5 Major Fields Of Environmental Science

- There are five major fields of environmental science; each one made up of multiple smaller disciplines. These five fields are atmospheric sciences, ecology, environmental chemistry, geosciences, and social sciences.
- Atmospheric sciences mostly deal with global warming and its effect. Scientists can create special computer models that depict how the atmosphere circulates, how chemicals react within it, and how animals contribute to carbon dioxide emissions.
- Ecologists research a plethora of things, including how a specific species or a group of living creatures are influenced by their environment or some specific aspects of it.
- Environmental chemistry goes into more detail, and it explores things like chemical effects on different plants, the chemical degradation of the environment, and the way chemicals get transported through the environment.
- Geosciences are often considered a branch of planetary sciences, and they explore the chemical and physical constitution of our planet, but also its atmosphere.
The importance of environmental science has never been higher than during these times. With climate change becoming an even more significant issue than ever before, we need to explore all of the ways we can use to solve environmental problems. Environmental science is an academic field that combines multiple scientific disciplines to explore and better understand the environment. It merges biological, physical, and information sciences such as biology, chemistry, physics, ecology, zoology, oceanography, geology, and many more.
Environmental science aims to solve problems such as the extinction of specific animal or plant species and deal with important issues such as climate change. It also tries to understand human relationships with nature and its various aspects by integrating social sciences among all of the other disciplines it encapsulates.
The discipline started to gain traction during the 1960s and the 1970s when people realized they needed to focus more on environmental problems. There are five major fields of environmental science; each one made up of multiple smaller disciplines. These five fields are atmospheric sciences, ecology, environmental chemistry, geosciences, and social sciences.
5. Atmospheric Sciences

Atmospheric sciences study the Earth’s atmosphere and how it relates to other systems, mostly its relation with the environment. The atmosphere and all of the processes that occur in it have a large impact on the environment, so it is extremely important to learn as much as we can about it. Several sciences fall under the atmospheric sciences, including meteorology and the studies of airborne contaminants, greenhouse gas phenomena, and even sound propagation phenomena.
The latter is related to noise and light pollution, which have recently begun gaining attention as problems of modern society. Atmospheric sciences mostly deal with global warming and its effect. Scientists can create special computer models that depict how the atmosphere circulates, how chemicals react within it, and how animals contribute to carbon dioxide emissions. This is only a small part of the contributions made by atmospheric sciences.
4. Ecology

