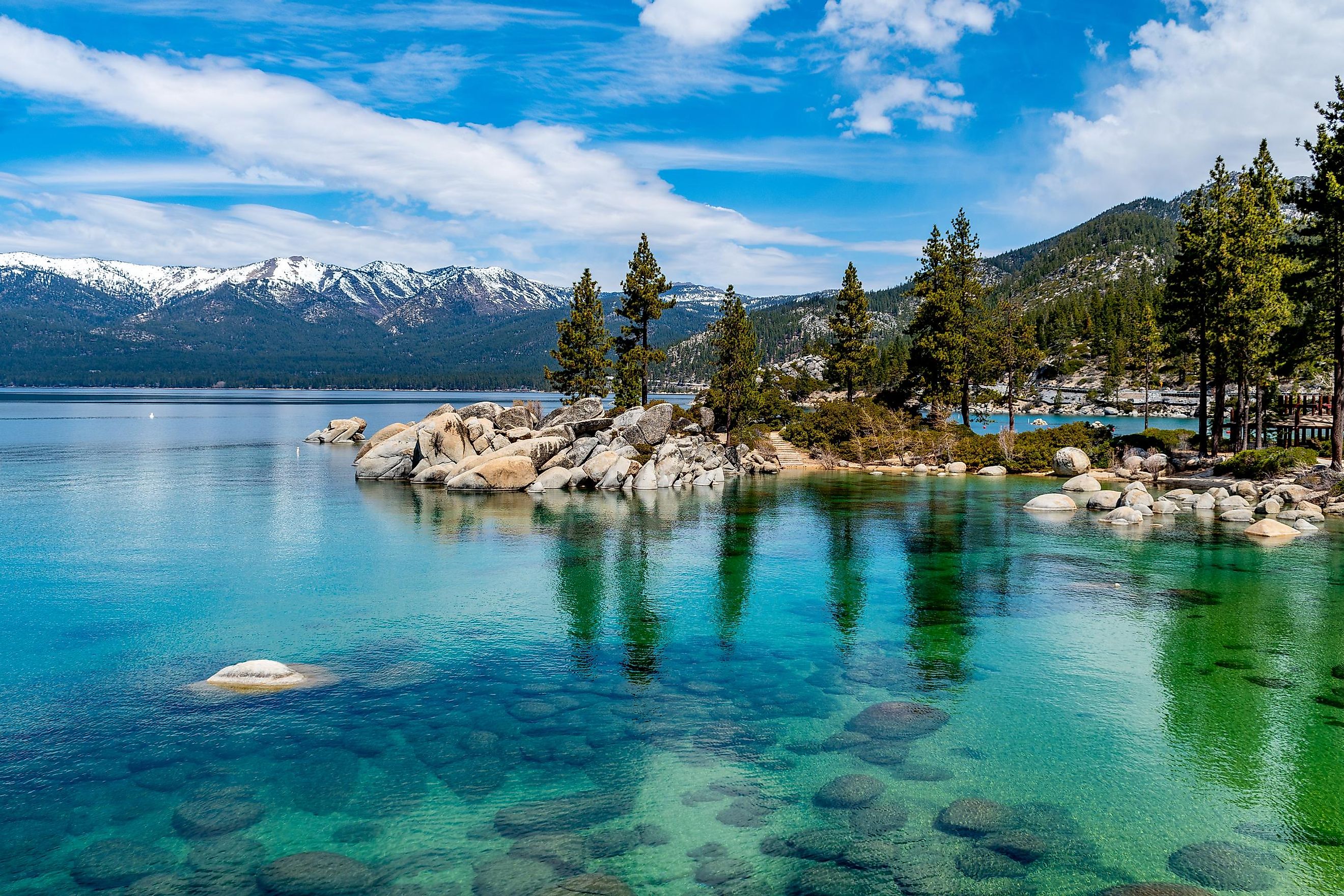
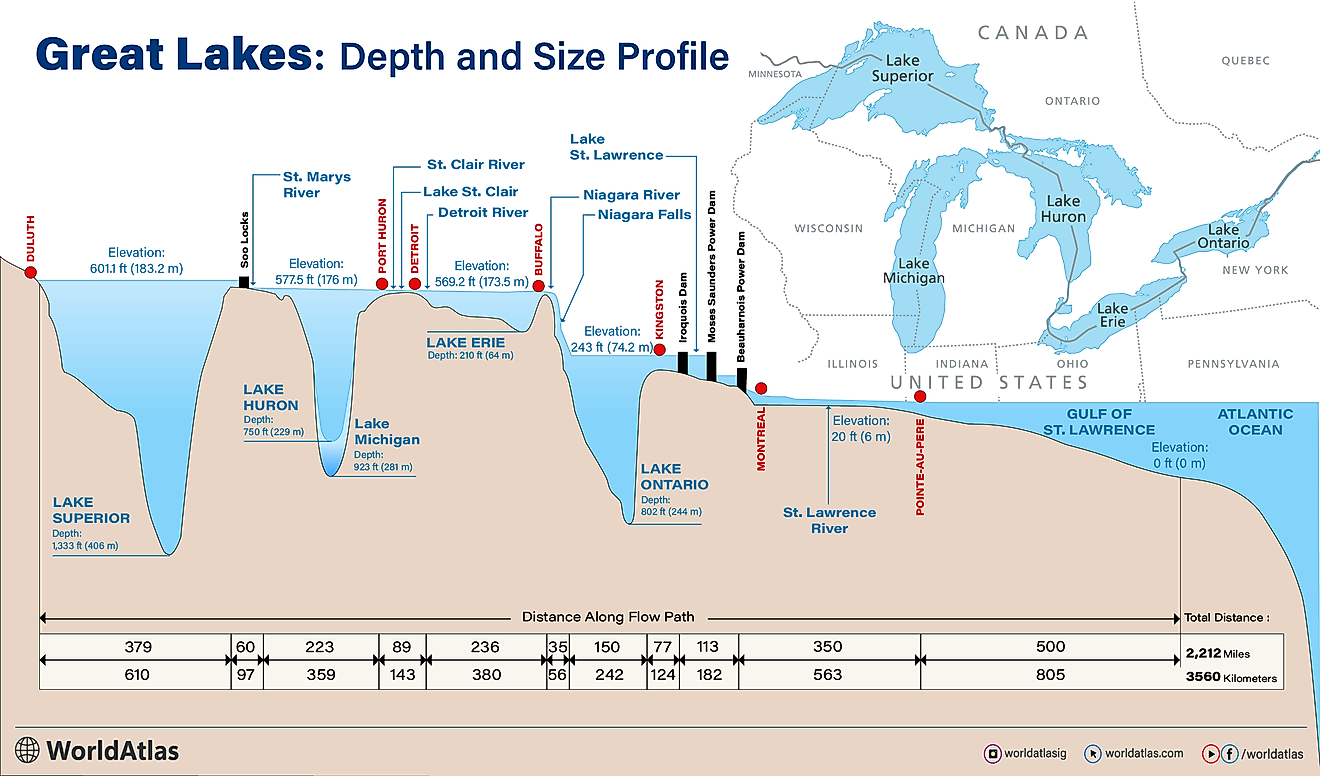
A lake is defined as a large water body that is surrounded by land. Covering an area of 490 km2, Lake Tahoe is a large freshwater lake that is surrounded by the majestic Sierra Nevada mountain range and straddles the boundary between the US states of California and Nevada. This spectacular crystal-blue lake is situated at an elevation of 1,897 m above sea level and is the highest lake in the United States as well as North America’s largest alpine lake.
