The Ten Largest Galaxies In The Universe
- The largest known galaxy in the universe is IC 1101 at four million light years across
- All of the largest galaxies are either elliptical galaxies or spiral galaxies
- Most galaxies grow to their current size by absorbing other galaxies
Galaxies come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. If we think of galaxies as singular objects, they are some of the largest structures in the universe. Most of the stars and planets in the universe are contained within galaxies. Astronomers estimate that the universe contains more than 200-billion galaxies. Of all the known galaxies, which ones happen to be the largest and how big are they?
The Largest Known Galaxy: IC 1101
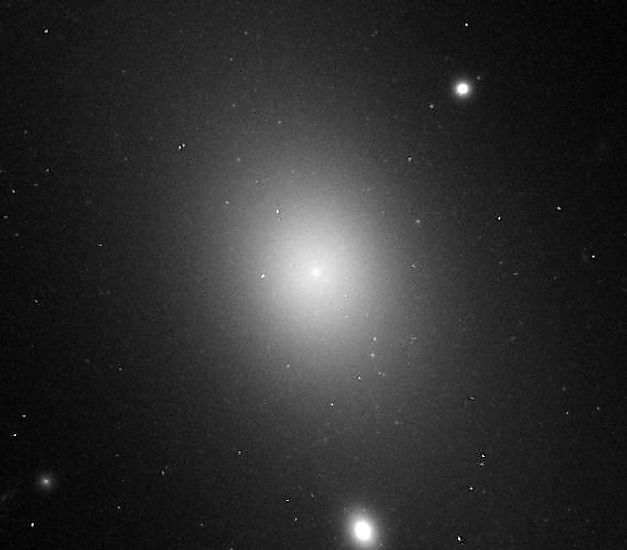

To date, the biggest galaxy that has been discovered is IC 1101. IC 1101 is classified as a supergiant elliptical galaxy, and it looks far different than the Milky Way. As an elliptical galaxy, IC 1101 contains an abundance of low to medium mass red and yellow stars, most of which are quite old. At the center of IC 1101, there exists a supermassive black hole, which happens to be the largest black hole ever discovered. IC 1101 has an estimated diameter of four million light-years. In comparison, the Milky Way is roughly 100,000 light-years in diameter, making IC 1101, 40 times larger than the Milky Way. If you were to place IC 1101 where the Milky Way is, it would completely engulf the Andromeda Galaxy at 2.5 million light-years away. IC 1101 is located roughly one billion light-years away from the Milky Way and likely contains over 100 trillion stars.
Second: Hercules A
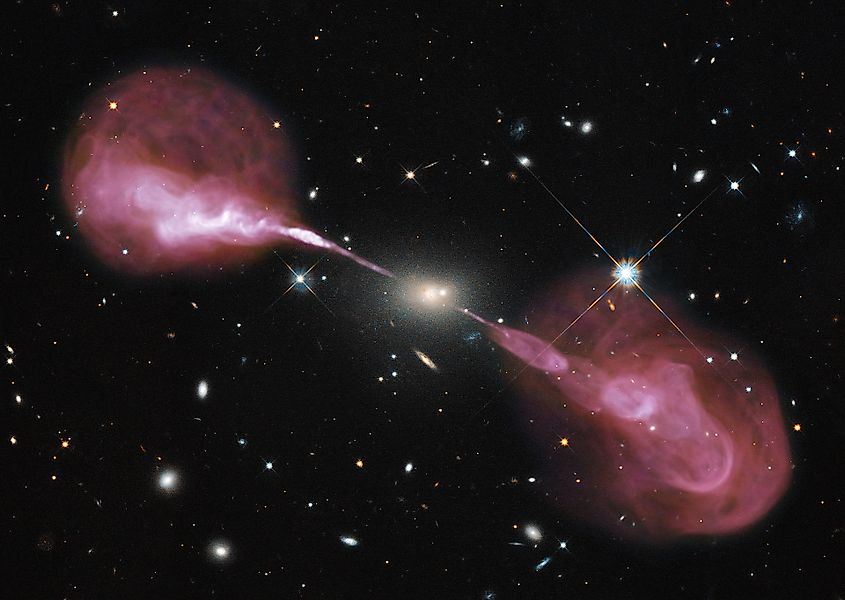
The elliptical galaxy designated as Hercules A is the second-largest galaxy known to exist. Hercules A has an estimated diameter of 1.5 million light-years, and like IC 1101, it is classified as a supergiant elliptical galaxy. Other than its size and galaxy type, not much is known about Hercules A, and there is a reason for this. The supermassive black hole at the center of Hercules A is currently emitting two gigantic beams of radio waves. These beams are so energetic that they make it difficult to study the rest of the galaxy in detail. Even these beams of radio waves are gigantic, measuring over one million light-years in length.
