The Richest Countries in Asia
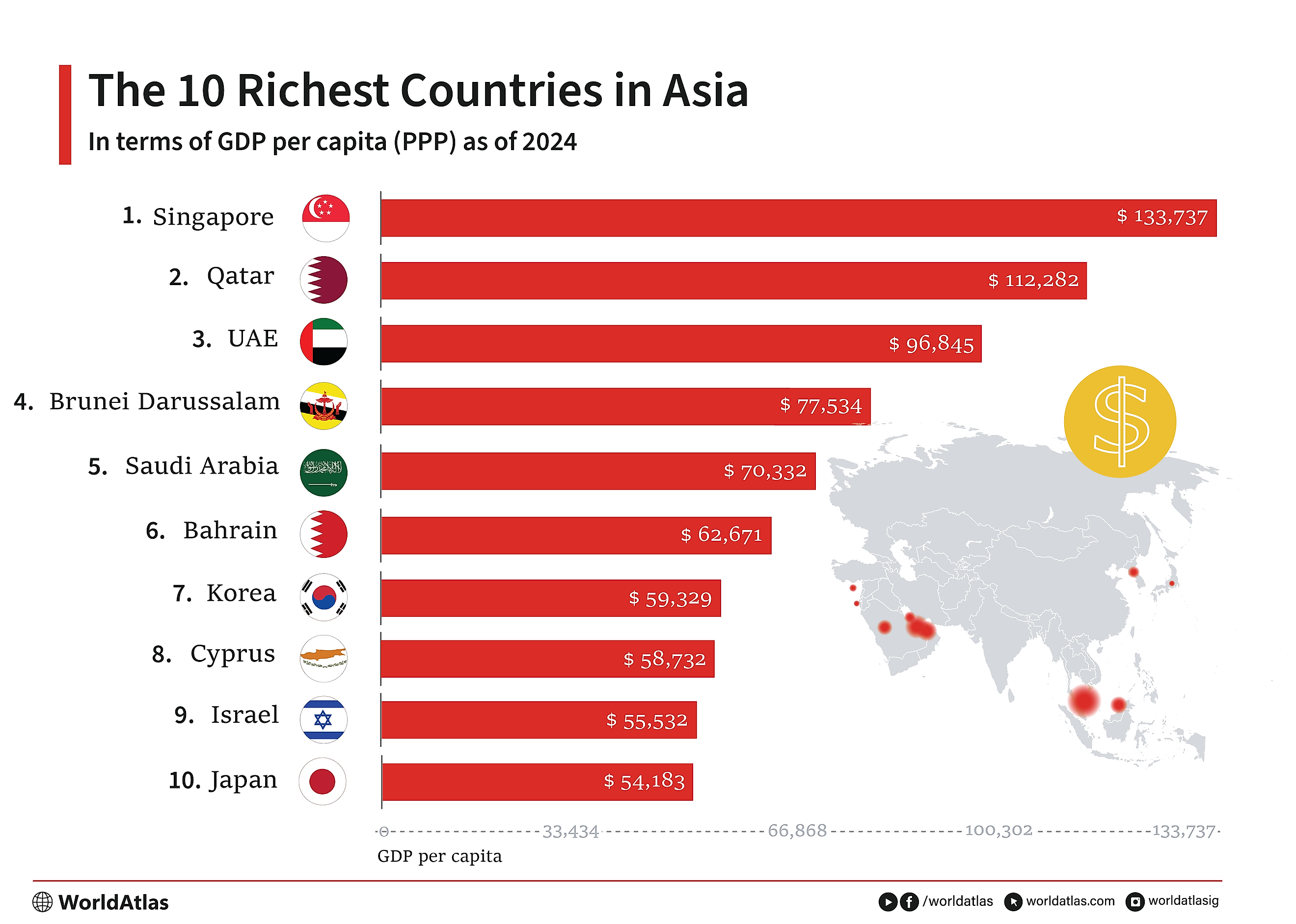
Asia is home to some of the most diverse and thriving economies on the planet. Singapore has the highest GDP per capita in PPP at $133,737 (USD.) Next is Qatar at $112,282 and the United Arab Emirates in third at $96,845. There are plenty more rich countries in Asia that are growing rapidly. These countries are ranked by GDP per capita PPP because it is by far the best way to assess how a country's resources impact the lives of citizens.
Top 10 Richest Countries In Asia (2024)
| Rank | Country | GDP per Capita in PPP |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Singapore | $133,737 |
| 2 | Qatar | $112,282 |
| 3 | United Arab Emirates | $96,845 |
| 4 | Brunei Darussalam | $77,534 |
| 5 | Saudi Arabia | $70,332 |
| 6 | Bahrain | $62,671 |
| 7 | Korea | $59,329 |
| 8 | Cyprus | $58,732 |
| 9 | Israel | $55,532 |
| 10 | Japan | $54,183 |
1. Singapore - $133,737

