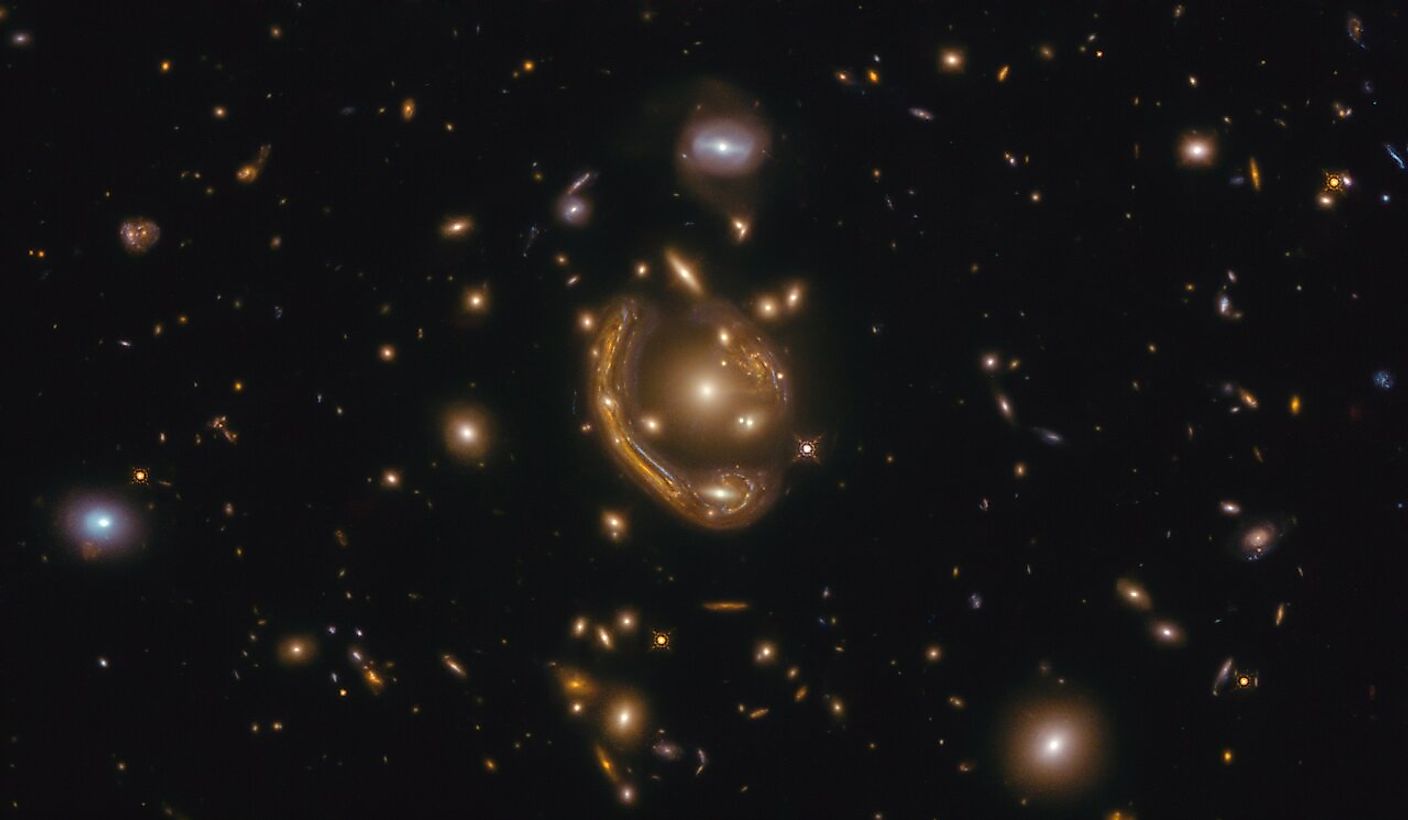
What Is An Einstein Ring?
Isaac Newton first described the force of gravity in 1665, and Albert Einstein later refined it in his theory of General Relativity, which he published in 1916. Newton had been unable to define gravity, yet Einstein discovered that gravity was the warping of space itself. The first concrete proof of Einstein’s description of gravity came during a solar eclipse in 1919. If gravity was due to the warping of space, the light would travel along curved space. It would result in a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing. To prove General Relativity, scientists observed the light from distant stars during a solar eclipse. If Einstein were correct, then the light from those stars would bend around the sun. Sure enough, observations confirmed Einstein’s theory. Gravitational lensing may also result in the formation of what’s called an Einstein Ring.
Gravitational Lensing

An Einstein Ring is basically a unique form of gravitational lensing. An Einstein Ring forms when the observer, source, and lens all happen to align perfectly with each other. For example, if there is a galaxy located behind another galaxy, and both objects happen to be aligned with the Earth, then the gravitational lensing observed will come in the form of an Einstein Ring. Interestingly, Einstein Rings can be used to observe distant objects in more detail. When gravity bends light, it has a magnifying effect on that light, making objects appear larger and closer. Large telescopes, such as Hubble and James Webb, take advantage of gravitational lensing and use it to observe distant objects in much more detail than would otherwise be possible.
Dark Matter

Gravitational lensing is one of the strongest forms of evidence for the existence of dark matter. Dark matter is a mysterious form of matter that does not interact with regular matter through both chemical reactions and light. As of yet, dark matter is only known to generate a gravitational field. Like regular matter, gravity from dark matter warps the fabric of space, which in turn leads to gravitational lensing. Interesting enough, scientists can use gravitational lensing to estimate the mass of distant objects. The amount of gravitational lensing will be dependent on the strength of gravity, and the strength of gravity is dependent on how much mass there is. Thus, by knowing how much gravitational lensing there is, scientists can calculate the strength of gravity and the amount of mass. When this is done for large galaxy clusters, the amount of mass present far exceeds the amount that is visible. That missing mass is dark matter, and scientists can even use gravitational lensing to estimate how much dark matter there is in the universe. Dark matter makes up roughly 27% of the entire universe.