10 Stunning Images Taken By Hubble
The Hubble Space Telescope was launched in 1990. Hubble is one of the most powerful telescopes ever built, and until the launch of James Webb in 2021, it was the most powerful telescope in space. Being in operation for over three decades, Hubble has drastically transformed our understanding of the cosmos, as well as offering us a new perspective through its array of stunning images. What are some of Hubble’s best images?
1.Jupiter and Europa

While Hubble is mostly known for its images of far away stars, nebulae, and galaxies, it has taken a number of stunning images of the planets and moons in our solar system. On August 25, 2020, Hubble captured an absolutely magnificent view of the largest planet in our solar system, Jupiter, along with its icy moon, Europa. At the time this image was taken, Jupiter was located 406-million miles (653-million kilometres) away.
2. The Butterfly Nebula

The Butterfly Nebula is a planetary nebula located roughly 4,000-light years away in the constellation Scorpius. The nebula itself is about 3-light years across. As a planetary nebula, this structure was once a star not so different from our sun. As the star ran out of fuel, it became a red giant and gradually began blowing its outer layers into space, forming the vast nebula that now surrounds the dying star. Eventually, the core of the star will become a white dwarf.
3. The Tadpole Galaxy

Hubble has captured hundreds of stunning images of distant galaxies, yet some appear more peculiar than others. The Tadpole Galaxy is one such galaxy as it appears to have a comet-like tail. Located 420-million light years away, astronomers believe that the tail of the Tadpole Galaxy is likely the result of another galaxy passing near the Tadpole Galaxy, with its gravitational pull having stretched out gas, dust, and stars to form a long filament of material. The tail itself is about 280,000-light years long, which makes it larger than the diameter of our own galaxy, which is around 100,000-light years.
4. The Cigar Galaxy

The Cigar Galaxy is an oddly shaped galaxy located 12-million light years away, which also makes it one of the closest galaxies to the Milky Way. The Cigar Galaxy is classified as an active starburst galaxy, meaning that star-formation is currently occurring at an accelerated rate. Astronomers believe that the Cigar Galaxy may have undergone a brief collision with another galaxy in the past, which resulted in the now high-rate of star-formation. In addition to star-formation, astronomers have also observed supernovae within the galaxy, as well as one of the brightest known pulsars.
5. The Bubble Nebula

The Bubble Nebula is one of the most intriguing objects in space. Located about 7,100-light years away, the Bubble Nebula is the result of strong solar winds from a nearby massive star. While we do not generally think of space as being windy, high energy particles from massive stars can in fact blow away interstellar material, in some cases resulting in the formation of large bubbles in space.
6. The Horsehead Nebula

The Horsehead Nebula is among Hubble’s most famous images. The nebula itself is located 1,375-light years away in the constellation Orion and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. The Horsehead Nebula contains vast amounts of interstellar gas that have become so dense that the nebula blocks incoming starlight, making the central structure appear rather dark when compared to surrounding areas. The red color of the nebula is caused by the ionization of hydrogen gas, which has become ionized due to the high energy radiation emitted from nearby stars.
7. The Antennae Galaxies
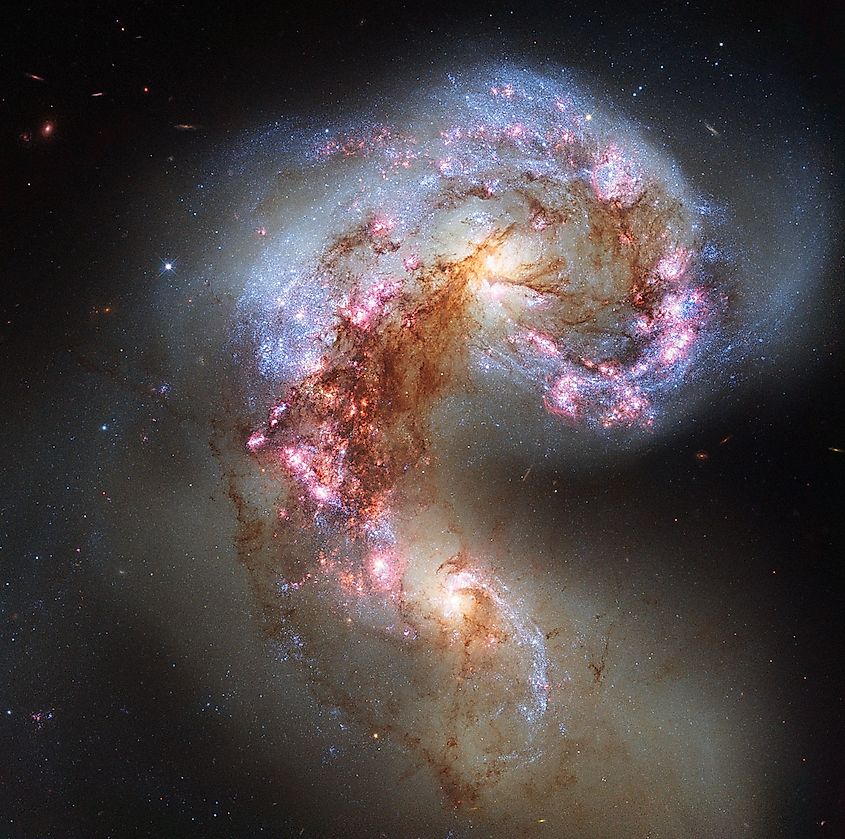

This stunning image may look like a single galaxy, yet it is in fact an image of two galaxies currently merging together. If one looks closely, you can see two bulges, one at the top of the structure and one below. At one point, this entire structure was likely two separate spiral galaxies. Over the course of many millions of years, the gravitational pull between them caused them to collide and merge together. We are fortunate enough to be able to observe this cosmic dance as it is still ongoing. As the two galaxies merge together, stars are routinely flung from their galactic neighborhoods, forming vast filaments of stars that look like insect antennae.
8. Mystic Mountain

There are some Hubble images that look so stunning that our minds are nearly incapable of truly grasping their beauty. One such image is Mystic Mountain, a large collection of stellar material located in the Carina Nebula around 7,500-light years away. The colors of Mystic Mountain alone are stunning, yet there is more to this structure than meets the eye. Within the structure itself, stars are currently forming. The high energy winds from so many young stars are actually tearing Mystic Mountain apart from the inside, and eventually the entire structure may cease to exist entirely. Amazingly, the central pillar is about 3-light years tall. If Mystic Mountain were placed in our solar system, the largest pillar would stretch over half-way to the nearest star.
9. Arp 273

Arp 273, which has also been nicknamed the Cosmic Rose, is a collection of two spiral galaxies that are currently undergoing an early stage of collision. The two galaxies, drawn to each other by their mutual gravity, are currently trapped in a gravitational cosmic dance. The shapes of the two galaxies have already become noticeably distorted as their spiral arms stretch under the force of gravity. Arp 273 is located about 300-million light years away.
10. The Pillars of Creation

Any list of stunning Hubble images simply has to have the Pillars of Creation as they are perhaps the most iconic image ever taken by Hubble. The Pillars of Creation are named for the fact that star-formation is currently underway within the pillars, which are located within the Eagle Nebula some 7,000-light years away. Hubble has imaged the Pillars multiple times over its lifetime, and they have become a kind of symbol for the telescope itself. The largest pillar is about 5-light years tall, making it larger than the distance between the sun and the nearest star.