Aptly known as the "Lion City," Singapores' transformation over the 20th century is nothing short of extraordinary. What was once just a small collection of fishing villages and tenant farms, has now grown into the wealthiest country in all of Asia.
With virtually zero natural resources at its disposal, Singapore's massive economy is fueled by manufacturing, transport, engineering, logistics, electronics, biotechnology, and chemical production. Its stellar infrastructure and high standard of living has also turned this modern-day city-state into a high-end tourist destination for global travelers.
2. Qatar - $112,282

The richest of the Gulf States, Qatar's economy has seen steady growth since the late 1990s. Oil is of course the largest export. Qatar's booming oil industry has become even more vital as it fuels the heavily oil-dependent countries of China, Korea, and Japan.
In 2022, Qatar hosted the World Cup which significantly helped drive its tourism industry and rebranded the small country as a high-end tourist destination similar to Dubai. Qatar has also invested heavily in tech startups and financial institutions while diversifying its portfolio through shrewd investments in hedge funds and foreign real estate on the international scene.
3. United Arab Emirates - $96,845

Known as a playground for the rich elite, the UAE has become nearly unrecognizable from what it once resembled in the 1990s. Its capital city Abu Dhabi is now one of the business and financial centers of Asia and the Middle East.
While oil production remains a significant source of prosperity, the government has taken measures to expand its revenue streams by investing in technology and renewable energy sectors alongside substantial infrastructure development initiatives.
4. Brunei Darussalam - $77,534

The economy of Brunei has exploded in the 2020s as the oil-starved economies of East Asia have been in desperate need of more oil imports. This problem was only exacerbated thanks to the COVID-19 pandemic. While devasting for some, this has generated a much-needed demand for Brunei's main export.
The LNG (liquifying natural gas) industry generates more than half of Brunei's total GDP despite only making up a fraction of its workforce. While Brunei is more than happy to supply its rich neighbors with oil and gas, its current growth does not seem sustainable and will likely begin to taper off in the near future.
5. Saudi Arabia - $70,332

Ever since vast oil reserves were discovered in Saudi Arabia in the 1930s, the once remote country has since transformed into one of the wealthiest places in Asia, Saudi Arabia has consistently been one of the world's leading oil producers and exporters, mainly shipping its energy to China and other East Asian countries.
In the last decade or so there has been a considerable effort to try and diversify the Saudi economy. It is not lost on the Saudi government that as the world searches for alternative forms of energy, their cash cow could run dry. It appears as though its tourism and manufacturing sectors might be a new focus in the coming decades.
6. Bahrain - $62,671

Despite its small size and population, Bahrain has managed to forge one of the strongest economies in Asia thanks to strong policies and its favorable position in the Persian Gulf making it a key player in trade and transportation.
Additionally, Bahrain has invested heavily in infrastructure projects such as transportation and telecommunications, which have helped attract foreign investment and businesses. Bahrain, similar to other Gulf States, also boasts large oil reserves which are desperately needed across the continent.
7. Korea - $59,329

Another rags-to-riches story, South Korea was once an impoverished country that was given little thought until its economic might was fully realized in the 1980s. First focusing on industries such as iron, steel, and chemical manufacturing, since the dawn of the 20th century a stronger effort has been made in other sectors.
The modern Korean economy has a thriving tech and electronics industry. Korea has also seen considerable success exporting affordable and reliable cars and other forms of transportation across the world.
8. Cyprus - $58,732

Although Cyprus is largely considered to be a part of Europe, it is technically a part of Asia. Cyprus is a small island country that can be found off the southern coast of Turkey. Its favorable geographic location has allowed it to act as a bridge between trade traveling from Europe to the Middle East.
The Cypriot government has also made sure to try and create a business-friendly environment that attracts foreign investment. Its close economic ties to places like Israel and Egypt have proven fruitful as well.
9. Israel - $55,532
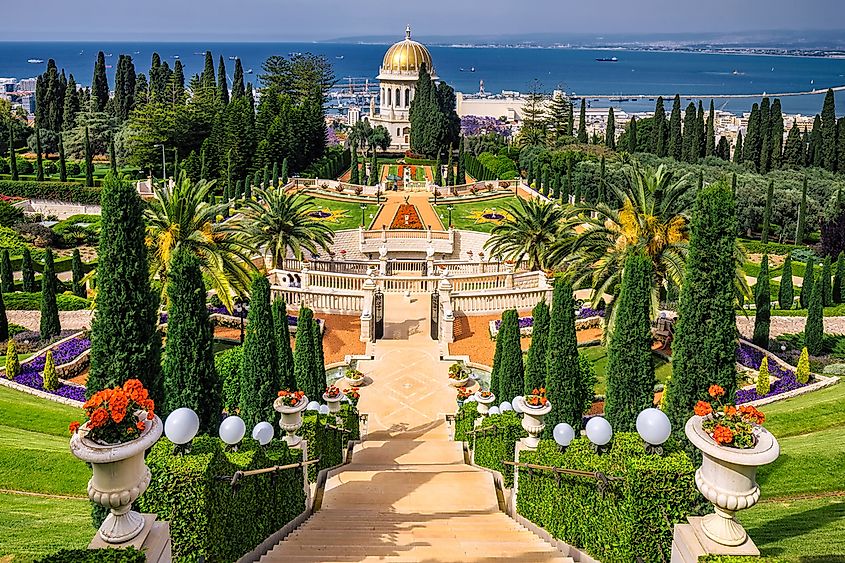