Third: A2261-BCG
A2261-BCG is the third-largest known galaxy in the universe, having a diameter of one million light-years, roughly ten times the size of the Milky Way. A2261-BCG is a supergiant elliptical galaxy and is estimated to contain over ten trillion stars. A2261-BCG is a rather strange galaxy for one simple fact: it does not contain a supermassive black hole at its center. The vast majority of large galaxies in the universe have a supermassive black hole at their center, yet for unknown reasons, A2261-BCG does not. A2261-BCG is located three billion light-years away from us.
Fourth: ESO 306-17
The fourth-largest known galaxy in the universe is ESO 306-17, with a diameter of roughly one million light-years. Like the galaxies discussed previously, ESO 306-17 is a supergiant elliptical galaxy, yet there is something that makes this particular galaxy unique. While most galaxies find themselves within vast clusters of galaxies, ESO 306-17 is alone, with all of the surrounding space being empty. Astronomers believe that ESO 306-17 may have once been one of many galaxies in its area, yet it eventually merged with and absorbed every nearby galaxy, causing it to grow in size and become one of the largest known galaxies in the universe. ESO 306-17 is roughly 500 million light-years away from us.
Fifth: Comet Galaxy

The Comet Galaxy is the fifth largest known galaxy and the first on the list that is not an elliptical galaxy. The Comet Galaxy is a spiral galaxy that measures 600,000 light-years across. The Comet Galaxy is also one of the fastest galaxies in the universe, moving at a speed of two million miles per hour (3.22 million kilometers per hour). As this galaxy speeds through space, it is actually being ripped apart by the gravitational force of other nearby galaxies. These gravitational forces, combined with the speed of the galaxy, cause the formation of a vast tail of material, making it look like a comet. The Comet Galaxy is located 3.2 billion light-years away from us.
Sixth: Condor Galaxy
The Condor Galaxy is the sixth largest known galaxy in the universe with a diameter of 522,000 light-years. The Condor Galaxy is a large spiral galaxy that has two prominent arms that stretch outwards. Interestingly, astronomers believe that the reason behind the highly elongated spiral arms in the Condor Galaxy is due to a brief collision with another nearby galaxy many millions of years ago. The Condor Galaxy is located 212 million light-years away from us.
Seventh: UGC 2885
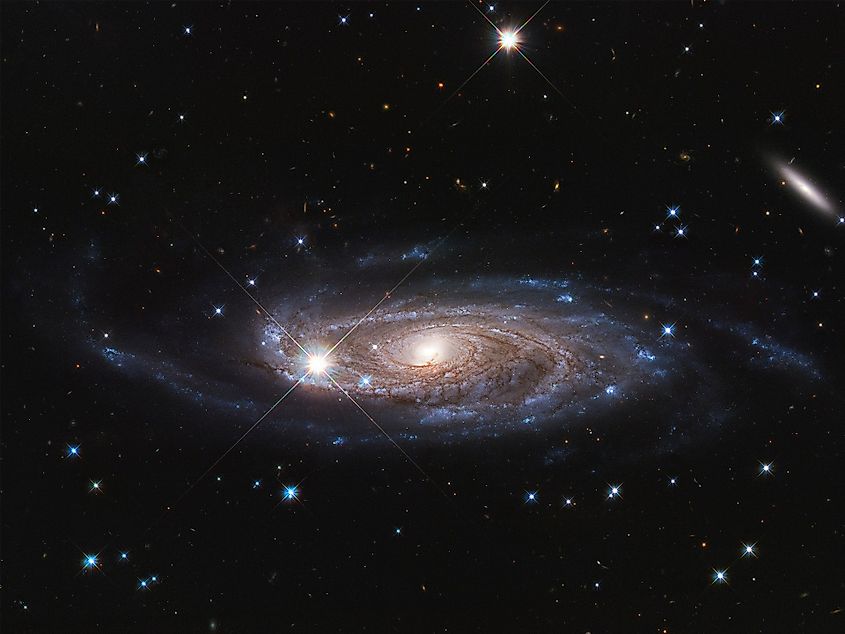

The seventh-largest known galaxy is UGC 2885, with a diameter of 463,000 light-years. Unlike the first four galaxies discussed, UGC 2885 is a spiral galaxy, much like our own Milky Way. Interestingly, UGC 2885 exists in a fairly empty region of space, with no other galaxies located within the vicinity of UGC 2885. Unlike ESO 306-17, which grew to its immense size by absorbing all of the galaxies in its neighborhood, UGC 2885 likely grew from the accretion of vast amounts of hydrogen. UGC 2885 is located 232 million light-years away.
Eighth: ESO 444-46
ESO 444-46 is the eighth largest known galaxy in the universe with a diameter of 400,000 light-years. ESO 444-46 is classified as a supergiant elliptical galaxy, and it is believed to have grown to its current size by merging with and absorbing a multitude of other galaxies. ESO 444-46 is home to one of the largest populations of star clusters in the universe, having an estimated 27,000 of them. ESO 444-46 is roughly 640 million light-years away.