Naturally, ecology plays a large role in environmental science. Ecology is defined as the study of how living organisms on our planet interact with each other. This includes humans, animals, plants, and their environment. Ecologists research a plethora of things, including how a specific species or a group of living creatures are influenced by their environment or some specific aspects of it.
They can also research how several different types of organisms interact with each other and try to explain their relationship in more detail. These types of relationships can have a large impact on our environment. Ecology is an interdisciplinary field, and it can combine many other disciplines such as chemistry, physics, geology, and biology. All of these fields have a way of dealing with the topics explored by ecology and can approach the same problem from different perspectives and explore various aspects of that problem.
3. Environmental Chemistry
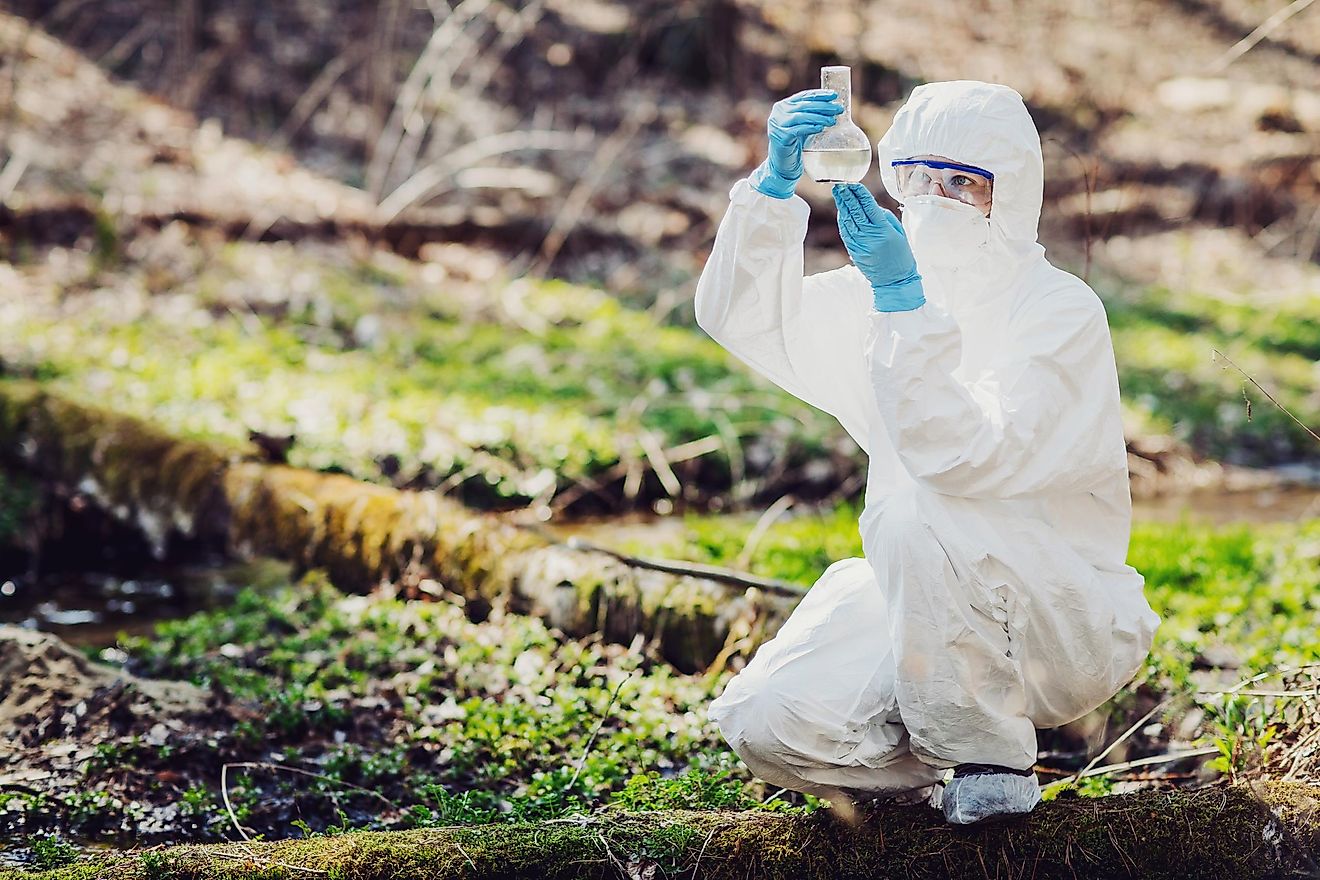

As one could conclude, just by looking at the name of this field, environmental chemistry explores the various chemical processes and the changes they make to the environment. This field mostly deals with water pollution and soil contamination. It makes sense because chemical processes and various chemicals can play a large role in these processes.
Environmental chemistry goes into more detail, and it explores things like chemical effects on different plants, the chemical degradation of the environment, and the way chemicals get transported through the environment. This field is also able to create computer models that serve as examples for research. These models allow scientists to view the molecular structure of chemicals, and they can explore its impact on the environment. This impact can most often be seen on soil, on various plants, and in certain cases on animals.
2. Geosciences

Geosciences are also known as earth sciences and are a field that deals with and connects all scientific disciplines that explore our planet directly. These include geology, the exploration of volcanic phenomena, environmental soil science, and the research on the development of the Earth’s crust.
Geosciences are often considered a branch of planetary sciences, and they explore the chemical and physical constitution of our planet, but also its atmosphere. Four main branches fall under geosciences, divided by their area of study, and those areas are the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere. Each one of these branches is divided even further, creating more specialized branches. Geosciences also collect perspectives from various other sciences such as physics and biology.
1. Social Sciences

Social sciences in the context of environmental science are most easily defined as specific fields that deal with the relationship between humans and nature. They are mostly divided into three larger fields, geography, anthropology, and sociology. Geography studies the various ways that the populations of humans can affect many features of our planet; it deals with specific data and is mostly based on quantitative research.
Anthropology seeks to examine how many different facets of humankind interact with each other and the environment. This includes the biology, geography, culture, and history of humankind. Finally, sociology explores the various dynamics in human society and provides environmental science with many crucial statistics.