How Many Dwarf Planets Are There?
- Ceres was the first dwarf planet discovered
- Most dwarf planets were initially thought to be planets
- In 2006, astronomers defined what a planet is, and in the process, also defined what objects were dwarf planets
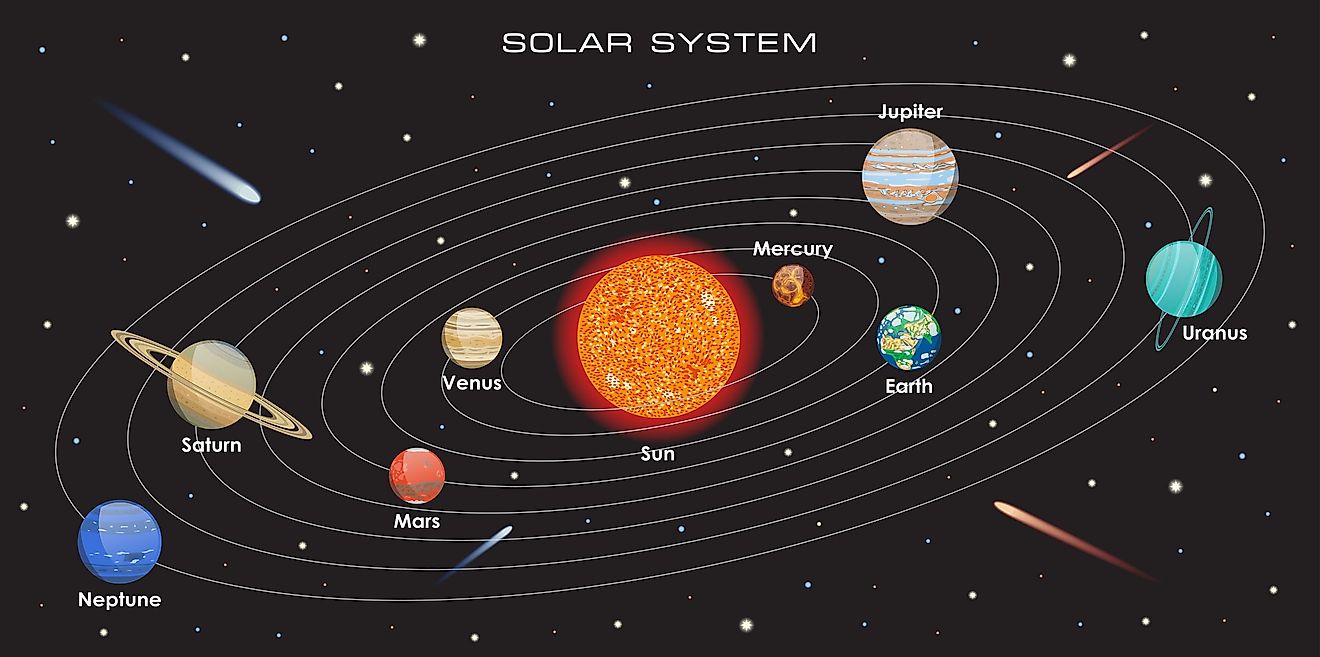
Our solar system is home to eight planets, over 200 moons, and countless asteroids, comets, and meteors. In addition to these objects, our solar system also contains a multitude of dwarf planets. A dwarf planet is a celestial object whose size and mass are not large enough to be defined as a planet, yet too large to be defined as an asteroid or comet. What are the dwarf planets in our solar system and how many of them are there?
The First Dwarf Planets

The first dwarf planets discovered were often considered to be planets. Although Pluto is the most popular dwarf planet in our solar system, it was not the first to be discovered. The first dwarf planet discovered was Ceres, which was first observed in 1801. Ceres orbits in what we now know to be the Asteroid Belt, located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. When Ceres was first discovered, astronomers believed they had found a new planet. After the discovery of Ceres, astronomers began discovering a number of other objects between Mars and Jupiter, all of which were initially assumed to be planets. However, by the 1850s, the number of planets in the solar system grew to 23. Since more and more objects were being discovered, astronomers decided to re-classify many of these objects as asteroids, and that included Ceres.
Dwarf planets are small and dim, and so it comes as no surprise that they are difficult to detect. Thus, no dwarf planets were discovered after Ceres until the 1930s, when the astronomer Clyde Tombaugh discovered Pluto. Like Ceres, astronomers believed that Pluto was a planet, and for over 50 years, Pluto was believed to be the ninth planet of the solar system. Interestingly, astronomers believed that Pluto was larger than Mercury up until 1978, when astronomers discovered Pluto’s largest moon, Charon. With the discovery of Charon, astronomers were able to calculate the mass of Pluto, revealing that it was noticeably smaller than Mercury. This called into question whether or not Pluto should be considered a planet, yet it continued to be placed alongside the planets until 2006, when the International Astronomical Union defined the criteria for an object to be considered a planet. In order to be a planet, an object must be massive enough to become spherical, it must orbit the sun, and it must have a strong enough gravitational pull to clear its orbit of debris. Pluto met the first two criteria, yet it fails in the third. Pluto, along with several other objects, were reclassified as dwarf planets.
What initially ignited the debate about what it means to be a planet was the discovery of a dwarf planet called Eris, in 2005. Like Pluto, Eris orbits the sun in the far outer regions of the solar system, in an area known as the Kuiper Belt. When Eris was discovered, astronomers realized it was slightly larger than Pluto, yet it was not widely considered to be a planet. If Eris, which is larger than Pluto, was not considered a planet, it called into question whether or not Pluto should be a planet.
Dwarf Planets In The Solar System

Since the discovery of Ceres, the number of dwarf planets in the solar system has grown. However, there is actually no agreed upon definition of what a dwarf planet is, and so the number of dwarf planets varies depending on who you ask. When the International Astronomical Union defined what a planet is, there were ten objects that were reclassified as dwarf planets. That included Ceres, Pluto, and Eris, along with seven others. If we consider objects similar in size to these objects to be dwarf planets, the number of known dwarf planets in the solar system grows to 120. Although it is now easy to identify whether an object is a planet or not, there is no defined distinction between dwarf planets and spherical asteroids. Thus, there is no defined number of dwarf planets in our solar system, and depending on who you ask, the numbers range from as low as five to as high as 120.