Ninth: Tadpole Galaxy
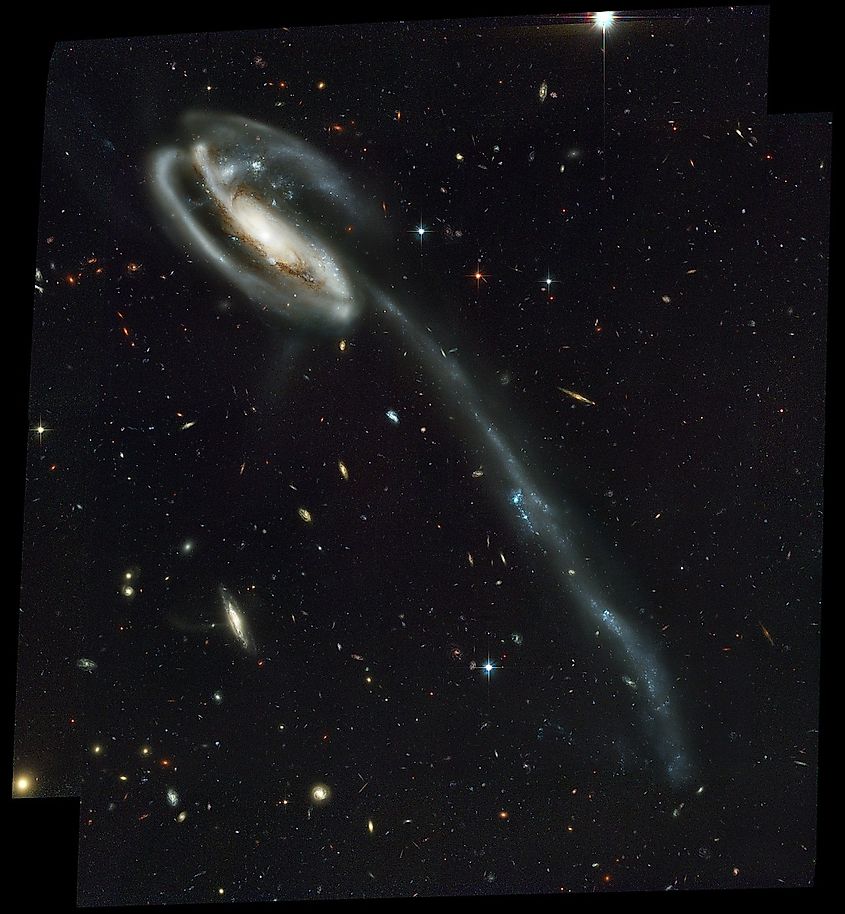

The Tadpole Galaxy is the ninth-largest known galaxy with a diameter of 280,000 light-years. Like the Milky Way, the Tadpole Galaxy is a spiral galaxy, yet it has one unique feature that sets it apart from most galaxies. The Tadpole Galaxy is followed by a vast string of stars that stretches outwards from the galaxy, forming what looks like a tadpole’s tail. It is this tail that makes the Tadpole Galaxy so vast, as it stretches for many thousands of light-years. Astronomers believe that this vast trail of stars formed after a nearby galaxy approached the Tadpole Galaxy in the distant past. The gravitational pull of the other galaxy would have disrupted the shape of the Tadpole Galaxy, pulling star’s outwards in the process. The Tadpole Galaxy is located 420 million light-years away.
Tenth: Andromeda Galaxy
The title for the tenth-largest galaxy in the universe goes to our nearest galactic neighbor, the Andromeda Galaxy. And Andromeda is about twice the size of the Milky Way, having a diameter of about 200,000 light-years. A lot of what we know about our own galaxy actually comes from observations of Andromeda, as both galaxies are very similar to one another. Andromeda is a spiral galaxy with a very similar shape to the Milky Way. One day, in the next ten billion years or so, the Milky Way and Andromeda will likely merge together and eventually form one, much larger galaxy. Andromeda is the nearest galaxy to the Milky Way at a distance of 2.5 million light-years.
|
Rank |
Galaxy Name |
Galaxy Diameter |
|
1 |
IC 1101 |
Four million light years |
|
2 |
Hercules A |
1.5 million light years |
|
3 |
A2261-BCG |
One million light years |
|
4 |
ESO 306-17 |
One million light years |
|
5 |
Comet Galaxy |
600,000 light years |
|
6 |
Condor Galaxy |
522,000 light years |
|
7 |
UGC 2885 |
463,000 light years |
|
8 |
ESO 444-46 |
400,000 light years |
|
9 |
Tadpole Galaxy |
280,000 light years |
|
10 |
Andromeda Galaxy |
200,000 light years |