Geography
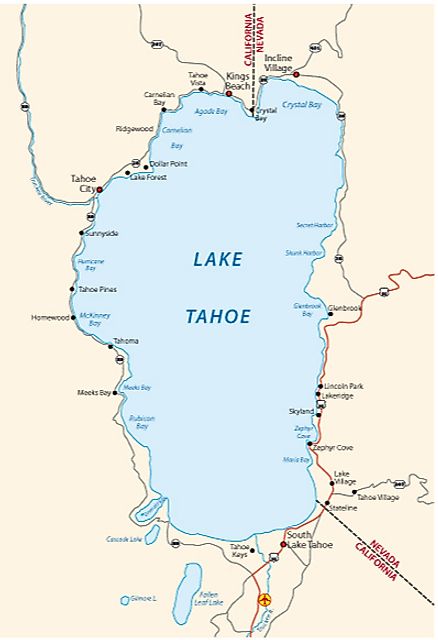
Lake Tahoe is about 35 km long and has a maximum width of 19 km. With a maximum depth of 501 m and an average depth of 300 m, the lake is considered the second-deepest lake in the US and the world’s 16th-deepest lake. About two-thirds of the lake is located within the boundaries of California in the counties of El Dorado and Placer, while one-third of it is located in Nevada in the counties of Douglas and Washoe as well as in the state’s capital Carson City.
Lake Tahoe, with a water volume of 150km3, is the largest lake by in the United States after the Great Lakes. 63 tributaries drain into Lake Tahoe. The lake’s only outlet is the Truckee River that is situated in California’s Tahoe City. Located on the Truckee River is the 5.5 m high Lake Tahoe Dam, which supplies water for Nevada’s Newlands Irrigation Project.
Geological studies have revealed that Lake Tahoe was formed more than 2 million years ago as a part of the Lake Tahoe Basin. Several major faults are located in the Lake Tahoe Basin including the West Tahoe Fault, the North Tahoe Fault, and the Incline Village Fault. The basin is also home to several high mountain peaks such as the Freel Peak, Pyramid Peak, Monument Peak, Mount Tallac, Mount Rose, Relay Peak, and Houghton Peak.
During the Ice Age, glaciers had carved many beautiful canyons and other significant landmarks such as Cascade Lake, Emerald Bay, and Fallen Leaf lake.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification, Lake Tahoe experiences a dry-summer continental climate with warm and dry summers and severely cold winters. The watershed areas on the western part of the lake receive more than 1,440 mm of rainfall annually, whereas the areas on the eastern side receive about 660 mm of annual rainfall. August is the warmest month with average temperatures ranging between 25.9 °C to 4.3 °C. January is the coldest month with average temperatures between 5 °C to -9.4 °C. The waters of the lake never freeze due to the constant movement of water from the lake’s bottom to its surface.
Wildlife

The vegetation of Lake Tahoe is mainly dominated by mixed coniferous forests which comprise different species of trees such as the Jeffrey pine, lodgepole pine, western white pine, ponderosa pine, sugar pine, California incense-cedar, red fir, and white fir. The Lake Tahoe Basin also contains large areas of riparian woodland, dry and wet meadows, rocky outcrops, and brush fields. Flowering plants like the Lake Tahoe yellowcress are found in the white sandy beaches of the lake. About 75% of the Lake Tahoe Watershed forms a part of the national forest and is protected by the United States Forest Service.