Similar to Japan and South Korea, Israel is virtually empty of any considerable amount of natural resources and has been forced to invest in other sectors which set it apart from other Asian economies. Israel has invested heavily in fields such as biotechnology, cybersecurity, and renewable energy. These industries have helped drive growth and attract foreign investment too.
One of the key drivers of Israel's economic success is its thriving startup ecosystem. The country is home to over 6,000 startups and has the world's highest number of startups per capita. This attraction is partly due to government support for research and development and a culture that values risk-taking and innovation.
10. Japan - $54,183
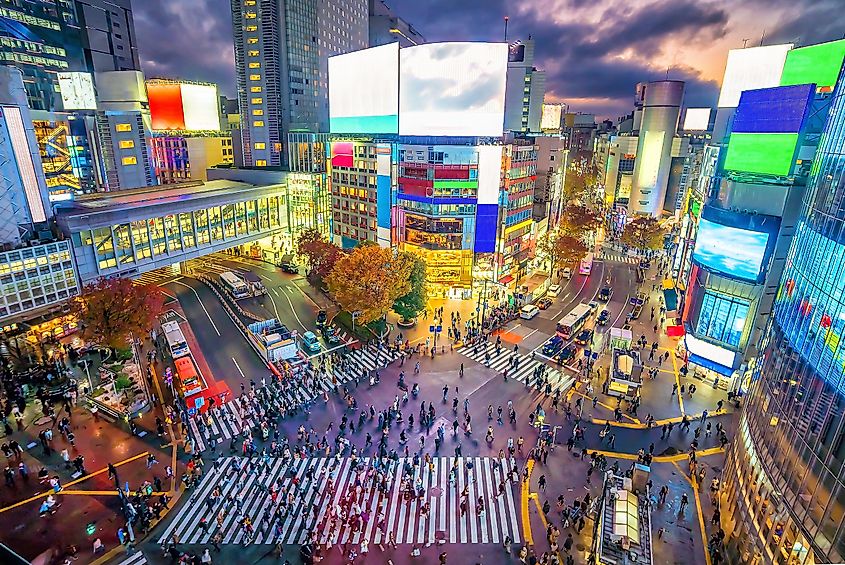

After emerging from WWII with what little was left of their economy, the Japanese government was able to rebound in only a short few decades. Japan invested heavily in manufacturing top-notch consumer products that quickly took the world by storm in the 1970s and 1980s.
Even today, Japanese products are considered to be of the best quality, whether it be automobiles or tech. Additionally, Japan's high savings rate has allowed for sustained investment in both domestic and foreign markets.
Final Thoughts
There are dozens of economies in Asia that are growing rapidly. Considering that much of the continent was underdeveloped for the first half of the 20th century, it is amazing to see various places rebound and thrive.
Top 20 Richest Countries In Asia (2024)
| Rank | Country | GDP per Capita in PPP |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Singapore | $133,737 |
| 2 | Qatar | $112,282 |
| 3 | United Arab Emirates | $96,845 |
| 4 | Brunei Darussalam | $77,534 |
| 5 | Saudi Arabia | $70,332 |
| 6 | Bahrain | $62,671 |
| 7 | Korea | $59,329 |
| 8 | Cyprus | $58,732 |
| 9 | Israel | $55,532 |
| 10 | Japan | $54,183 |
| 11 | Kuwait | $52,274 |
| 12 | Turkey | $43,920 |
| 13 | Oman | $39,858 |
| 14 | Malaysia | $39,029 |
| 15 | Maldives | $37,433 |
| 16 | Kazakhstan | $34,533 |
| 17 | Georgia | $25,248 |
| 18 | China | $25,015 |
| 19 | Armenia | $21,746 |
| 20 | Islamic Republic of Iran | $21,219 |