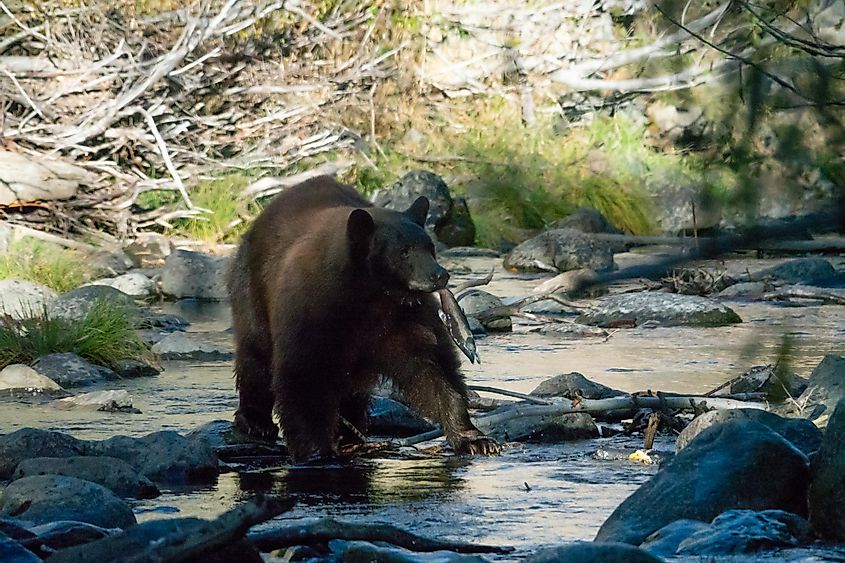
Numerous fish species are native to the waters of Lake Tahoe including the Lahontan cutthroat trout, mountain whitefish, Lahontan speckled dace, Lahontan redside, Lahontan Lake tui chub, Tahoe sucker, Lahontan mountain sucker, and Paiute sculpin. Several fish have been introduced in Lake Tahoe including lake trout, sockeye salmon, brown bullhead, western mosquitofish, and rainbow trout. The US Forest Service and the California Wildlife and Fish Department had re-introduced the North American beaver to the Lake Tahoe basin.
Brief History

Lake Tahoe and its surrounding areas were originally inhabited by the Indigenous Washoe peoples. Located in the lake’s southeastern shore is the Cave Rock which was regarded as a sacred place by the Washoe. The explorer Lt. John C. Frémont first visited the lake in 1844 and named it “Lake Bonpland” in the honor of the French botanist Aimé Jacques Alexandre Bonpland. However, the usage of this name never became much popular. After several debates and name changes, the California State Legislature accepted Lake Tahoe as the official name of the lake. The name Tahoe was suggested by Dr. Henry DeGroot, as a local tribal name that meant “water in a high place.” The discovery of gold in the South Fork of the American River and Comstock Lode silver in the lake attracted a large number of people from all over the world, and eventually, the lake became a transportation center for the surrounding area.
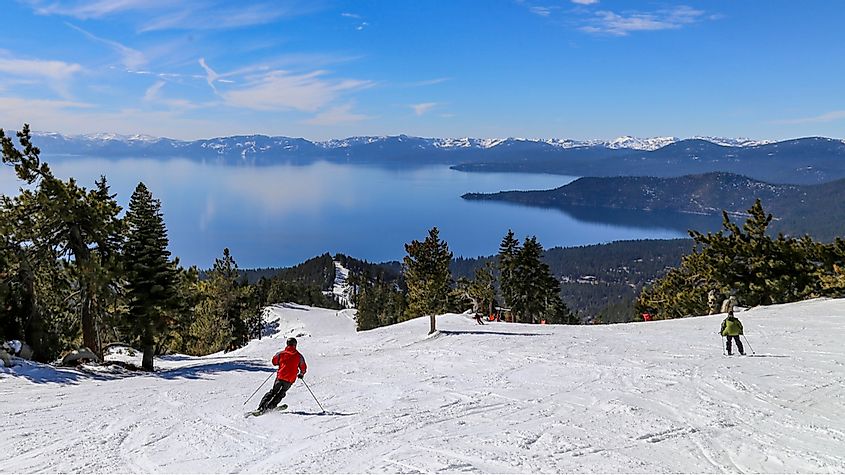
Lake Tahoe serves as a major tourist attraction and hosts winter sports, summer outdoor recreations, and spectacular scenery that can be enjoyed throughout the year. Numerous alpine ski resorts and ski centers are located along the shores of the lake. Snowmobiling, sleigh rides, winter cruises, golfing, hiking, and fishing are some of the major recreation activities that tourists can enjoy in the Lake Tahoe region. The Nevada side of the lake contains a myriad of casinos, motels, gaming centers, celebrity showrooms, and nightclubs.